India Size and Location
List of National Parks in India Updated 2022 …… Latest
Q 1. In which hemisphere does India lie?
Ans. India lies in the Northern hemisphere.
Q 2. What is the latitudinal extent of India?
Or
What are the degrees of the southernmost latitude of mainland India?
Or
What are the degrees of the northernmost latitude of India?
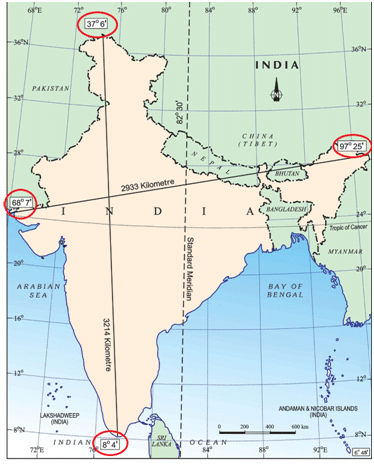
Ans. The latitudinal extent of India is between 8°4′N (southernmost) and 37°6’N (northernmost) latitude.
Q 3. What are the degrees of the easternmost and westernmost longitude of India?
Or
What is the longitudinal extent of India?
Ans. The longitudinal extent of India is 68°7′ E (westernmost) to 97°25′ E (easternmost) longitude.
Q 4. Name the parallel of latitude which divides India roughly into two equal halves.
Ans. The parallel of latitude which roughly divides India into two equal halves is the Tropic of Cancer (23° 30′ N).
Q 5. Name the two seas located around India.
Ans. The two seas located around India are the Arabian Sea in the west and the Bay of Bengal in the east.
Q 6. What is the southernmost point of the Union of India?
Ans. Southernmost point of the Union of India is Indira Point.
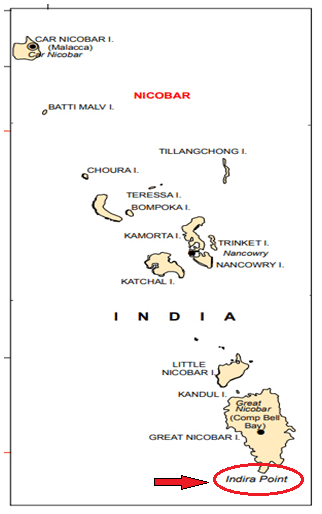
Q 7. In which year did ‘Indira Point’ submerge under water due to tsunami?
Ans. In 2004 ‘Indira Point’ got submerged under the sea water.
Q 8. What is the total area of the Indian landmass?
Ans. The landmass of India has an area of 3.28 million square km. It is 2.4% of the total area of the world.
Q 9. What is the size of India among the countries of the world?
Ans. India is the seventh largest country in the world after Russia, Canada, the United States of America, China, Brazil, and Australia.
Q 10. What is the total land frontier of India?
Ans. The total land frontier of India is 15,200 kms.
India Size and Location Class 9
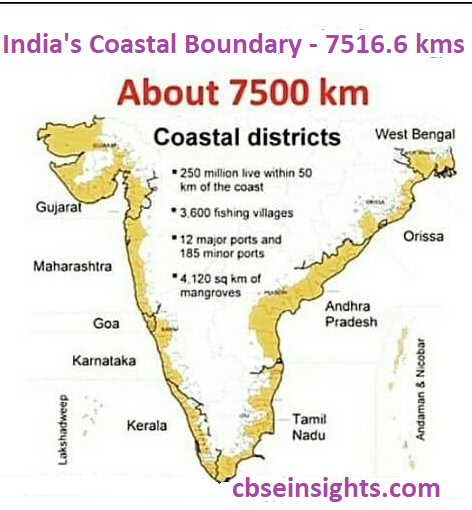
Q 11. Give the total length of the Indian coastline including the Indian islands.
Ans. The total length of the Indian coastline is 7,516.6 kms.
Q 12. In which direction India is bound by young fold mountains?
Ans. In the north, northwest, and northeast direction, India is bound by young fold maintains.
Q 13. Why is the north-south extent of India larger than the east-west extent even though the latitudinal and longitudinal extent in degrees is of the same value?
Ans. This is because the distance between two latitudes is always 111 km i.e. always the same whereas, between two longitudes, it is the maximum at the equator and decreases towards the poles. Therefore the North-South extent of India is 3214 Kms and the East-West extent of India is 2933 Kms.
