Force and laws of motion class-9-mcq-for-physics are available for students, along with their answers. We, at cbseinsights.com, have prepared MCQ’s as per the latest exam pattern. These multiple-choice questions are prepared as per the latest CBSE syllabus (2022 – 2023) and NCERT guidelines. Solving these objective questions will help students build their problem-solving skills and score good marks in the board exams.
Q 1 – A plate, a ball, and a child all have the same mass. The one having more inertia is the
(a) plate
(b) ball
(c) child
(d) All have equal inertia
(d) All have equal inertia
Q 2 – A goalkeeper in a game of football pulls his hands backward after holding the ball shot at the goal. This enables the goalkeeper to:
(a) Exert large force on the ball
(b) Increases the force exerted by the ball on hands
(c) Increase the rate of change of momentum
(d) Decrease the rate of change of momentum
(d) Decrease the rate of change of momentum
Q 3 – The inertia of an object tends to cause the object
(a) to increase its speed
(b) to decrease its speed
(c) to resist any change in the state of rest or of motion
(d) to decelerate due to friction
(c) to resist any change in the state of rest or of motion
Q 4 – An object of mass 2 kg is sliding with a constant velocity of 4 m/s on a frictionless horizontal table. The force required to keep the object moving with the same velocity is:
(a) 32 N
(b) 0 N
(c) 2 N
(d) 8 N
(b) 0 N
class 9 force and laws of motion mcq for concept building
Q 5 – Among the equal-sized stone and a football, the inertia will be higher of:
(a) football
(b) stone
(c) both
(d) none of them
(b) stone
Q 6 – The rate of change of momentum with respect to time is measured in
(a) kg ms-2
(b) kg ms-1
(c) kg m
(d) kg
(a) kg ms-2
Q 7 – When unbalanced forces act on a body, the body:
(a) Must move with uniform velocity
(b) Must remain at rest
(c) Must experience acceleration
(d) Must move in a curved path
(c) Must experience acceleration
Q 8 – Newton’s third law of motion explains the two forces namely ‘action’ and ‘reaction’ coming into action when the two bodies are in contact with each other. These two forces:
(a) Always act on the same body
(b) Always act on the different bodies in opposite directions
(c) Have the same magnitude and direction
(d) Acts on either body at normal to each other
(b) Always act on the different bodies in opposite directions
Q 9 – A man throws a ball weighing 200 g vertically upwards with a speed of 10m/s. Its momentum at the highest point of its flight will be:
(a) 2 kg. m/s
(b) 2000 kg.m/s
(c) Insufficient data to find the momentum.
(d) zero
(d) zero
Q 10 – In a rocket, a large volume of gases produced by the combustion of fuel is allowed to escape through its tail nozzle in the downward direction with tremendous speed and makes the rocket move upward.
Which principle is followed in this take-off of the rocket?

Rocket propulsion
(a) Moment of inertia
(b) Conservation of momentum
(c) Newton’s third law of motion
(d) Newton’s law of gravitation
(b) Conservation of momentum
Q 11 – Quantitative expression of force is given by:
(a) Newton’s second law of motion.
(b) Newton’s third law of motion.
(c) Newton’s first law of motion.
(d) Newton’s law of gravitation.
(a) Newton’s second law of motion.
Q 12 – A water tank filled up to 2/3 of its height is moving with a uniform speed. On sudden application of the brake, the water in the tank would
(a) Move backward
(b) Move forward
(c) Come to the rest
(d) Be unaffected
(b) Move forward
Q 13 – Find the time taken by a body of mass 16 kg to come to rest from a uniform velocity of magnitude 10 m/s, when a force of 4N is
applied continuously
(a) 20 s
(b) 30 s
(c) 40 s
(d) 50 s
(c) 40 s
physics mcq for class 9 with answers pdf
Q 14 – The velocity versus time graph of a ball of mass 50 g rolling on a concrete floor is shown in the figure below. What will be the frictional force of the floor on the ball?
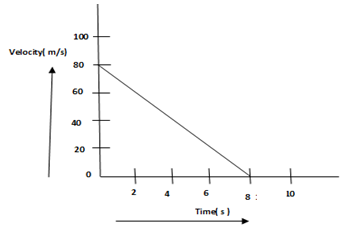
(a) 0.5 N
(b) 50 N
(c) 5 N
(d) 0.05 N
(a) 0.5 N
Q 15 – The S.I. unit of force is
(a) Newton-metre
(b) Newton
(c) Newton per second
(d) Newton per square metre
(b) Newton
Q 16 – The seat belts are provided in the cars so that if the car stops suddenly due to an emergency braking, the persons sitting on the front seats are not thrown forward violently and saved from getting injured. Can you guess the law due to which a person falls in the forward direction on the sudden stopping of the car?
(a) Newton’s first law of motion
(b) Newton’s second law of motion
(c) Newton’s third law of motion
(d) Newton’s law of gravitation
(a) Newton’s first law of motion
Q 17 – A force of ‘P* N acts on a particle so as to accelerate it from rest to a velocity ‘v’ m/s. The force ‘P’ is then replaced by ‘Q’ N which decelerates it to rest.
