CLASS 10 BIOLOGY LIFE PROCESSES CHAPTER 6 IMPORTANT QUESTION AND ANSWERS
CBSE Class 10 Biology Life processes Important Question of Science Life Processes material will help you in scoring more marks which consist of 1 mark Questions and 3 Mark Questions and 5 Marks Questions and also previous year questions from Life Processes Chapter.
Class 10 Biology Life processes provides answers as student learn easily. Solved the very best collection of Life Processes as Class 10 Science Important Questions and Answers Chapter 6 latest NCERT edition books, It will help you in scoring more marks in CBSE Exams. Class 10 Biology Life processes Important Question are below :
Important Question Class 10 Biology Life processes – Very Short Questions
Q 1 – In which mode of nutrition an organism de-rives its food from the body of another living organism without killing it?
(a) Saprotrophic nutrition
(b) Parasitic nutrition
(c) Holozoic nutrition
(d) Autotrophic nutrition
Ans 1 – (b) Parasitic nutrition
Q 2 – Roots of the plants absorb water from the soil through the process of:
(a) diffusion
(b) transpiration
(c) osmosis
(d) None of these
Ans 2 – (a) diffusion
Q 3 – In amoeba, food is digested in the:
(a) food vacuole
(b) mitochondria
(c) pseudopodia
d) chloroplast
Ans 3 – (a) food vacuole
Q 4 – Which of the following events in the mouth cavity will be affected if salivary amylase is lacking in the saliva?
(a) Starch breaking down into sugars.
(b) Proteins breaking down into amino acids.
(c) Absorption of vitamins.
(d) Fats breaking down into fatty acids and glycerol.
Ans 4 – (a) Starch breaking down into sugars.
Q 5 – Glycolysis process occurs in which part of the cell?
(a) Cytoplasm
(b) Nucleus
(c) Mitochondria
(d) Chloroplast
Ans 5 – (a) Cytoplasm
Q 6 – Which plant tissue transports water and minerals from the roots to the leaf?
(a) Xylem
(b) Phloem
(c) Parenchyma
(d) Collenchyma
Ans 6 – (a) Xylem
Q 7 – Single circulation, i.e., blood flows through the heart only once during one cycle of passage through the body, is exhibited by which of the following:
(a) hyla, rana, draco
(b) whale, dolphin, turtle
(c) labeo, chameleon, salamander
(d) hippocampus, exocoetus, anabas
Ans 7 – (d) hippocampus (sea horse), exocoetus (a genus flying fishes) , anabas (is a species of fish in the family Anabantidae)
Q 8 – Identify the correct path of urine in the human body.
(a) Kidney → urinary bladder → urethra → ureter
(b) Urinary bladder → ureter → kidney → urethra
(c) Kidney → ureter → urethra → urinary bladder
(d) Kidney → ureter → urinary bladder → urethra
Ans 8 – (d) Kidney → ureter → urinary bladder → urethra
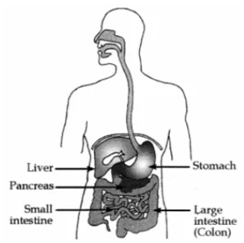
Q 9 – Label the various parts of the Alimentary Canal.
Ans 9 – Label the various parts of the Alimentary Canal
Q 10 – Fill in the Blanks.
1. The exit of food from the stomach is regulated by a __________ muscle.
2. ________ is the longest part of the alimentary canal.
3. The process of breakdown of glucose, (a six-carbon molecule) into pyruvate, (a three-carbon molecule), takes place in the __________
4. __________ is the site of the complete digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats.
5. Breaking of pyruvate using oxygen takes place in the ____________
6. Rings of cartilage are present in the wind pipe to ensure that the ___________
7. The blood has _________ cells which plug the leakage in the vessels by helping to clot the blood at the point of injury.
8. __________ transports products of photosynthesis from the leaves to other parts of the plant.
Ans 10 – 1. Sphincter
2. Small intestine
3. cytoplasm
4. Small intestine
5. mitochondria
6. air-passage does not collapse
7. platelet
8. phloem
Q 11 – Where is the dirty blood in our body filtered?
