Matter in Our Surroundings
Q 1. In which phenomena water changes into water vapour below its B.P.?
(a) Evaporation
(b) Condensation
(c) Boiling
(d) No such phenomena exist
Ans. (a) Evaporation
Q 2. The quantity of matter present in an object is called its:
(a) Weight
(b) Gram
(c) Mass
(d) Density
Ans. (c) Mass
Q 3. The liquid which has the highest rate of evaporation is:
(a) Petrol
(b) Nail- polish remover
(c) Water
(d) Alcohol
Ans. (b) Nail- polish remover
Q 4. At higher altitudes:
(a) Boiling point of a liquid decreases
(b) Boiling point of a liquid increases
(c) No change in boiling point
(d) Melting point of solid increases
Ans. (a) Boiling point of a liquid decreases
Q 5. The boiling point of water on Celsius and Kelvin scale respectively is:
(a) 373, 273
(b) 0, 273
(c) 273, 373
(d) 100, 373
Ans. (d)100, 373
Q 6. The boiling point of alcohol is 78 C. What is this temperature in Kelvin scale:
(a) 373 K
(b) 351 K
(c) 375 K
(d) 78 K
Ans. (b) 351 K
Q 7. When we put some crystals of potassium permanganate in a beaker containing water, we observe that after sometime whole water has turned pink. This is due to:
(a) Boiling
(b) Melting of potassium permanganate crystals
(c) Sublimation of crystals
(d) Diffusion
Ans. (d) Diffusion
Q 8. The volume of a gas at a particular temperature and atmospheric pressure is 200 ml. Keeping the temperature constant if pressure is increased to 5 atmospheres, then the volume of the gas will be:
(a) 100 ml
(b) 40 ml
(c) 200 ml
(d) 205 ml
Ans. (b) 40 ml
Q 9. The state of matter which consists of super-energetic particles in the form of ionized gases is called:
(a) Gaseous state
(b) Liquid state
(c) Bose-Einstein condensate
(d) Plasma state
Ans. (d) Plasma state
Q 10. Which of the following statements best explains why a closed balloon filled with helium gas rises in air?
(a) Helium is a mono-atomic gas, whereas nearly all the molecules that make up air, such as nitrogen and oxygen, are diatomic.
(b) The average speed of helium atoms is higher than the average speeds of air molecules, and the higher speed of collisions with the balloon walls propels the balloon upward.
(c) Because the helium atoms are of lower mass than the average is molecules, the helium gas is less dense than air. The balloon thus weighs less than the air displaces by its volume.
(d) Because helium has a lower molar mass than the average air molecules, the helium atoms are in faster motion. This means that the temperature. Hot gases tend to rise.
Ans. (c) Because the helium atoms are of lower mass than the average is molecules, the helium gas is less dense than air. The balloon thus weighs less than the air displaces by its volume.
Matter in Our Surroundings
Q 11. The force that binds the particles of matter together is known as:
(a) Intermolecular space
(b) Bond
(c) Intermolecular force
(d) Nuclear force
Ans. (c) Intermolecular force
Q 12. The change of a liquid into vapour is called:
(a) Vaporization
(b) Solidification
(c) Sublimation
(d) None of these
Ans. (a) Vaporization
Q 13. Equal volumes of all gases under similar conditions of temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of molecules. This statement was made by:
(a) Gay- lussae
(b) Avogadro
(c) Berzilius
(d) John Dalton
Ans. (b) Avogadro
Q 14. Which of the following describes the liquid phase?
(a) It has a definite shape and a definite volume
(b) It has a definite shape but not a definite volume
(c) It has a definite volume but not a definite shape
(d) It has neither a definite shape nor a definite volume
Ans. (c) It has a definite volume but not a definite shape
Q 15. Boyle’s law states that the:
(a) Pressure of a gas is directly proportional to the temperature at constant volume
(b) Pressure of a gas is inversely proportional the volume at constant temperature
(c) Volume is directly proportional to the temperature at constant pressure
(d) None of the above
Ans. (b) The pressure of a gas is inversely proportional the volume at constant temperature
Q 16. When a teaspoon of solid sugar is dissolved in a glass of liquid water, what phase or phases are present after mixing:
(a) Liquid only
(b) Still solid and liquid
(c) Solid only
(d) None of these
Ans. (a) Liquid only
Q 17. As of the 1990s, scientists have proved the existence of how many states of matter?