(a) P may be equal to Q
(b) P must be equal to Q
(c) P must be unequal to Q
(d) none of these
(a) P may be equal to Q
Q 18 – When a balloon held between the hands is pressed, its shape changes. This happens because:
(a) Balanced forces act on the balloon
(b) Unbalanced forces act on the balloon
(c) Frictional forces act on the balloon
(d) Gravitational force acts on the balloon
(a) Balanced forces act on the balloon
Q 19 – A batsman hits a cricket ball which then rolls on the ground. After covering a short distance, the ball comes to rest. The ball slows to a stop because:
(a) the batsman did not hit the ball hard enough.
(b) velocity is proportional to the force exerted on the ball.
(c) there is a force on the ball opposing the motion.
(d) there is no unbalanced force on the ball so the ball would want to come to rest
(c) there is a force on the ball opposing the motion.
Q 20 – If the force acting on the body is zero. Its momentum is:
(a) Zero
(b) Constant
(c) Infinite
(d) None of the above
(b) Constant
force and laws of motion mcq
Q 21 – Which of the following situations involves Newton’s second law of motion?
(a) A force can stop a lighter vehicle as well as a heavier vehicle which are moving
(b) A force exerted by a lighter vehicle on collision with a heavier vehicle results in both the (vehicles coming to a standstill
(c) A force can accelerate a lighter vehicle more easily than a heavier vehicle which is moving
(d) A force exerted by the escaping air from a balloon in the downward direction makes the balloon to go upwards
(c) A force can accelerate a lighter vehicle more easily than a heavier vehicle which are moving
Q 22 – When a force is exerted on an object, it can change its:
(a) State
(b) Position
(c) Shape
(d) All the above
(d) All the above
Q 23 – The speed of a car weighing 1500 kg increases from 36 km/h to 72 km/h uniformly. What will be the change in momentum of the car?
(a) 15000 kg km/h
(b) 15000 kg m/s
(c) 54000 kg m/s
(d) 54000 g m/s
(b) 15000 kg m/s
Q 24 – What is the momentum of an object of mass m, moving with a velocity v?
(a) (mv)2
(b) mv2
(c) 1/ 2 mv2
(d) mv
(d) mv
Q 25 – What force can change the velocity of a body of mass 1kg from 20 m/s to 30m/s in 2 seconds?
(a) 10 N
(b) 15 N
(c) 5 N
(d) 25 N
(c) 5 N
Q 26 – A passenger in a moving train tosses a coin which falls behind him. Observing this statement what can you say about the motion of the train?
(a) Accelerated
(b) Retarded
(c) Along circular tracks
(d) Uniform
(a) Accelerated
Q 27 – One way that you can recognize that a force is acting on an object:
(a) is to note any change in the object’s state of motion.
(b) is to determine its mass at different locations.
(c) is to measure the instantaneous velocity of a moving object.
(d) A and C
(a) is to note any change in the object’s state of motion.
Q 28 – Newton’s first law of motion says that a moving body should continue to move forever unless some external forces act on it. But a moving cycle comes to rest after some time if we stop pedaling it. Can you choose the correct reason for the stoppage of the cycle?
i. Air resistance
ii. Gravitational pull of the earth
iii. Friction of the road
iv. Heat of the environment
Choose the correct option:
(a) (iii) and (iv)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) (ii) and (iii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
Q 29 – When the driver of a fast-moving car suddenly applies brakes, the passengers in the car:
(a) fall backward
(b) fall forward
(c) are not affected
(d) none of the above
(b) fall forward
Q 30 – 1-kg object is lying on the ground. An unbalanced force of magnitude 1 N is applied to the object. Which of these options explains the motion of the object as a result of the acting force?
(a) The object will accelerate in the direction of the applied force.
(b) The object will accelerate in a direction perpendicular to the applied force.
(c) The object will decelerate in the direction of the applied force.
(d) The object will remain at rest
(a) The object will accelerate in the direction of the applied force.
Q 31 – A man wearing a bullet-proof vest stands on roller skates. The total mass is 80 kg. A bullet of mass 20 g is fired at 400 m/s. It is stopped by the vest and falls to the ground. What is then the velocity of the man?