(a) Heart
(b) Lungs
(c) Ureter
(d) Kidneys
Ans 11 – (d) Kidneys
Q 12 – Name the tube which connects the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
(a) Urethra
(b) Nephron
(c) Tubule
(d) Ureter
Ans 12 – (d) Ureter
Q 13 – The movement of food in phloem is called:
(a) transpiration
(b) translocation
(c) respiration
(d) evaporation
Ans 13 – (b) translocation
Q 14 – The mode of nutrition found in fungi is:
(a) Parasitic nutrition
(b) Holozoic nutrition
(c) Autotrophic nutrition
(d) Saprotrophic nutrition
Ans 14 – (d) Saprotrophic nutrition
Q 15 – The exit of unabsorbed food material is regulated by
(a) liver
(b) anus
(c) small intestine
(d) anal sphincter
Ans 15 – (d) anal sphincter
Q 16 – What are the products obtained by anaerobic respiration in plants?
(a) Lactic acid + Energy
(b) Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy
(c) Ethanol + Carbon dioxide + Energy
(d) Pyruvate
Ans 16 – (c) Ethanol + Carbon dioxide + Energy
Q 17 – The breakdown of pyruvate to give carbon di-oxide, water and energy takes place in
(a) cytoplasm
(b) mitochondria
(c) chloroplast
(d) nucleus
Ans 17 – (b) mitochondria
Important Question Class 10 Biology Life processes – Very Short Questions
Q 18 – Name the substances whose build up in the muscles during vigorous physical exercise may cause cramps?
(a) Ethanol + Carbon dioxide + Energy
(b) Lactic acid + Energy
(c) Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy
(d) Pyruvate
Ans 18 – (b) Lactic acid + Energy
Q 19 – Name the pores in a leaf through which respiratory exchange of gases takes place.
(a) Lenticels
(b) Vacuoles
(c) Xylem
(d) Stomata
Ans 19 – (d) Stomata
Q 20 – The respiratory pigment in human beings is:
(a) carotene
(b) chlorophyll
(c) haemoglobin
(d) mitochondria
Ans 20 – (c) haemoglobin
Q 21 – Name the living plant in xylem tissue.
(a) Sieve tubes
(b) xylem sclerenchyma
(c) trachea
(d) xylem parenchyma
Ans 21 – (d) xylem parenchyma
Q 22 – A blood vessel which pumps the blood from the heart to the entire body:
(a) artery
(b) capillary
(c) Vein
(d) Haemoglobin
Ans 22 – (a) artery
Q 23 – What are raphides ?
Ans 23 – Some of the plant wastes get stored in the fruits of the plant in the form of solid bodies called raphides. Raphides are sharp needle-shaped crystals of calcium oxalate (Figure 1) found in various tissues including leaves, roots, shoots, fruits, etc., of wide varieties of plant species, and are typically kept in highly specialized cell called idioblast.
Q 24 – The scientific name of touch me not plant is ______________.
Ans 24 – Mimosa pudica plant
Q 25 – The procedure used for cleaning the blood of a person by separating urea from it is called:
(a) osmosis
(b) Filtration
(c) dialysis
(d) double circulation
Ans 25 – (c) dialysis
Q 26 – Which is the correct sequence of body parts in the human alimentary canal?
(a) Mouth → stomach → small intestine → large intestine → oesophagus
(b) Mouth → oesophagus → stomach → small intestine → large intestine
(c) Mouth → stomach → oesophagus → smallintestine → large intestine
(d) Mouth → oesophagus → stomach → large intestine → small intestine
Ans 26 – (b) Mouth → oesophagus → stomach → small intestine → large intestine
Q 27 – The basic life process common to all the living organisms are ___________, _________, _________,_________,__________ and __________.
Ans 27 – respiration and nutrition, control and coordination, transport and excretion, growth, movement and reproduction
Q 28 – What is the difference between parasitic nutrition and saprotrophic nutrition?
Ans 28 –
Saprotrophic nutrition is that nutrition in which an organism obtains its food from decaying organic matter of dead plants, dead animals and rotten bread, etc. | The parasitic nutrition is that nutrition in which an organism derives its food from the body of another living organism (called its host) without killing it. |
| Example : Mushroom (fungus) has saprophytic mode of nutrition. | Example: the micro organism (plasmodium) which causes malaria disease is a parasite. |
Q 29 – Complete the following reaction:
6CO2 + 6H2O + Light Energy __________ _________ + ________
Ans 29 –

Q 30 – Name the two plants which eat insects.
Ans 30 – Venus fly-trap, the pitcher plant
Q 31 – The different steps in the process of nutrition in animals are _______, digestion, _______, ________ and egestion.