(a) Two
(b) Three
(c) Four
(d) Five
Ans. (d) Five
Q 18. Out of the following which is the densest state of matter?
(a) Solids
(b) Liquids
(c) Gases
(d) Plasmas
Ans. (a) Solids
Q 19. Densities of two gases are in the ratio 1: 2 and their temperatures are in the ratio 2 : 1, then the ratio of their respective pressure is:
(a) 1 : 1
(b) 1 : 2
(c) 2 : 1
(d) 4 : 1
Ans. (a) 1 : 1
Q 20. Which of the following expression at constant pressure represents Charles law?
(a) VT = constant
(b) PV = constant
(c) V/ T = constant
(d) None of the above
Ans. (c) V/ T = constant
Matter in Our Surroundings
Q 21. All gases will occupy zero volume when the temperature is reduced to:
(a) 273°C
(b) 273°C
(c) -273°C
(d) 0°C
Ans. (d) 0°C
Q 22. Which of the following is not matter
(a) Blood
(b) Moon rock
(c) Electron
(d) Humidity
Ans. (a) Blood
Q 23. Which is more effective in cooling?
(a) Ice at 273K
(b) Water at 273 K
(c) Water at 373K
(d) Ice at 373K
Ans. (a) Ice at 273K
Q 24. 0 ° C temperature is equal to
(a) 0 K
(b) 273 K
(c) -273 K
(d) 300 K
Ans. (b) 273 K
Q 25. Non- reacting gases have a tendency to mix with each other. This phenomenon is known as:
(a) Chemical reaction
(b) Diffusion
(c) Effusion
(d) Explosion
Ans. (c) Effusion
Q 26. Zig-zag movement of the solute particle in a solution is known as
(a) Linear motion
(b) Circular motion
(c) Brownian motion
(d) Curved motion
Ans. (c) Brownian motion
Matter in Our Surroundings
Q 27. A gas which obeys the gas laws is known as:
(a) An ideal gas
(b) A heavier gas
(c) A lighter gas
(d) A real gas
Ans. (a) An ideal gas
Q 28. A gas can be compressed to a fraction of its volume. The same volume of a gas can be spread all over a room. The reason for this is that:
(a) The volume occupied by molecules of a gas is negligible as compared to the total volume of the gas.
(b) Gases consists of molecules which are in a state of random motion
(c) Gases consists of molecules having very large inter- molecular space which can be reduced or increased under ordinary conditions
(d) None of these
Ans. (c) Gases consists of molecules having very large inter- molecular space which can be reduced or increased under ordinary conditions.
Q 29. What is the term used to describe the phase change of a liquid to a gas?
(a) Boiling
(b) Condensation
(c) Melting
(d) None of the above
Ans. (a) Boiling
Q 30. What term is used to describe the phase change of a solid to a liquid?
(a) Freezing
(b) Melting
(c) Boiling
(d) None of the above
Ans. (b) Melting
Q 31. The one, in which inter-particle forces are strongest, is:
(a) Sodium chloride
(b) Hydrogen
(c) Either
(d) Carbon dioxide
Ans. (a) Sodium chloride
Matter in Our Surroundings
Q 32. The melting point temperature of the solid state of a substance is 40°C. The freezing point temperature of the liquid state of the same substance will be:
(a) 35°C
(b) 40°C
(c) 45°C
(d) Can’t predict
Ans. (b) 40°C
Q 33. What is the term used to describe the phase change as a liquid becomes a solid?
(a) Evaporation
(b) Condensation
(c) Freezing
(d) None of the above
Ans. (c) Freezing
Q 34. Which has the least energetic molecules?
(a) Solids
(b) Liquids
(c) Gases
(d) Plasmas
Ans. (a) Solids
Q 35. In which phase of matter would you expect compound (alcohol exists) at room temperature?
(a) Solid
(b) Liquid
(c) Gas
(d) Plasma
Ans. (b) Liquid
Q 36. Which of these choices will not change the state of matter?
