Q 1 – What is precipitation?
Ans. (a) Falling of moisture in the form of rainfall, snow, fog, sleet, and hailstone is termed as precipitation.
Q 2 – What is the water cycle?
Ans. (b) The water cycle is the process by which water continually changes its form and circulates between oceans, atmosphere, and land.
Q 3 – What are the factors affecting the height of the waves?
Ans. (c) Winds, earthquakes, volcanic eruption, or underwater landslides are the factors affecting the height of the waves. The stronger the wind blows, the bigger the wave becomes.
Q 4 – Which factors affect the movement of ocean water?
Ans. (d) Temperature, winds, the gravitational pull of the sun, the earth, and the moon; warm and cold currents are the factors that affect the movement of ocean water.
Q 5 – What are tides and how are they caused?
Ans. (e) Tides are the rhythmic rise and fall of ocean water that occurs twice in a day. The strong gravitational pull exerted by the sun and the moon on the earth’s surface cause the tides.
Q 6 – What are ocean currents?
Ans. (f) Ocean currents are streams of water flowing constantly on the ocean surface in definite directions.
Q 7 – Give reasons:
(a) Ocean water is salty.
(b) The quality of water is deteriorating.
Ans. (a) The water of the oceans is salty as it contains a large amount of dissolved salts.
(b) Water is being used injudiciously. Whatever potable water is available, its quality is not good. It is because industrial effluents and untreated water of industries get mixed into streams and rivers. Sewerage water also gets mixed into these water bodies. As a result, the quality of water is deteriorating day by day
Q 8 – Tick the correct answer.
(a) The process by which water continually changes its form and circulates between oceans, atmosphere and land
(i) Water cycle
(ii) Tides
(iii) Ocean currents.
(b) Generally the warm ocean currents originate near
(i) Poles
(ii) the Equator
(iii) None of these.
(c) The rhythmic rise and fall of ocean water twice in a day is called
(i) Tide
(ii) Ocean current
(iii) Wave
Ans. (a)—(i), (b)—(ii), (c)—(i)
Q 9 – What is a terrarium?
Ans. It is an artificial enclosure for keeping small house plants. .
Q 10 – Which type of water do the ocean bodies and the seas contain?
Ans. They contain salty water.
Q 11 – What do you mean by salinity?
Ans. Salinity is the amount of salt in grams present in 1000 grams of water.
Q 12 – What is the average salinity of the oceans?
Ans. The average salinity of the oceans is 35 parts per thousand.
Q 13 – What is the salinity of the Dead sea?
Ans. The salinity of the Dead sea is 45 parts per thousand.
Q 14 – Why do swimmers float in the Dead Sea?
Ans. Swimmers float in the Dead sea because the increased salt content makes it dense.
Q 15 – What is the significance of World Water Day?
Ans. On the occasion of World Water Day (22nd March) the need to conserve water is reinforced in different ways.
Q 16 – What is a Tsunami?
Ans. Tsunami is a Japanese word that means ‘Harbour Waves’ as the harbors get destroyed whenever there is a Tsunami.
Q 17 – What happens during high Ode?
Ans. During high tide, waves rise high and water covers much of the shore.
What happens during low tide?
Ans. During low tide waterfalls to its lowest level and recedes from the shore.
Q 18 – How are tides caused?
Ans. The strong gravitational pull exerted by the sun and the moon on the earth’s surface cause tides.
Q 19 – Name one warm current and one cold current.
Ans. Warm current — The Gulf Stream
Cold current — The Labrador Ocean current.
Q 20 – What happened to the Indira point during the tsunami of 2004?
Ans. It got submerged.
Q 21 – How are spring and neap tides formed?
Ans. During the full moon and new moon days, the sun, the moon, and the earth are in the same line and the tides are highest. These tides are called spring tides. But when the moon is in its first and last quarter, the ocean waters get drawn in diagonally opposite directions by the gravitational pull of the sun and earth resulting in low tides. These tides are called neap tides.
Q 22 – How are high tides important?
Ans. High tides are important for various reasons:
- They help in navigation
- They raise the water level close to the shores. This helps the ships to arrive at the harbour more easily.
- The high tides also help in fishing. Much more fish come closer to the shore during the high. This enables the fisherman to get a plentiful catch.
- The rise and fall of water due to tides is being used to generate electricity in some places.
Q 23 – What are the waves? Write a short note on it
Ans. Waves are the rise and fall of the water on the surface of the ocean. Waves are formed when winds scrape across the ocean surface. The stronger the wind blows, the bigger the wave becomes. During the storm, the winds blow at very high speed and therefore huge waves are formed. These waves are very strong, hence very destruction. They may cause huge devastation.
Q 24 – Write a brief note on Tsunami.
Ans. . Tsunami is a Japanese word that means ‘harbour waves’ as the harbours get destroyed whenever there is a tsunami. An earthquake, a volcanic eruption or underwater landslides can shift large amounts of ocean water. As a result tsunami occurs which may be as high as 15 m. The tsunami of 2004 is still in our minds. It caused huge death and destruction in the coastal areas of India. The Indira Point in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands got submerged after the tsunami.
Q 25 – Write a note on the importance of water
Ans. Water is life. Without water, we can not think of life. Its scarcity may create numerous problems but its absence would definitely lead to the non-existence of all the living beings on the earth. It is a precious resource of nature. We drink water whenever we feel thirsty. We use water in numerous activities such as washing clothes, cleaning house floors, watering the garden, etc. Industries also need water for their functioning. Thus, water is very essential and therefore we must conserve it. Our careless use of water has created several problems. Whatever water is there, it is not of good quality. We should think about the ways of its conservation for our own sake.