Ans 31 – Ingestion, Absorption, Assimilation
Q 32 – The three substances present in the gastric juice are
a) Trypsin, Pepsin, Mucus
b) Hydrochloric acid, Amylase, Mucus
c) Mucus, Enzyme pepsin, hydrochloric acid
d) Fatty acid, Lipase, Bile
Ans 32 – (c) Mucus, Enzyme pepsin, hydrochloric acid
Q 33 – Define Dental Plaque.
Ans 33 – If the teeth are not cleaned regularly, they become covered with a sticky, yellowish layer of food particles and bacteria cells called dental plaque.
Q 34 – When the cell needs energy then the ATP can be broken down using water to release energy. Complete the following reaction

The energy released in the process is ________ KJ per mole.
Ans 34 – When the cell needs energy then the ATP can be broken down using water to release energy. Complete the following reaction

The energy released in the process is 30.5 KJ per mole.
Q 35 – Define Glycolysis.
Ans 35 – The oxidation of glucose to pyruvic acid (or pyruvate) is called glycolysis. It occurs in the cytoplasm of a cell and not in mitochondria. The oxidation of glucose to pyruvic acid (or pyruvate).
Q 36 – Write the chemical formula of Pyruvic acid and lactic acid.
Ans 36 –


Q 37 – What are the living organisms that cannot make their own food called?
Ans 37 – Heterotrophs
Q 38 – In insects like grasshopper, cockroach, housefly and a mosquito, the tiny holes ________ present on the body and the air tubes called ________ are the respiratory organs.
Ans 38 – Spiracles, Tracheae
Q 39 – The lungs are covered by two thin membranes called
a) Gleura
b) Palate
c) Pleura
d) Ribs Gleura
Ans 39 – c) Pleura
Q 40 – The Voice box in the trachea is known as _________ & the part of throat between the Mouth and Windpipe is called __________ .
Ans 40 – Larynx, Pharynx
Important Question Class 10 Biology Life processes – Very Short Questions
Q 41 – The Normal range of Haemoglobin in the blood of a person is from
a) 12.5 to 17.5 g/10 dL
b) 12.7 to 17.2 g/dL
c) 12 to 18 g/dL
d) 12 to 18 g/10ml
Ans 41 – c) 12 to 18 g/dL
Q 42 – In Xylem the flow of water is _______ directional and in Phloem the flow of water is ________ directional .
Ans 42 – Uni directional, bi directional
Q 43 – The fighter cells present in the body are
a) WBC’s
b) RBC’s
c) Platelets
d) Blood Plasma
Ans 43 – a) WBC’s
Q 44 – The Lymphatic system consists of the following parts. Choose the correct option .
- Smaller lymph vessels, lymph glands , lymph, lymph Capillaries.
- lymphocytes , lymph glands, larger lymph vessels , lymph nodes .
- lymph , lymph nodes , larger Lymph vessels , lymph capillaries.
- Lymphocytes, lymph nodes, smaller lymph vessels , lymph capillaries.
Ans 44 – c) lymph , lymph nodes , larger Lymph vessels , lymph capillaries.
Q 45 – The instrument use to measure the blood pressure is _________.
Ans 45 – Sphygmomanometer
CBSE Class 10 Biology Life processes – Short Questions
Q 46 – What is saliva? State its role in the digestion of food.
Ans 46 – Saliva is a watery fluid secreted by the salivary glands in the mouth. The digestive functions of saliva include moistening food, and helping to create a food bolus, so it can be swallowed easily. Saliva contains the enzyme amylase that breaks some starches down into maltose and dextrin.
Q 47 – In single celled organisms diffusion is sufficient to meet all their requirements of food, exchange of gases or removal of wastes but it is not in case of multicellular organisms. Explain the reason for this difference.
Ans 47 – Unicellular organisms can absorb sufficient oxygen because of its complete contact with the atmosphere, but in multicellular organisms the rate of absorption and diffusion becomes very less because all cells are not in direct contact with the atmosphere.
Multicellular organisms require greater amount of oxygen to sustain life processes which cannot be fulfilled by the process of diffusion.
Q 48 – What would be the consequences of deficiency of hemoglobin in your body?
Ans 48 – The deficiency of hemoglobin in our body is called anemia. In anemia, the blood is unable to carry the sufficient amount of oxygen required by the body. So, respiration would be less and less energy will be available to the body.
The hemoglobin deficient person will feel weak, pale, lethargic and will be unable to perform heavy physical work.
