Some of the Breeds of Indian Sheep : Nali, Marwari, Patanwari, Bhakakwal, Rampur Bushair, Lohi.
1. Nali : Features
- medium-sized sheep
- face is light brown in colour
- skin is pink
- ears are large and leafy
- fleece is white with brownish tinge, coarse and dense
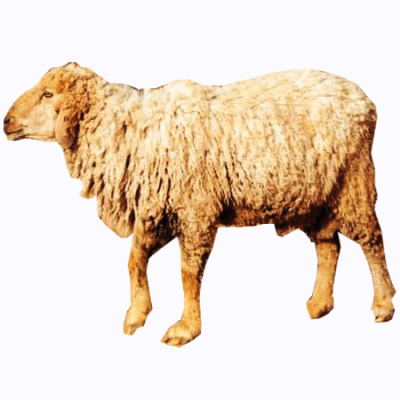

2. Marwari : Features
- medium-sized sheep
- black face with colour
- extending up-to the lower part of the neck
- fleece is white and not very dense
3. Patanwari: Features
- medium- to large-sized animals,
- white coat with fine fleece
- brown face and legs
4. Bhakakwal: Features
- medium-sized breed derived from the nomadic tribe who rear these sheep
- a typical Roman nose.
- The fleece is coarse and is generally white, although the coloured fleece is occasionally observed.

5. Rampur Bushair: Features
- Roman nose,
- convex head,
- large eyes and
- long and drooping ears (10 cm to 15 cm long)
- The fleece colour is predominantly white, with brown, black and tan also seen in varying proportions.
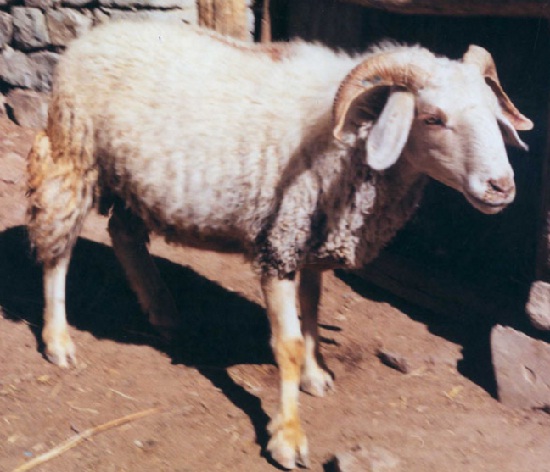

6. Lohi: Feature
- medium sized
- white colored body.
- fleece is dense and coarse
- face is light brown in color.
- ears are large and leafy.

WILD BREEDS OF SILK MOTH FOUND IN INDIA
Antheraea assamensis is a Scientific Name.
Assam is an adult Silk Moth.
Muga silkworm is a Larvae/Silk Worm.
Feeds on leaves of Cinnamomum bay leaves oak

Antheraea paphia / Antheraea mylitta is a Scientific Name.
South India small tussore is an adult Silk Moth.
Tasar silkworm is a Larvae/Silk Worm.
Feeds on leaves of silver-grey wood, Arjun.

Samia cynthia is a Scientific Name.
ailanthus silkmoth is an adult Silk Moth.
Eri silkworm is a Larvae/Silk Worm.
Feeds on leaves of castor plants
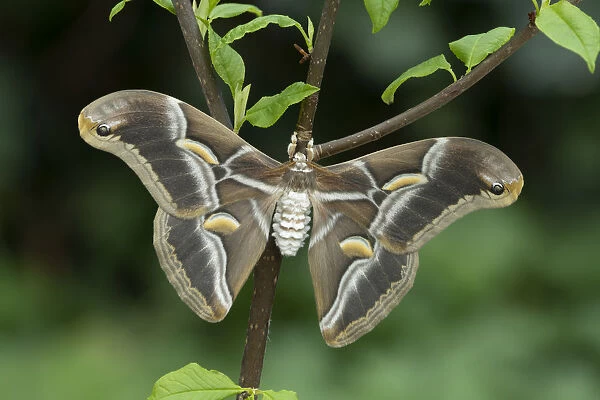

WILD SILK MOTH
Wild silks are usually harvested after the moths have left the cocoons, cutting the threads in the process, so that there is not one long thread, as with domesticated silkworms.
Wild silks are often referred to in India as ‘Vanya’ silks:
The term ‘Vanya’ is of Sanskrit origin, meaning untamed, wild, or forest-based.
Muga, Tasar, and Eri silkworms are not fully tamed and the world calls the silks they produce ‘wild silks.
India produces four kinds of silk: Mulberry, Tasar, Muga, and Eri. The silkworm Bombyx mori is fed on mulberry leaves cultivated in plantations. Silkworms are also found wild on forest trees for eg. Antheraea paphia which produces the Tasar silk (Tussah).
Wild silkworm (Antheraea assamensis) produces Muga silk and another wild silkworm Samia Cynthia produces seri silk.
SILK FIBRE
Silk is a fiber produced by the silkworm in the production of its cocoon.
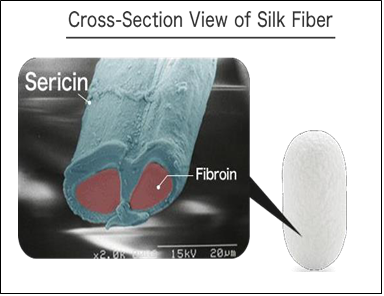
- It consists mainly of two proteins, fibroin, and sericin.
- Silk consists of 70–80% fibroin and 20–30% sericin;
- Fibroin being the structural center of the silk, and Sericin being the gum coating the fibers and allowing them to stick to each other.
- The cocoon is made of a single continuous thread of raw silk around 1 kilometer (2/3 of a mile) long. About 2,000 to 3,000 cocoons are required to make a pound of silk.
- However the length may vary in most cases as different cocoons are of different sizes and shape, therefore, having a varied amount of silk within them.
Life Cycle of Antheraea paphia/Antheraea mylitta (Tussar Silk Moth)