(a) Temperature
(b) Crushing a crystal
(c) Pressure
(d) Heat
Ans. (b) Crushing a crystal
Matter in Our Surroundings
Q 37. If you leave water in a glass and some molecules turn into a gas, it is called:
(a) Condensation
(b) Evaporation
(c) Extinction
(d) Condensation
Ans. (b) Evaporation
Q 38. Name the term used for the solid which is directly formed from the gas.
Ans. Sublimate.
Q 39. Define the term volatile liquid.
Ans. Those liquids which can change into vapor easily are termed as volatile liquids.
Q 40. What is the effect of pressure on boiling point?
Ans. The boiling point increases with an increase in pressure.
Q 41. Name any two substances which sublime.
Ans. Camphor, napthalene, iodine, ammonium chloride.
Q 42. Define condensation.
Ans. The change of a gaseous state to a liquid state on cooling is known as condensation.
Matter in Our Surroundings
Q 43. Define the term ‘matter’.
Ans. The matter is defined as anything that occupies some space and has a definite mass.
Q 44. What is the Law of Conservation of Mass?
Ans. The Law of Conservation of Mass states that mass can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
Q 45. Define melting point.
Ans. It is the temperature at which a solid becomes liquid at atmospheric pressure by absorbing heat.
Q 46. Out of water and alcohol, which is more volatile?
Ans. The boiling point of alcohol (78°C or 351K) is lower than that of water (100°C or 373K), therefore, alcohol is more volatile than water.
Q 47. What is sublimation?
Ans. Direct conversion of a solid into vapour and vice-versa (i.e., vapour into solid) is called sublimation.
Q 48. Is dry ice the same thing as ordinary ice?
Ans.No, dry ice is solid carbon dioxide while ordinary ice is solid water.
Q 49. Define latent heat of fusion.
Ans. It is the heat energy required to convert 1 kg of solid into liquid at its melting point at atmospheric pressure.
Q 50. Define vapourization.
Ans. The process of change from liquid state to gaseous (vapour) state is called vapourisation.
Matter in Our Surroundings
Q 51. Give the important properties on the basis of which the three states of matter can be distinguished.
Ans. The three states of matter can be distinguished on the basis of shape, volume, compressibility, packing of molecules, number of free surfaces, etc.
Q 52. State the effect of surface area on rate of evaporation.
Ans. If the surface area is increased, the rate of evaporation increases.
Q 53. Define evaporation.
Ans. Evaporation is a physical process in which a liquid changes to its gaseous state, at a temperature lower than its boiling point.
Q 54. What are the ways in which a gas can be liquefied?
Ans. Applying pressure and reducing temperature can liquefy gases.
Q 55. What is plasma?
Ans. It is a state of matter which consists of super energetic and super excited particles. These particles are in the form of ionised gases.
Matter in Our Surroundings
Q 56. How do solids, liquids and gases differ in shape and volume?
Ans. Solids have a definite shape and a fixed volume, liquids have a definite volume but no fixed shape while gases neither have a definite volume nor a definite shape.
Q 57. Kelvin scale of temperature is regarded as better scale than Celsius. Why?
Ans. As it has a wide range of measurement and temperature in kelvin scale always has a positive sign, hence regarded as better scale than Celsius.
Q 58. What are characteristics of particles of matter?
Ans. The particles of matter have following characteristics:
- Particles of matter are very small.
- Particles of matter have space between them.
- Particles of matter attract each other.
- Particles of matter are constantly moving.
Q 59. Write four main characteristics of solid state of matter.
Ans. Solids have definite mass, volume and shape.
- The particles in solid state are closely packed and empty spaces in them are negligible.
- Solids are rigid.
- Solids can have a number of free surfaces.
Q 60. Write four main characteristics of liquid state of matter.
Ans.
- Liquids have a definite mass and volume.
- A liquid can take the shape of a container.
- Liquids have only one free surface.
- Liquids show the property of diffusion.
Q 61. Write four characteristics of gaseous state of matter.
Ans.
- A gas has definite mass but it has neither definite shape nor definite volume.
- Gases can occupy the whole of the space available to them.
- There are larger vacant spaces between the molecules of a gas.