(a) 1 m/s
(b) 0.1 m/s
(c) 0.01 m/s
(d) 0 m/s
(b) 0.1 m/s
Q 32 – When a 12 N force acts on 3 kg mass for a second, the change in velocity is (in m/s)
(a) 36
(b) 4
(c) 2
(d) 18
(b) 4
Q 33 – An object of mass 20 kg is moving with a velocity of 10 m/s. Its momentum will be:
(a) 2000 kg.m/s
(b) 20 kg.m/s
(c) 2 kg.m/s
(d) 200 kg.m/s
(d) 200 kg.m/s
Q 34 – A passenger in a moving train tosses a coin which falls behind him. It means that the motion of the train is
(a) accelerated
(b) uniform
(c) retarded
(d) along circular tracks
(a) accelerated
force and laws of motion class 9 mcq
Q 35 – The unit of measuring the momentum of a moving body is:
(a) m/s
(b) kg.m/s
(c) kg.m/s2
(d) N m2/kg2
(b) kg.m/s
Q 36 – Force is defined as
(a) change in momentum
(b) rate of change of momentum
(c) the quantity that opposes inertia
(d) the quantity that keeps the velocity constant
(b) rate of change of momentum
Q 37 – The inertia of a moving object depends on:
i. Mass of the object
ii. Momentum of the object
iii. Speed of the object
iv. Shape of the object
(b) only (i)
Q 38 – A force is defined as a
(a) Fall
(b) Pull
(c) Push or Pull
(d) Push
(c) Push or Pull
Q 39 – The acceleration of an object is inversely proportional to:
(a) Force.
(b) Momentum.
(c) Mass.
(d) Velocity.
(c) Mass.
Q 40 – __________ is a force, which always opposes the motion of one body over the other body in contact with it
(a) Gravitational force
(b) Reaction force
(c) Normal force
(d) Frictional force
(d) Frictional force
Q 41 – Two equal masses m each moving in the opposite direction with the same speed v collide and stick to each other. The velocity of the combined mass is
(a) v
(b) 2v
(c) v/2
(d) zero
(d) zero
force and laws of motion class 9 mcq
Q 42 – In high jump competition the athlete is made to fall on a cushioned bed to:
(a) To decrease his momentum fast.
(b) Make him stop quickly.
(c) Increase the time to stop.
(d) Make him sleep comfortably
(c) Increase the time to stop.
Q 43 – When balanced forces act on a body, the body:
(a) Must remain in its state of rest
(b) Must continue moving with uniform velocity, if already in motion
(c) Must experience some acceleration
(d) Both (A) and (B)
(d) Both (A) and (B)
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Q 44 – What is the momentum of a body of mass 2m and velocity v/2?
(a) mv/4
(b) mv
(c) 2mv
(d) mv/2
(b) mv
Q 44 – Momentum of a body of mass 0.5 kg moving with a speed of 10 m/s is
(a) 2.5 kg.m/s
(b) 5 kg.m/s
(c) 0.5 kg.m/s
(d) 50 kg.m/s
(b) 5 kg.m/s
Q 45 – An object of mass of 2 kg is sliding with a velocity of 4 ms-1 on a frictional horizontal surface. The retarding force necessary to stop the object in 1 second is
(a) 2 N
(b) 4 N
(c) 8 N
(d) 0 N
(c) 8 N
Q 46 – The acceleration of an object is
(a) inversely proportional to its mass
(b) directly proportional to the applied force
(c) resisted by inertia
(d) all of the above
(d) all of the above
Q 47 – Which of the following has the largest momentum?
(a) A cat running down the street
(b) A pickup truck travelling down the highway.
(c) A large truck parked in a parking lot.
(d) A car parked in a parking lot.
(b) A pickup truck travelling down the highway
Q 48 – According to Newton’s third law of motion, action and reaction
(a) always act on the same body
(b) always act on different bodies in the opposite direction
(c) have same magnitudes and direction
(d) act on either body at normal to each other
(b) always act on different bodies in the opposite direction
Q 49 – Which one of the following statements is not correct for an object moving along a straight path in an accelerated motion?
(a) Its speed keeps changing
(b) Its velocity always changes
(c) It always goes away from earth
(d) A force is always acting on it
(c) It always goes away from earth
force and laws of motion class 9 mcq with answers
Q 50 – Change in momentum when a car weighing 700kg changes its speed from 100m/s to 200 m/s is:
(a) 14000 kg.m/s
(b) 10500000 kg.m/s
(c) 21000000 kg.m/s
(d) 70000 kg.m/s
(d) 70000 kg.m/s
Q 51 – If an object moves with a uniform velocity we can conclude that
(a) there is no force acting on the body
(b) no unbalanced force acts on it
(c) an unbalanced force acts on the body
(d) it has uniform acceleration
(b) no unbalanced force acts on it
Q 52 – Find the time for which a force of 1kgwt acts on a body of mass 1 kg moving with a uniform speed of 4m/s to stop the body.
(a) 0.8 s
(b) 0.2 s
(c) 0.6 s
(d) 0.4 s
(d) 0.4 s
force and laws of motion class 9 mcq online test
Q 53 – Match the Following
Choose the correct option:
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) only (i)
(c) only (ii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
| A 1. Unit of force 2. Unit of pressure 3. Test of purity of milk 4. Force 5. S.I unit of momentum |
B (i) Mass × acceleration (ii) kgms (iii) Pascal (iv) Lactometer (v) Newton |
Ans –
| A 1. Unit of force 2. Unit of pressure 3. Test of purity of milk 4. Force 5. S.I unit of momentum |
B |
For Updated MCQ’s :- Click the below links