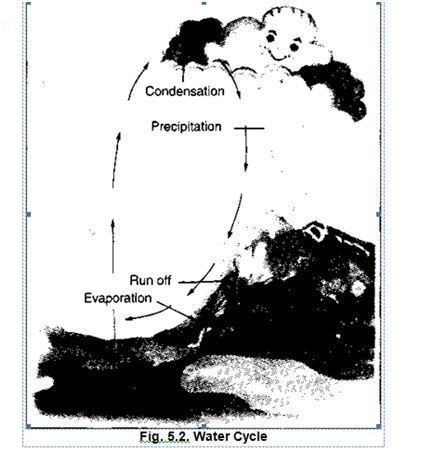
Q 26 – Explain the water cycle with a neat and labelled diagram.
Ans. The sun’s heat causes evaporation of water, flowing down to stream or drains into water vapour. When the water vapour cools down, it condenses and forms clouds. These clouds,
when become too heavy to float, start falling on the land or sea in the form of rain, snow, or sleet. Thus, the process by which water continually changes its form and circulates between oceans, atmosphere, and land is known as the water cycle.
Q 27 – Give an account of ocean currents.
Ans. Ocean currents are streams of water flowing constantly on the ocean surface in definite directions. The ocean currents may be warm or cold. The warm ocean currents originate near the equator and move towards the poles. The cold current carries water from polar or higher latitudes to tropical or lower latitudes. For example, the Labrador Ocean current is a cold current while the Gulf Stream is a warm current.
The ocean current influences the temperature conditions of the area. Warm currents bring about warm temperatures over the land surface. The areas where the warm and cold currents meet provide the best fishing grounds of the world. For example seas around Japan and the eastern coast of North America. The areas where a warm and cold current meet also experience foggy weather and therefore navigation becomes difficult.
Q 28 – How do we classify ocean movements? Explain.
Ans. Ocean movements can be classified into waves, tides, and currents
When the water on the surface of the ocean rises and falls alternately, they are called waves. Waves are formed when winds scrape across the ocean surface. The stronger the wind blows, the bigger the wave becomes.
The rhythmic rise and fall of ocean water twice in a day is known as a tide. Tides may be high or low. It is high tide when water covers much of the shore by rising to its highest level. It is low tide when waterfalls to its lowest level and recedes from the shore. Tides are caused due to the strong gravitational pull exerted by the sun and moon on the earth’s surface. High tides help in navigation and fishing. The rise and fall of water due to tides is being used to generate electricity in some places.
Ocean currents. These are streams of water flowing constantly on the ocean surface in definite directions. The ocean currents may be warm such as the Gulf Stream and cold such as the Labrador Ocean current. The areas where the warm and cold currents meet provide the best fishing ground of the world. For example, seas around Japan and the Eastern Coast of North America.
Q 29 – Which day is celebrated as world water day?
Ans.22nd march.
Q 30 – Why is the ocean water saline?
Ans. The ocean water is saline as it contains large amount of dissolved salts.
Q 31 – _____ is the southernmost point of India.
Ans. Indira Point.
Q 32 – Salinity is the amount of salt in grams present in _____ grams of water.
Ans. 1000.
Q 33 – Rapid withdrawal of water f rom the coastal region gives the warning of ______.
Ans. Tsunami.
Q 34 – _____ are f ormed when gentle winds scraps across the ocean surf ace
Ans. Tsunami
Q 35 – What is water cycle?
Ans. The process by which water continually changes its f orm and circulates between oceans, atmosphere and land is known as the water cycle
Q 36 – Distinguish between high tide and low tide.
Ans. The rise in the water level is called the high tide while the f all in the water level is called the low tide.
• In high tide, water covers much of the shore by rising to its highest level. In low tide, water f alls to its lowest level and recedes from the shore.
Q 37 – Define vertical distribution of sea water.
Ans. When surf ace water gets heated by sun, water evaporates and increases the concentration of salts. Surf ace water becomes denser sinks and sub surf ace water rises up. Thus, salinity of se a water causes vertical circulation.
Q 38 – Name the two types of ocean current and its movement on earth.
Ans. Two types of ocean currents are warm and cold currents. The warm currents f low from low latitudes in tropical zones towards the high latitudes in the temperate and sub polar zones. The cold current f low from high latitudes to low latitudes.
Q 39 – The movement of ocean water takes place in three dif f erent. Explain them.
Ans. The movement of ocean water takes place in three dif f erent ways. These are:
• Waves: When the water on the surf ace of the ocean rises and f alls alternately, they are called waves. Waves are f ormed in the seas and oceans when wind blows across the water surf ace. The shape and size of the wave depend on the speed of the winds. The stronger the wind blows, the bigger the wave becomes. During a storm, the winds blowing at very high speed f rom huge waves may cause tremendous destruction.
• Tides: The continual rise and fall of ocean water is called a tide. The rise in the water level is high tide, when water falls to its lowest level and recedes f rom the shore it is called low tide. Tides help in fishing, navigation and trade. The rise and f all of water due to tides is being used to generate electricity in some places.
• Ocean currents: These are streams of water following constantly on the ocean surf ace in definite directions. There are two types of ocean currents- warm and cold. The warm ocean currents originate near the equator and move towards the poles. For example, the Gulf stream. The cold currents carry water from polar or higher latitudes to tropical or lower latitudes. For example, the Labrador Ocean Current.