- Gases are highly compressible.
Q 62. Explain evaporation and its cooling effect in terms of kinetic energy of particles.
Ans. During evaporation, the molecules which possess higher kinetic energy leave the liquid and go into the space above the liquid as vapour. The remaining molecules possessing lower kinetic energy are left in the liquid state. Consequently, the average kinetic energy decreases which results in the fall of temperature of the liquid.
Matter in Our Surroundings
Q 63. How is heat transferred when a solid sublimes?
Ans. Certain solids like iodine, naphthalene, solid CO sublimes on heating. Heat is absorbed by the molecules of these solids rapidly which provides enough kinetic energy to show phase change into gaseous state.
Q 64. Why do gases diffuse rapidly?
Ans. Gases diffuse rapidly due to high speed of the particles and large space between them.
Q 65. For any substance, why does the temperature remain constant during the change of state?
Ans. On increasing the temperature of a substance, for example a solid, the kinetic energy of the particles increases which is used to overcome the forces of attraction between the particles therefore the temperature remains constant during the change of state.
Q 66. Explain compressibility in gases with an example.
Ans. Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) cylinders are used in our homes for cooking, contains gases in the compressed state. Similarly, compressed natural gas (CNG) is used as a fuel in vehicles. Large volume of gases can be compressed in small cylinders and are transported to distant places.
Matter in Our Surroundings
Q 67. Why solids cannot be compressed like gases?
Ans. The particles in solids are so tightly packed that there are no or little interparticle spaces left among them. Therefore solids are not compressible like gases. Gases which have large interparticle spaces are therefore compressible.
Q 68. Define boiling. Why is boiling considered as bulk phenomenon?
Ans. Rapid and breaking of bubbles in the bulk of a liquid being heated is called boiling. During boiling particles from the bulk of liquid gain enough energy to get converted to vapour. Therefore it is a bulk phenomenon.
Q 69. Why do we see water droplets on the outer surface of a glass containing ice-cold water?
Ans. The water vapour present in air, on coming in contact with the cold glass of water, loses energy and gets converted to liquid state, which we see as water droplets.
Q 70. Why do we sprinkle water on the roof or open ground in summer?
Ans. During hot summer evenings, we often sprinkle water on the roof of the house or open ground in front of our house. The water evaporates by absorbing heat from the ground and the surrounding air. By losing heat, the ground becomes cool and we feel comfortable.
Matter in Our Surroundings
Q 71. Why is ice rubbed on a burnt part of the skin?
Ans. When a Ginger or some part of our body gets burnt, we rub the burnt portion with an ice cube. The reason being that due to burning, the temperature of the injured skin increases. When ice is rubbed, the excess heat from the skin is taken away by large latent heat of fusion of water. As a result, the temperature of the injured skin decreases and we feel less pain.
Q 72. How will you demonstrate that particles of matter are continuously moving?
Ans. When an incense stick is lit in one corner of a room, we get the smell while sitting at a distance from the stick. This is because the particles of matter are continuously moving. Because of their random motion, the particles of incense mix with the particles of air rapidly and the smell of the incense reaches us even when we are sitting at a distance from the incense stick.
Matter in Our Surroundings
Q 73. Why do solids expand a bit on heating and contract a bit on cooling?
Ans. The solid molecules do not have sufficient intermolecular (or interparticle) space thus its expands a bit on heating. The interparticle forces of attraction are very strong which do not let solid particles leave their mean positions. Therefore solid contracts a bit on
cooling.
Q 74. Draw a diagram to shown interconversion among states of matter.
Ans.
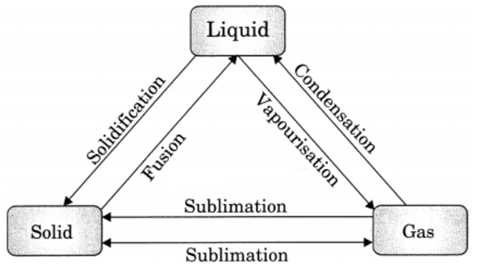
Q 75. Why is light not considered matter?
Ans. Matter occupies space and has mass. Light has neither of the two and that is why it is not considered as matter. It is considered as a form of energy and electromagnetic radiation.