Q 49 – What are cramps and the cause of cramps? How can we get relief from them?
Ans 49 –
The painful contractions of muscles are called cramps. During heavy physical exercise most of the energy in muscle is produced by aerobic respiration. Anaerobic respiration in muscles provides only some extra energy which is needed under the conditions of heavy physical activity.
The anaerobic respiration by muscles bring about partial break down of glucose to form lactic acid. This lactic acid accumulates in the muscles. The accumulation of lactic acid in the muscles causes muscle cramps.
We can get relief from cramps by taking a hot water bath or a massage. Hot water bath or massage improve the circulation of blood in the muscles which results in the increased oxygen supply.
This oxygen breaks down lactic acid accumulated in muscles into carbon dioxide and water, hence gives us relief from cramps.
Q 50 – In mammals and birds why is it necessary to separate oxygenated and de-oxygenated blood ?
Ans 50 – Mammals and birds are warm blooded animals. This means they can control their body temperature and do not have to depend on environment for their body temperature regulation. Because of this birds and mammals require optimum oxidization of glucose which would be possible with good supply of oxygen.
So it is required to have separate oxygenated and de-oxygenated blood to supply the required amount of oxygen.
CBSE Class 10 Biology Life processes – Long Questions
Q 51 – Name three different glands associated with the digestive system in humans. Also name their secretions.
Ans 51 – Three glands associated with the digestive system are as follows:
1. Salivary glands in the mouth produce saliva. Saliva contains an enzyme called salivary amylase which digests the starch present in food into sugar.
2. Liver is the largest gland which secretes bile and pours its secretion in the duodenum (part of the small intestine). Bile makes the acidic food coming from the stomach alkaline so that pancreatic enzymes can act on it. Bile salts also break the fats present in the food into small globules.
3. Pancreas is also a large gland which secretes pancreatic juice into the duodenum. Pancreatic juice contains
- pancreatic amylase which breaks down the starch.
- Trypsin digests the protein.
- lipase which breaks down the emulsified fats.
- Pancreatic juice acts on alkaline medium.
Or
Q 52 – How are water and minerals transported in plants ?
Ans 52 – (a)
1. Old stem and old root. By diffusion through lenticels which possess intercellular spaces amongst complementary cells for exchange of gases between atmosphere and stem interior.
2. Young root. By diffusion between root interior and soil interspaces through the epiblema root hair complex in young roots.
3. Young stem and leaves. Diffusion across stomata between atmosphere and intercellular spaces.
(b) Transport of water and minerals.
Water and minerals absorbed by the plant roots are passed into xylem as sap. Sap present in xylem is under tension or negative pressure as mesophyll and other cells of aerials parts lose water to the outside through transpiration. Development of Negative Pressure.
Loss of water by mesophyll and other cells of aerial parts in transpiration increases their suction pressure. They withdraw water from xylem channels.
As there are billions of transpiring mesophyll cells withdrawing water from xylem channels, water present in xylem comes under negative pressure of 10-20 atmospheres. However, water column does not break due to
1. Cohesive force amongst water molecules and
2. Adhesion force between walls of xylem channels and water molecules.
3. Rise of Sap (Water and Minerals): Tension or negative pressure of water column results in upward pull just as cold-drink is sucked with the help of straw pipe.
4. Since it develops due to transpiration, it is called transpiration pull. The mechanism of this ascent of sap was put forth by Dixon and Joly in 1894.
Q 53 – In human alimentary canal, name the site of complete digestion of various components of food. Explain the process of digestion.
Ans 53 – In small intestine, complete digestion of various components of food take place. The process of digestion of food in mouth, stomach and small intestine in human body are as follows:
Mouth: Digestion of food begins in the mouth. Saliva present in mouth contains a digestive enzyme, called salivary amylase, maltose and dextrins, which breaks down starch into sugar.
Stomach: Stomach stores and mixes the food received from the oesophagus with gastric juices.
The main components of gastric juice are hydrochloric acid, mucus and pepsinogen. Hydrochloric acid dissolves bits of food and creates an acidic medium. In this medium, pepsinogen is converted to pepsin which is a protein-digesting enzyme. Mucus protects the inner lining of the stomach from the action of HCI.
Small Intestine: Small intestine is the site of complete digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Small intestine produces intestinal juice from the glands present in its wall.
The intestinal juice helps in further digestion of food. Small intestine also obtains digestive juices from liver and pancreas.
