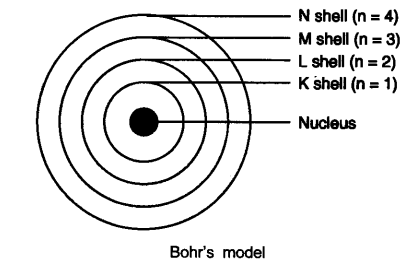
Bohr’s model of the atom
(1) Atom has a nucleus in the center.
(2) Electrons revolve around the nucleus.
(3) Certain special orbits known as discrete orbits of electrons are allowed inside the atom.
(4) While revolving in discrete orbits the electrons do not radiate energy.
(5) These orbits or shells are called energy levels.
(6) These orbits or shells are represented by the letters K, L, M, N or the numbers n = 1, 2, 3, 4