Matter in Our Surroundings
Q 76. Convert the following temperatures:
(a) – 78.0°C to kelvin
(b) 775 K to °C
(c) 489 K to °C
(d) 24°C to Kelvin
Ans.
(a) – 78 + 273 = 195 K
(b) 775 – 273 = 502°C
(c) 489-273 = 216°C
(d) 24 + 273 = 297 K
Q 77. Mention the difference between gas and vapour.
Ans. Gas – The gas is a substance which exists in the gaseous state at a temperature equal to or more than the boiling point of its liquid state. For example oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, etc.
Vapour – A vapour is a substance which exists in the gaseous state such that its temperature is lower than that of boiling point of its liquid state. For example, water vapour, iodine vapour, etc.
Q 78. A sample of water under study was found to boil at 102″C at normal temperature and pressure. Is the water pure? Will this water freeze at 0°C? Comment.
Ans. It’s freezing point will be below 0°C due to the presence of a non-volatile impurity in it.
Matter in Our Surroundings
Q 79. Water as ice has a cooling effect, whereas water as steam may cause severe burns. Explain these observations.
Ans. In case of ice, the water molecules have low energy while in the case of steam the water molecules have high energy. The high energy of water molecules in steam is transformed as heat and may cause burns. On the other hand, in case of ice, the water molecules take energy from the body and thus gave a cooling effect.
Q 80. It is a hot summer day, Priyanshi and Ali are wearing cotton and nylon clothes respectively. Who do you think would be more comfortable and why?
Ans. Cotton being a better absorber of water than nylon helps in absorption of sweat followed by evaporation which leads to cooling. So Priyanshi would be more comfortable than Ali.
Matter in Our Surroundings
Q 81. You want to wear your favourite shirt to a party, but the problem is that it is still wet after a wash. What steps would you take to dry it faster?
Ans. Conditions that can increase the rate of evaporation of water are:
- An increase of surface area by spreading the shirt
- An increase in temperature by putting the shirt under the Sun
- An increase the wind speed by spreading it under the fan.
Q 82. What is evaporation? Why does evaporation cause cooling?
Ans. The process in which a liquid changes into its vapour state at a temperature below the boiling point is called evaporation. Evaporation is an endothermic process i.e., the liquid absorbs heat during evaporation. This heat may be provided either by the surrounding or by the liquid itself. When the evaporating liquid takes the required heat from other parts of the liquid, the rest of the liquid cools down.
On the other hand, if the liquid takes heat from the surroundings, it causes cooling of the surroundings. For example, on a hot day (sunny day) we perspire. When this sweat evaporates, it absorbs the required heat from our body, and we feel cool.
Q 83. What factors affect the rate of evaporation?
Ans. Factors that affect the rate of evaporation are:
- Temperature: Evaporation increases with increase in temperature.
- Humidity: Evaporation decreases with an increase in humidity.
- Wind speed: Evaporation increases with an increase in wind speed.
Q 84. What is a dry ice and what are its properties?
Ans. Solid carbon dioxide is known as dry ice. It is stored under high pressure. Solid CO2 gets converted directly to gaseous state on decrease of pressure to 1 atmosphere without passing through the liquid state (i.e., sublimes). This is the reason that solid carbon dioxide is also known as dry ice.
It is mainly used as a cooling agent because its temperature is very low than ice formed from water. Dry ice is commonly used in theaters and in movies to produce the effect of fog.
Q 85. Why should we wear cotton clothes in summer?
Ans. During summer, we perspire more because of the mechanism of our body which keeps us cool. We know that during evaporation, the particles at the surface of the liquid gain energy from the surroundings or body surface and change into vapour. The heat energy equal to latent heat of vapourisation is absorbed from the body leaving the body cool. Cotton, being a good absorber of water helps in absorbing the sweat and exposing it to the atmosphere for easy evaporation.
Matter in Our Surroundings
Q 86. Give the main postulates of kinetic theory of matter.
Ans. The main postulates of kinetic theory are:
- All matter is made up of a large number of extremely small particle called molecules.
- The molecules are always in a state of rapid random motion.
- The molecules possess kinetic energy.
- There are attractive forces between the molecules.