Q 14. What is the time lag between Gujarat and Arunachal Pradesh?
Ans. The time lag between Gujarat and Arunachal Pradesh is 2 hours.
Q 15. Why has 82°30′ been selected as the standard meridian of India?
Ans. 82°30′ E has been selected as the standard meridian of India because it passes through the center of India, i.e. Mirzapur in Uttar Pradesh.
Q 16. Which route connects countries of Europe in the west to the countries of East Asia?
Ans. The Trans Indian Ocean route.
Q 17. In which year Suez Canal opened?
Ans. Suez Canal opened up in 1869.

Q 18. What is the significance of the Suez Canal?
Ans. With the Suez Canal, India’s distance from Europe has been reduced by 7,000 km.
Q 19. What is the total north-south extent of India in km?
Ans. The north-south extent of India in kilometre is 3,214 km.
Q 20. What is the total east-west extent of India in km?
Ans. The total east-west extent of India is 2,933 km.
India Size and Location Class 9
Q 21. How had India kept its relationship with the world in ancient times?
Ans. Passes in the mountains of the Himalayas provided passages to the ancient travelers while the oceans restricted this as people were afraid to travel by oceans.
Q 22. Which ideas of India could reach the world?
Ans. The ideas of the Upanishads and the Ramayana, the stories of Panchtantra, the Indian numerals, decimal system could reach many parts of the world.
Q 23. Which commodities were exported from India?
Ans. The spices, muslin cloth, and many other commodities were exported from India.
Q 24. From which regions and styles were India got influenced in ancient times?
Ans. India got influenced by Greek sculpture, the architectural styles of domes, and minarets from west Asia in ancient times.
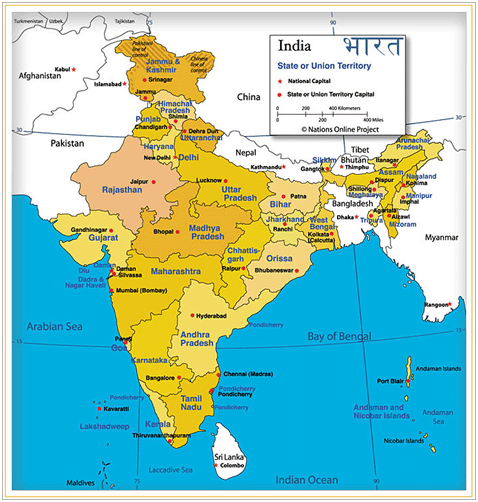
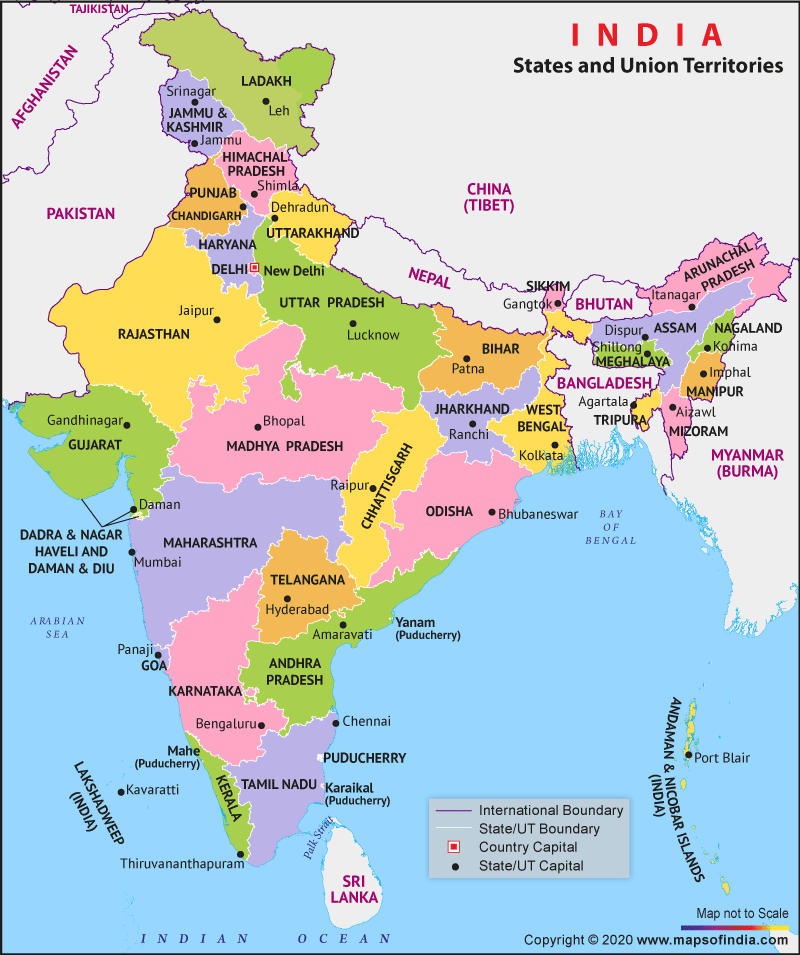
Q 25. Which is the largest and smallest state of India area-wise?