The liver produces bile juice that causes emulsification of fats and the pancreas produces pancreatic juice for digesting proteins and emulsified fats. This digested food is finally absorbed through the intestinal walls.
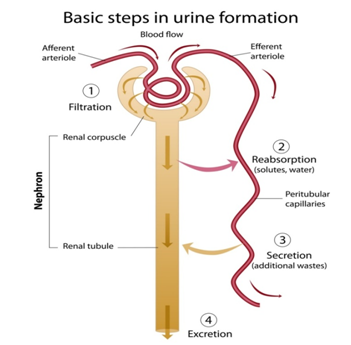
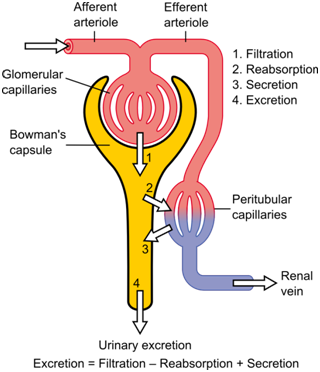
Q 54 – Explain the process of excretion in Human beings ?
Ans 54 – In human beings, the excretory system consists of a pair of kidneys, a pair of ureters, a urinary bladder and a urethra. Kidneys are a pair of reddish brown bean-shaped structures that lie dorsally in the abdominal cavity.
A renal artery and a renal vein occur on the concave hilus region of each kidney. About a million structural and functional units called nephrons occur in each kidney.
Blood is filtered in the glomerular region of a nephron. Useful substances (e.g. glucose, amino acids, salts, water) are reabsorbed and urine passes into collecting ducts.
Ureters are pulsatile drainage tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. Urinary bladder is a pear-shaped distensible sac that stores urine till its volume becomes 300-800 ml.
Urethra is a the tube that carries urine from urinary bladder to the Urethra.
Or
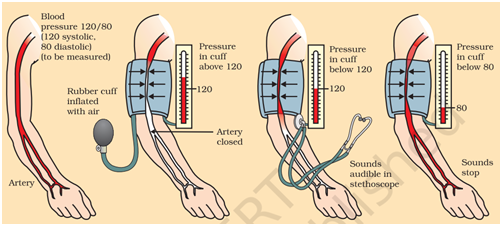
Q 54- Explain in detail the blood pressure in human beings and how can be measure it.
Ans- The pressure at which blood is pumped around the body by the heart is called blood pressure. The blood pressure of a person is always expressed in the form of two values called ‘systolic pressure’ and ‘diastolic pressure’.
In order to understand this, we should first know the meaning of ‘systole’ and ‘diastole’. The phase of the heart beat when the heart contracts and pumps the blood into arteries is called ‘systole’. And the phase of heart beat when the heart relaxes (or expands) and allows the chambers to fill with blood is called ‘diastole’.
The force that blood exerts against the wall of a vessel is called blood pressure. This pressure is much greater in arteries than in veins. The pressure of blood inside the artery during ventricular systole (contraction) is called systolic pressure and pressure in artery during ventricular diastole (relaxation) is called diastolic pressure.
The normal systolic pressure is about 120 mm of Hg and diastolic pressure is 80 mm of Hg. Blood pressure is measured with an instrument called sphygmomanometer.
High blood pressure is also called hypertension and is caused by the constriction of arterioles, which results in increased resistance to blood flow. It can lead to the rupture of an artery and internal bleeding.
Q 55 – Explain the Lymphatic System in the human body.
Ans 55 –
1) A system of tiny tubes called lymph vessels (or lymphatics) and lymph nodes (or lymph glands) in the human body which transports the liquid called lymph from the body tissues to the blood circulatory system is called lymphatic system. The lymphatic system consists of the following parts:
- Lymph capillaries,
- Larger lymph vessels,
- Lymph nodes (or Lymph glands), and
- Lymph
2) Lymph capillaries are tiny tubes which are present in the whole body (just like blood capillaries) Lymph capillaries, however, differ from blood capillaries in two ways: lymph capillaries are closed ended (the end of lymph capillaries in the tissues of the body is closed), and the pores in the walls of lymph capillaries are bigger in size (than that of blood capillaries).
3) Lymph is a light yellow liquid which is somewhat similar in composition to blood plasma. Lymph is not red like blood because it does not contain red blood cells.
Lymph contains large protein molecules and digested food (which come into it from the tissue fluid between the cells). It also contains germs from the cells and fragments of dead cells. Lymph is another medium of circulation in the human body.