- The kinetic energy of molecules increases with increase in temperature.
Q 87. Identify each of the following changes of state as evaporation, boiling or condensation. Give reason for your answer.
(a) Wet clothes dry when spread on wire.
(b) After a hot shower, your bathroom mirror is covered with water.
(c) Lava flows into the ocean and forms steam.
Ans. (a) Evaporation, because conversion of liquid water to vapour occur at room temperature.
(b) Condensation, because hot water vapour condense to form liquid water.
(c) Boiling, because heat of lava makes liquid water boil and hence steam is formed.
Matter in Our Surroundings
Q 88. Why do surgeons often spray some ether on the skin before performing minor surgery?
Ans. Quite often doctors spray ether on a portion of skin the before performing minor surgery. The reason being that a ether has very low boiling point (308 K). Therefore, it evaporates quite rapidly. The heat energy needed for evaporation is taken from the skin. As a result, the temperature of the skin becomes so low that it almost becomes numb. Due to this numbness, the patient does not feel much pain when a minor cut is made in the skin in order to perform surgery.
Similarly, when a player gets injured during a game, ethyl chloride on the injured portion of the body. Since the boiling point of ethyl chloride (285.5K or 12.5°C) is very low, it quickly evaporates. The heat energy needed for evaporation is taken from the skin. By losing heat, temperature of the skin becomes so low that it almost becomes numb. Due to this numbness, the player does not feel much pain.
Q 89. Comment upon the following:
(i) Rigidity
(ii) Compressibility
(iii) Fluidity
Ans. (i) Rigidity means tendency to maintain shape when some outside force is applied due to strong interparticle force.
(ii) Compressibility means tendency to decrease volume when some outside force is applied. Due to large interparticle distances in
gases their volume decreases when some pressure is applied on them therefore, gases possess high compressibility.
(iii) Fluidity means tendency to flow. Due to large interparticle distances and weak forces of attraction gases have highest fluidity.
Q 90. Comment on the following statements:
(а) Evaporation produces cooling.
(b) Rate of evaporation of an aqueous solution decreases with increase in humidity.
(c) Sponge though compressible is a solid.
Ans.
(а) For evaporation to occur, heat energy is needed. This heat energy is taken out from the substance or the surroundings. As a result surrounding becomes cool. Thus, evaporation causes cooling.
(b) By humidity we mean, the amount of water vapours present in the air. With increase in humidity the rate of evaporation decreases. If the humidity of air is already high, it can hold only a little more amount of water vapour to reach that optimum level, therefore the rate
of evaporation decreases.
(c) Sponge has large number of minute holes in which air is trapped. When we press it, air expelled and sponge is compressed to a small amount of matter which has a definite shape as well as definite volume.
Matter in Our Surroundings
Q 91. List any five physical properties of liquids.
Ans. Liquids do not have fixed shape or boundaries.
- They have fixed volume.
- They exhibit fluidity i.e., they can flow.
- Less compressible as compared to gases but higher than solids.
- Lower density as compared to solids.
- Compared to solids, liquids have higher kinetic energy but less than gases.
- The intermolecular forces of attraction are weaker than those of solids.
- Show the property of intermixing i.e., can diffuse.
Q 92. Fill in the blanks:
(а) Evaporation of a liquid at room temperature leads to a ………………… effect.
(b) At room temperature the forces of attraction between the particles of solid substances are ………………… than those which exist in the
gaseous state.
(c) The arrangement of particles is less ordered in the state. However, there is no order in ………………… the state.
(d) is the change of gaseous state directly to solid state without going through the ………………… state.
(e) The phenomenon of change of a liquid into the gaseous state at any temperature below its boiling point is called …………………
Answer:
(a) cooling
(b) stronger
(c) liquid, gaseous
(d) Sublimation, liquid
(e) evaporation
Q 93. Classify the following into osmosis/diffusion
(a) Swelling up of a raisin on keeping in water.
(b) Spreading of virus on sneezing.
(c) Earthworm dying on coming in contact with common salt.
(d) Shrinking of grapes kept in thick sugar syrup.
(e) Preserving pickles in salt.
Ans.