Ans. The largest state is Rajasthan and the smallest state in Goa.
Q 26. Name the states of India which do not have an international border or lie on the coast.
Ans. The states are Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Haryana, and Jharkhand.
Q 27. Name the states of India which have a common border with Pakistan.
Ans. The states are Gujarat, Rajasthan, Punjab, and Jammu & Kashmir.
Q 28. Name the states of India which have a common border with China.
Ans. The states are Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, and Arunachal Pradesh.
Q 29. Name the states of India which have a common border with Myanmar.
Ans. The states are Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram.
Q 30. Name the countries which share borders with India.
Ans. The countries are Pakistan and Afghanistan in the northwest, China (Tibet), Nepal and Bhutan in the north, Myanmar and Bangladesh in the east.
India Size and Location Class 9
Q 31. Which two island countries are India’s neighbors?
Ans. Sri Lanka and the Maldives are the two island countries.
Q 32. Name the two water bodies which separate India from Sri Lanka.
Ans. The two water bodies that separate India is Palk Strait and the Gulf of Mannar.
Q 33. Mention the types of states in India present before 1947.
Ans. The two types of states in India were:
(a) the provinces
(b) the princely states.
Q 34. Who ruled the princely states?
Ans. Princely states were ruled by the local hereditary rulers who in turn acknowledged the British Sovereignity in return of Local Autonomy.
Q 35. Name the country that has common land frontier with the states of Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal and Sikkim.
Ans. The country is Nepal.
Q 36. Name the states through which the Tropic of Cancer passes.
Ans. Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Tripura, and Mizoram.
Q 37. Name the Union Territories of India.
Ans. The Union Territories are Jammu & Kashmir, Ladakh, Chandigarh, Delhi, Andaman and Nicobar, Lakshadweep, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman & Diu, Puducherry.
Q 38. Which country shares International boundary with Jammu & Kashmir, Punjab, Rajasthan, and Gujarat?
Ans. The country is Pakistan.
Q 39. Name the states of India which lie along the eastern coast of India from North to South.
Ans. The states lying along the eastern coast are West Bengal, Odisha, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.
Q 40. Name the two states of India which are parts of Indian desert.
Ans. Gujarat and Rajasthan are parts of Indian Desert.
Q 41. Write the size and extent of India.
Ans. (a) India is the 7th largest country in the world. It has an area of 3.28 million square km. It accounts for 2.4% of the world’s total area.
(b) India has a land frontier of 15,200 km.
(c) India has a coastline of 7516.6 km including the Andaman and Nicobar islands and the Lakshadweep islands.
Q 42. Explain why 82°30′ E an odd value has been chosen as the standard meridian of India.
Ans. The odd value has been chosen as the standard meridian because the longitudinal extent of India is 68°7′ E to 97° 25′ E and this meridian passes through the centre of India.
It passes through Mirzapur i.e. the centre of India. Then there is an understanding among the countries of the world that the degrees of the meridian should be divisible by 7°30′ , i.e. 82° 30′ E. This enables us to overcome the difference of 2 hours of time between Arunachal Pradesh and Gujarat. The time is Indian Standard Time.
Q 43. Why is the difference between the durations of day and night hardly felt at Kanyakumari but not so in Kashmir?