4) But lymph flows in only one direction – from body tissues to the heart. Since lymph is derived from the tissue fluid which remains outside the cells of the body, so it is also called extracellular fluid.
5) Lymph contains a special type of white blood cells called lymphocytes which help in fighting infection and disease.
6) Lymph containing large protein molecules, digested fat, germs and fragments of dead cells from the tissue fluid around the body cells seeps into the lymph capillaries present throughout the body.
7) From lymph capillaries, lymph passes into larger lymph vessels containing lymph nodes. In the lymph nodes, lymph is cleaned by white blood cells called lymphocytes. These white blood cells eat the germs and dead cells and also make antibodies for protecting the body from disease.
8) The cleaned lymph containing large protein molecules, digested fat and other useful materials is transported by lymph vessels to the large veins (called subclavian veins) which run just beneath the collar bone. These veins carry the lymph to the heart. In this way, the circulation of lymph from the body tissues to the heart is completed.
Class 10 Biology Life processes
Q 56 – Explain in detail the Human Circulatory system and also explain Why heart is called Double Pump or Double Circulation system.
Ans 56 – The human circulatory system consists of a network of arteries, veins, and capillaries, with the heart pumping blood through it. Its primary role is to provide essential nutrients, minerals, and hormones to various parts of the body.
Alternatively, the circulatory system is also responsible for collecting metabolic waste and toxins from the cells and tissues to be purified or expelled from the body.
Features of Circulatory System
The crucial features of human circulatory are as follows:
The human circulatory system consists of blood, heart, blood vessels, and lymph.
It circulates blood through two loops (double circulation) – One for oxygenated blood, another for deoxygenated blood.
The human heart consists of four chambers – two ventricles and two auricles.
It possesses a body-wide network of blood vessels. These comprise arteries, veins, and capillaries.
The primary function of blood vessels is to transport oxygenated blood and nutrients to all parts of the body. It is also tasked with collecting metabolic wastes to be expelled from the body.
Most circulatory system diagrams do not visually represent is its sheer length. Theoretically, if the veins, arteries, and capillaries of a human were laid out, end to end, it would span a total distance of 1,00,000 kilometres (or roughly eight times the diameter of the Earth).
Organs of Circulatory System
The human circulatory system comprises 4 main organs that have specific roles and functions. The vital circulatory system organs include:
- Heart
- Blood (technically, blood is considered a tissue and not an organ)
- Blood Vessels
- Lymphatic system
Heart
The heart is a muscular organ located in the chest cavity, right between the lungs. It is positioned slightly towards the left in the thoracic region and is enveloped by the pericardium.
The human heart has four chambers; namely, two upper chambers called atria (singular: atrium), and two lower chambers called ventricles.
Though other animals possess a heart and the way in which their circulatory system functions is quite different from humans.
The human circulatory system is much more evolved when compared to insects or molluscs in which the heart is not much evolved
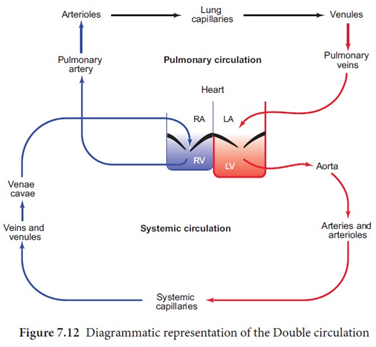
Double Circulation
The way blood flows in the human body is unique and it is quite efficient too. The blood circulates through the heart twice and is called double circulation.
The animals like fish have single circulation where blood circulates through the entire animal only once.
The main advantage of double circulation is that every tissue in the body has a steady supply of oxygenated blood, and it does not get mixed with the deoxygenated blood.
Q 57 – Bile juice does not contain any enzyme but bile salts are important for digestion and absorption of fats. State reason.
Ans – Bile is a digestive juice secreted by the liver. Although it does not contain any digestive enzymes, it plays an important role in the digestion of fats.
Bile is an alkaline and contains salts which help to emulsify or break the fats (or lipids) present in the food. Thus, bile performs two functions:
Makes the acidic food coming from the stomach alkaline so that pancreatic enzymes can act on it.
Bile salts break the fats present in the food into small globules making it easy for the enzymes to act and digest them.
I hope cbseinsights.com helps you to provide good material and Class 10 Biology Life processes Important Question and Answers easily learn and score good marks in board examinations.