(a) Osmosis
(b) Diffusion
(c) Osmosis
(d) Osmosis
(e) Osmosis
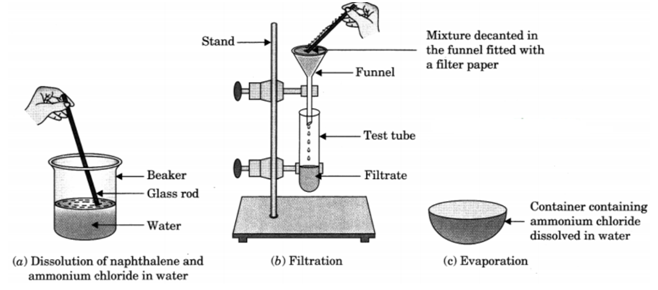
Q 94. You are provided with a mixture of naphthalene and ammonium chloride by your teacher. Suggest an activity to separate them with well labelled diagram.
Ans. Naphthalene is insoluble in water but soluble in ether an organic solvent. It is volatile at room temperature. Ammonium chloride is soluble in water and volatile at higher temperature. It decomposes on heating to dryness.
Q 95. Why does the temperature of a substance remain constant during its melting point or boiling point?
Ans. The temperature of a substance remains constant at its melting and boiling points untill all the substance melts or boils because, the heat supplied is continuously used up in changing the state of the substance by overcoming the forces of attraction between the particles. This heat energy absorbed without showing any rise in temperature is given the name latent heat of fusion/latent heat of vapourisation.
Matter in Our Surroundings
Q 96. With proper explanation, explain whether the following statements are true or false?
(a) Sublimation occurs only when the solid is heated.
(b) A lighter gas can move downwards and a heavier gas can move upwards.
(c) Interconversion of matter is a constant temperature process.
Ans.
(a) Statement is wrong. Sublimation may occur on its own or by heating, e.g., camphor, naphthalene, iodine, etc., sublime slowly at room temperature.
(b) Statement is true. Diffusion occurs against the law of gravitation. Therefore, lighter gases can also diffuse downwards and heavier gases can also diffuse upwards. However rate of diffusion of lighter gases is faster than those of heavier gases.
(c) Statement is true. During interconversion of state of matter from solid to liquid or from liquid to gas, it tends to reach its melting point or boiling point. At this point, the temperature remains constant unit it has changed in another state.
Matter in Our Surroundings
Q 97. What is meant by Bose-Einstein Condense?
Ans. (a) In 1920, Indian scientist Satyendra Nath Bose did some calculations, based on which Albert Einstein predicted that a new state of matter should exist.
(b) This new state was named as Bose-Einstein Condensate (BEC). In 2001, Cornell, Ketterie and Wieman of USA received Noble Prize for actually making this state in laboratory. BEC is made by cooling gas of very low density to super low temperature.
Q 98. A student heats a beaker containing ice and water. He measures the temperature of the content of the beaker as a function of time.
Which of the following figure would correctly represent the result? Justify your choice.

Ans.
Since ice and water are in equilibrium, the temperature would be zero. When we heat the mixture, energy supplied is utilised in melting with the ice and the temperature does not change till all the ice melts because of latent heat of fusion. On further heating, the temperature of the water would increase. Therefore the correct option is (d).
Q 99. Look at the figure and suggest in which of the vessels A, B, C or D the rate of evaporation will be the highest? Explain.
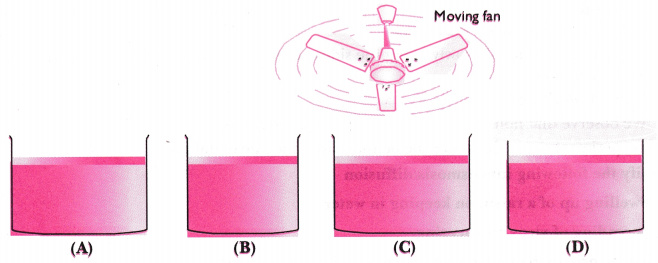
Ans. (c) The rate of evaporation increases with an increase in the surface area of absorption because of evaporation in a surface phenomenon. Also, with the increase in airspeed, the particles of water vapour will move away with the air, which will increase the rate
of evaporation.