Ans. The difference in the durations of day and night and Kanyakumari and Kashmir are respectively due to their latitudinal locations. Kanyakumari is located closer to the equator and experiences a maximum difference of 45 minutes between day and night.
However, Kashmir lies further away from the equator and experience a significant gap between the duration of day and night that can extend to as much as 3-5 hours because of the slanting rays falling over the Kashmir zone.
India Size and Location Class 9
Q 44. What is a subcontinent? Name the countries that constitute the Indian subcontinent. How is India different from other countries of Asia?
Ans. A subcontinent is a distinctive geographical unit which stands out distinctively from rest of the region because of its large size, varied climates, varied relief etc.
Countries that make up the Indian subcontinent are – India at the centre, Pakistan in the west, Nepal and China (Tibet) in the north, Bhutan and Bangladesh in the east. India is different from other countries of Asia regarding climate, vegetation and culture.
Q 45. Justify the naming of Indian Ocean after India.
Ans. India ocean is named after India because:
(a) India has a long coastline on the Indian Ocean.
(b) India has a central location between east and west Asia.
(c) India’s southernmost extension, the Deccan Peninsula, protrudes into the Indian Ocean which makes it significant to international trade done through the Indian Ocean.
(d) India was the favourite destination of the traders of the world.
Q 46. What do you know about India and her neighbours?
Ans.
(a) India occupies an important strategic position in south-east Asia. India has 28 states, 7 Union Territories and one National Capital Territory.
(b) India shares her land borders with Pakistan and Afghanistan in the north-west, China (Tibet), Nepal and Bhutan in the north, and Myanmar and Bangladesh in the east. Our southern neighbours across the sea consists of two island countries i.e. Sri Lanka and Maldives.
(c) Sri Lanka is separated from India by Palk Strait and Gulf of Mannar while Maldives islands are situated to the south of the Lakshadweep islands.
Q 47. India’s land routes have been important since ancient times. Explain.
Ans.
(a) India’s contacts with the outside world have continued through the ages, but her relationships through the land routes are much older than her maritime contacts.
(b) The various passes across the mountains in the north have provided passages to the ancient travellers. These routes (Kyber and Bolan pass) across the mountains have contributed in the exchange of ideas and commodities since ancient times.
(c) The ideas of Upanishads and the Ramayana, the stories of Panchatantra, the Indian numerals, the decimal system could reach many parts of the world through the land routes. The spices and muslin cloth along with other commodities were taken from India to other countries.
The Greek sculpture and the architectural style of dome and minarets from west Asia can be seen in many parts of our country. This is the result of the exchange of commodities and ideas movement of people.
Q 48. Why are Ahmedabad and Kolkata able to see the noon seen exactly overhead twice a year but not Delhi?
Ans. The sun’s apparent movement towards north and south of the equator is within two tropics.
(a) All the places located within the tropics have overhead sun twice a year.
(b) Both Ahmedabad and Kolkata lie to the south of the Tropic of Cancer or within the two tropics. That is why these two stations see the noon sun overhead twice a year.
(c) Delhi is located at 29°N latitude much to the north of Tropic of Cancer.
(d) The sun’s rays are near overhead in sub-tropical zone. It will never see noon sun overhead, at anytime of the year.
Q 49. India occupies an important strategic position in south Asia. Discuss.
Ans.
(a) The Indian landmass has a central location between the east and the west Asia. India is a southward extension of the Asian continent.
(b) The trans Indian Ocean routes which connect the countries of Europe in the west and the countries of east Asia provide a strategic central location to India.
(c) The part that is attached to the Asian continent connects India through the land routes and mountain passes to the various countries lying to its north, west and east.
(d) The Deccan Peninsula protrudes into the Indian Ocean, thus helping India to establish close contact with west Asia, Africa and Europe from the western coast and southeast and east Asia from the eastern coast.
India Size and Location Class 9
Q 50. Describe how the geographical features of India have fostered unity and homogenity in the Indian society.
Ans. India has a distinct physical and cultural identity: India’s unity and homogenity have been enabled by its physical diversity i.e., physical features.
(a) The lofty mountains in the north which run east-west for thousands of kilometres. They provide a natural wall against all possible intrusions. It gives India an intact structure.
(b) The southern part of India is surrounded by the seas and oceans on the sides. These physical features have also ensured that the people from outside could enter India only through well defended routes through sea or passes in the mountains.
(c) Standard meridian 82°30′ E has been taken as local time all over India providing uniformity.
(d) Rivers and their tributaries provide irrigation facility throughout the country bring uniform development.
(e) Monsoons foster unity. Many festivals are associated with it. Apart from that agricultural and domestic needs are also met by monsoons.
Thus, by adopting new norms and values and accepting as their own, unity and homogenity of India has been promoted.
India Size and Location Class 9
Q 51. Locate and Label the Indian States and Capital on the outline map of India.
Ans. Hyderabad is the Joint Capital of Telangana and Andhra Pradesh.
Q 52. The total length of the coastline of the mainland including Andaman and Nicobar and Lakshadweep is _________ .
Ans. 7,516.6 km
Q 53. The neighbouring countries that share their boundaries with India are _________.
Ans. Pakistan, Afghanistan, Myanmar, Bangladesh, China, Nepal and Bhutan.
Q 54. What is the longitudinal extent of India?
Ans. 68°7’E to 97°25’E
Q 55. What is the latitudinal extent of India?
Ans. 8°4’N and 37°6’N
Q 56. Which is the smallest state in India?
Ans. Goa
Q 57. The north-south extent of India is about _________ .
Ans. 3,214 kms .
Q 58. Which states do not share any international boundary?
Ans. Madhya Pradesh
Q 59. Which canal has reduced India’s distance from Europe by 7,000 km?
Ans. Suez Canal
India Size and Location Class 9
Q 60. What influences the duration of the day and night as one moves from south to north?
Ans. Latitudinal extent
Q 61. Which ocean has been named after a country?
Ans. Indian Ocean
Q 62. What is a strait?
Ans. A narrow channel of the sea that connects two-layer bodies of water.
Q 63. China is the _________ largest country in the world ?
Ans. Fourth
Q 64. From Gujarat to Arunachal Pradesh, the time lag is _________ .
Ans. 2 hours
Q 65. The southernmost point of the Indian mainland is _________.
Ans. Kanyakumari
Q 66. Suez Canal was opened in the year.
Ans. 1869
Q 67. India’s total area accounts for about of the total geographical area of the world.
Ans. 2.4%
Q 68. Which neighboring country of India is an island?
Ans. The Maldives.
Q 69. Name any two states of India that share international boundaries.
Ans. Punjab and Jammu and Kashmir.
Q 70. State the types of states India had before 1947.
Ans. Before 1947, there were two types of states in India such as the Provinces and the Princely States.
Q 71. Which is the largest state (area-wise) of India?
Answer: Rajasthan.
Q 72. Name the Indian states which are situated on the eastern coast of India.
Ans. West Bengal, Odisha, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu.
Q 73. Name the Indian states which are situated on the western coast of India.
Ans. Kerala, Karnataka, Goa, and Maharashtra.
Q 74. In which year did the Indira Point get submerged under the seawater?
Ans. Indira Point got submerged under the seawater in 2004 during the Tsunami.
Q 75. Name the state that shares a border with Myanmar.
Ans. Tripura, Mizoram, Manipur and Nagaland.
India Size and Location Class 9
Q 76. Which meridian has been selected as the Standard Meridian of India?
Ans. 82°32’E has been selected as the Standard Meridian of India.
Q 77. How does India occupy an important strategic position in South Asia?
Ans. India occupies an important strategic position in South Asia in the following ways :
(a) The Indian landmass has a central location between East and West Asia.
(b) The trans-Indian Ocean routes, which connect the countries of Europe in the West and the countries of East Asia, provide a strategic central location to India.
(c) The Deccan Peninsula protrudes into the Indian Ocean has helped India to establish close contact with West Asia, Africa, and Europe from the western coast and with Southeast and East Asia from the eastern coast.
Q 78. What is the name of the southernmost point of India? Why is it not visible today?
Ans. The southernmost point of India is Indira Point. The Indira point is situated in the Great Nicobar Group of Island in Andaman Nicobar island. It is not visible today because it was submerged under the seawater in 2004 during the Tsunami.
Q 79. What is latitude? What is the latitudinal extent of India?
Ans. The position of a place, measured in degrees north or south of the Equator. It is mostly calculated because of the angular distance of a place north-south of the equator, The mainland of India extends between latitudes 8°4′ N and 37°6′ N. The latitudinal extension shows that India is located in the Northern Hemisphere.
Q 80. Which ocean is named after India? Give two reasons as to why it was named after India.
Ans. The Indian Ocean is named after India. India is the only country that has the credit of an ocean named after it. The Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal, extensions of the Indian Ocean, lie to the west and east of the Indian Peninsula, and the Indian Ocean lies to its south. No other country has a long coastline on the Indian Ocean as India.
The central location of India at the head of the Indian Ocean has provided India a strategic location of great significance along the trans-Indian Ocean routes. It is India’s eminent position in the Indian Ocean that justifies the naming of the ocean after India.
Q 81. Why is India called a subcontinent?
Ans. India is called a subcontinent because :
It is a big landmass. This stands out as a distinct geographical unit from the rest of the continent.
It is separated by natural features like mountains and rivers.
India is also separated from the rest of the continent by the mighty Himalayas.
Q 82. How have been mountain passes been helpful in India since historic times? Explain.
Ans. India is bounded by the young fold mountains in the northwest, north, and northeast. The various passes across the mountains in the north have provided passages to the ancient travelers.
The spices, muslin, and other merchandise were taken from India to different countries through these passes. Mountain passes have contributed to the exchange of ideas and commodities since historic times.
India Size and Location Class 9
Q 83. What is the latitudinal extent of India? How is the latitudinal spread in India advantageous to her?
Ans. The latitudinal extent of India lies between 8°4’ N and 37°6’ N. This means that the longitudinal expanse is about 30° from west to east.
The advantages of longitudinal spread are :
(a) It influences the duration of the day and night as one moves from South to North.
(b) It also helps to take advantage of the Indian Ocean, the Arabian Sea on the west, and the Bay of Bengal on its east for sea movements.
Q 84. Why do the days and nights are almost of equal duration at Kanyakumari?
Ans. Kanyakumari in Tamil Nadu is located at the southernmost tip of / India’s mainland. The latitude 8°4’ N passes close to it.
The place is thus near the equator and lies close to the Equatorial region. As the sun shines directly over the Equator throughout the year, the duration of day and night are almost equal here.
Hence, in Kanyakumari, the difference in the duration of day and night is very little.
Q 85. Why Is the knowledge of latitude and longitude important for people?
Ans. The knowledge of latitude and longitude is important for people because it helps them to understand and locates the geographical location and globe better. The use of latitudes and longitudes offers a better and quick grasp of geographical facts.
It determines the time zones of the different regions of the world. With the help of longitudes and latitudes, it is easy to calculate local time and standard time. Longitudes and latitudes also help in calculating the distance from one place to another.
Q 86. What do you know about the neighbors of India?
Ans. India occupies an important strategic position in South Asia. India shares its land boundaries with Afghanistan and Pakistan in the northwest; China, Nepal, and Bhutan in the north, and Myanmar and Bangladesh in the east. The island states of Sri Lanka and the Maldives are our southern neighbors across the sea.
Sri Lanka is separated from India by a narrow channel of sea formed by the Palk Strait and the Gulf of Manner, while the Maldives Islands are situated to the South of the Lakshadweep Islands. Pakistan, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, and India form the most natural geographical unit, often referred to as the Indian subcontinent.
Q 87. How has the long coastline been beneficial to India?
Ans. The Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal, extensions of the Indian Ocean, lie to the west and east of the Indian Peninsula, and the Indian Ocean lies to its south. The total length of the coastline of the mainland of India including Andaman and Nicobar and Lakshadweep is 7516.6 km. The long coastline of India has helped in maritime trade for ages.
The central location of India at the head of the Indian Ocean has provided it a strategic location along the trans-Indian Ocean routes. India can establish close contact with West Asia, Africa, and Europe from the western coast and with Southeast and East Asia from the eastern coast.
The long coastline has also played a major role in influencing the climate of India. It provides opportunities for fishing and the extraction of petroleum. It serves as a natural boundary protecting India.
Q 88. What was the contribution of land routes to India in ancient times? Explain.
Ans. The contribution of land routes to India in ancient times are given below :
(a) The large land boundaries of India have helped to develop links with her neighboring countries.
(b) It contributed to the exchange of ideas and commodities since ancient times.
(c) The ideas of the Upanishads, the Ramayana, the Geeta, etc. have become known to the world.
(d) The Indian numerals as well as the decimal system long back crossed the border. The Arabs took these ideas to the West.
(e) The spices, muslin, and other merchandise were taken away from India to different countries through these land routes.
(f) On the other hand, the influence of Greek sculpture, and the architectural styles of dome and minarets from West Asia can be seen in different parts of our country. (Any five points)
Q 89. Write a note on the location and size of India.
Ans.
Location:-
India is a vast country. It lies entirely in the Northern hemisphere and the mainland extends between latitudes 8°4’N and 37°6’N and longitudes 68°7’E and 97°25’E. The Tropic of Cancer (23°30’N) divides the country into almost two equal parts.
And to the southeast of India’s mainland lie the Andaman and Nicobar Islands in the Bay of Bengal and to the southwest lie the Lakshadweep islands in the Arabian Sea.
Size:-
The landmass of India has an area of 3.28 million square km. India’s total area accounts for about 2.4 percent of the total geographical area of the world.
India is the seventh-largest country in the world. India has a land boundary of about 15,200 kms and the total length of the coastline of the mainland, including Andaman and Nicobar, and Lakshadweep is 7,516.6 kms.
So, it has an east-west extent of 2,933 km from Arunachal Pradesh to Kachchh in Gujarat and a north-south extent of 3,214 km from Kashmir to Kanyakumari. The southern part of the country is in form of a peninsula, tapering towards the Indian Ocean in the south. It is bounded by the Arabian Sea in the southwest and the Bay of Bengal in the southeast.
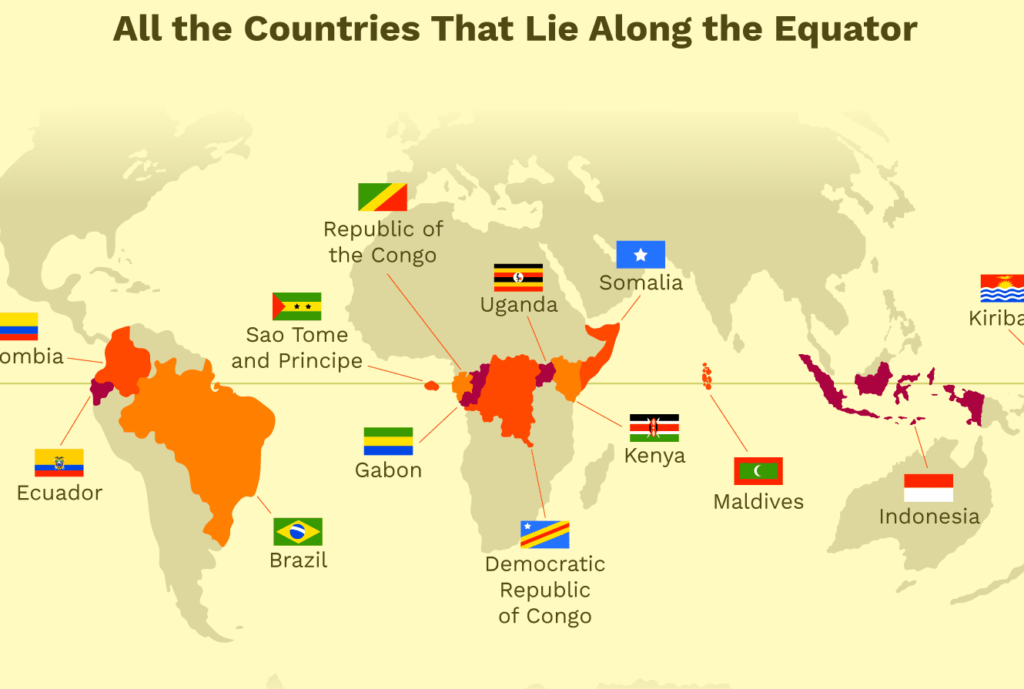
Q 90. Name the countries which lie on the Equator?
Ans. The Countries which lie on the Equator are as follows.
Download PDF Class 9 Geography India, Size and Location Extra Questions and Answers
Download PDF Class 9 Geography India, Size and Location Important Questions and Answers