Q 1 – The defect of vision in which the person is able to see distant objects distinctly but cannot see nearby objects clearly is called
(a) Long-sightedness
(b) Far-sightedness
(c) Hypermetropia
(d) All of the above
(d) All of the above
Q 2 – Myopia and hypermetropia can be corrected by
(a) Concave and a plano-convex lens
(b) Concave and convex lens
(c) Convex and concave lens
(d) Plano-concave lens for both defects.
Q 4 – When a person is myopic, he/ she can clearly see
(a) both nearby and far off objects
(b) Only nearby objects
(c) only far off objects
(d) Neither nearby nor far off objects
(b) Concave and convex lens
Q 3 – A person cannot see distinctly objects kept beyond 2 m. This defect can be corrected by using the lens of power
(a) +0.5 D
(b) – 0.5 D
(c) +0.2 D
(d) – 0.2 D
(b) -0.5 D
Q 4 – When a person is myopic, he/ she can clearly see
(a) both nearby and far off objects
(b) Only nearby objects
(c) only far off objects
(d) Neither nearby nor far off objects
(b) Only nearby objects
Q 5 – The defect of the eye in which the eyeball becomes too long is
(a) myopia
(b) hypermetropia
(c) presbyopia
(d) cataract
(a) myopia
Q 6 – A student sitting on the last bench can read the letters written on the blackboard but is not able to read / the letters written in his textbook. Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) The near point of his eyes has receded away.
(b) The near point of his eyes has come closer to him.
(c) The far point of his eyes has come closer to him.
(d) The far point of his eyes has receded away.
(a) The near point of his eyes has receded away.
(a) The near point of his eyes has receded away.
Q 7 – The ability of the eye lens to adjust its focal length to form a sharp image of the object at varying distances on the retina is called
(a) Power of observation of the eye
(b) Power of adjustment of the eye
(c) Power of accommodation of the eye
(d) Power of enabling of the eye
(c) Power of accommodation of the eye
Q 8 – The image formed on the retina of the human eye is
(a) virtual and inverted
(b) real and inverted
(c) real and erect
(d) virtual and erect
(b) real and inverted
Q 9 – The amount of light entering the eye can be controlled by the
(a) iris
(b) pupil
(c) cornea
(d) ciliary muscles
(b) pupil
Q 10 – A prism ABC (with BC as a base is placed in different orientations. A narrow beam of white light is incident on the prism as shown in the Figures given below. In which of the following cases, after dispersion, the third colour from the top corresponds to the colour of the sky?

(a) (i)
(b) (ii)
(c) (iii)
(d) (iv)
(b) (ii)
Q 11 – Bi-focal lenses are required to correct
(a) astigmatism
(b) coma
(c) myopia
(d) presbyopia
(d) presbyopia
Q 12 – At noon the sun appears white as
(a) light is least scattered.
(b) all the colours of the white light are scattered away.
(c) the blue colour is scattered the most.
(d) the red colour is scattered the most.
(a) light is least scattered.
Q 13 – The splitting of white light into different colours on passing through a prism is called
(a) reflection
(b) refraction
(c) dispersion
(d) deviation
(c) dispersion
Q 14 – The human eye can focus objects at different distances by adjusting the focal length
of the eye lens. This is due to
(a) Presbyopia
(b) Accommodation
(c) Near-sightedness
(d) Far-sightedness
(b) Accommodation
Q 15 – Which of the following phenomena of light are involved in the formation of a rainbow?
(a) Reflection, refraction and dispersion
(b) Refraction, dispersion and total internal reflection
(c) Refraction, dispersion and internal reflection
(d) Dispersion, scattering and total internal reflection
(c) Refraction, dispersion and internal reflection
Q 16 – The air layer of the atmosphere whose temperature is less than the hot layer behave optically
(a) denser medium
(b) rarer medium
(c) inactive medium
(d) either denser or rarer medium
(a) denser medium
Q 17 – Twinkling of stars is due to atmospheric
(a) dispersion of light by water droplets
(b) refraction of light by different layers of varying refractive indices
(c) scattering of light by dust particles
(d) internal reflection of light by clouds
Q 17 – Twinkling of stars is due to atmospheric
(a) dispersion of light by water droplets
(b) refraction of light by different layers of varying refractive indices
(c) scattering of light by dust particles
(d) internal reflection of light by clouds
(b) refraction of light by different layers of varying refractive indices
Q 18 – The human eye forms the image of an object at its
(a) Cornea
(b) Iris
(c) Pupil
(d) Retina
(d) Retina
Q 19 – The change in focal length of an eye lens is caused by the action of the
(a) Pupil
(b) Retina
(c) Ciliar muscles
(d) Iris
(c) Ciliary muscles
Q 20 – The clear sky appears blue because
(а) blue light gets absorbed in the atmosphere.
(b) ultraviolet radiations are absorbed in the atmosphere.
(c) violet and blue lights get scattered more than lights of all other colours by the atmosphere.
(d) light of all other colours is scattered more than the violet and blue colour lights by the atmosphere.
(c) violet and blue lights get scattered more than lights of all other colours by the atmosphere.
Q 21 – A person cannot see distinctly objects kept beyond 2 m. This defect can be corrected by using a lens of power
(a) + 0.5 D
(b) – 0.5 D
(c) + 0.2 D
(d) – 0.2 D
(b) – 0.5 D
Q 22 – One cannot see through the fog, because
(a) the refractive index of the fog is very high
(b) light suffers total reflection at droplets
(c) fog absorbs light
(d) light is scattered by the droplets
(d) light is scattered by the droplets
Q 23 – Near and far points of a young person normal eye respectively are
(a) 0 and infinity
(b) 0 and 25 cm
(c) 25 cm and infinity
(d) 25 cm and 150 cm.
(c) 25 cm and infinity
Q 24 – Which of the following statements is correct regarding the propagation of light of different colours of white light in the air?
(a) Red light moves fastest.
(b) Blue light moves faster than green light.
(c) All the colours of the white light move at the same speed.
(d) Yellow light moves with the mean speed as that of the red and the violet light.
(c) All the colors of the white light move at the same speed.
Q 25 – The focal length of the eye lens increases when the eye muscles.
(a) are relaxed and the lens becomes thinner
(b) contract and lens becomes thicker
(c) are relaxed and the lens becomes thicker
(d) Contract and lens become thinner.
(a) are relaxed and the lens becomes thinner
Q 26 – Which of the following is a natural phenomenon that is caused by the dispersion of sunlight in the sky?
(a) Twinkling of stars
(b) Stars seem higher than they actually are
(c) Advanced sunrise and delayed sunset
(d) Rainbow
(d) Rainbow
Q 27 – The colour that is scattered the least by the tiny particles and the atoms/ molecules of the atmosphere is
(a) Violet
(b) Green
(c) yellow
(d) Red
(d) Red
Q 28 – Assertion: The near-point of a hypermetropic eye is more than 25 km away.
Reason: Hypermetropia is corrected using spectacles containing concave lenses.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. (b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
(e) Both A and R are false.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(c) A is true but R is false.
Q 29 – The danger signals installed at the top of tall buildings are red in colour. These can be easily seen from a distance because among all other colours, the red light
(a) is scattered the most by smoke or fog.
(b) is scattered the least by smoke or fog.
(c) is absorbed the most by smoke or fog.
(d) moves fastest in air.
(b) is scattered the least by smoke or fog
Q 30 – Assertion: Concave mirrors are used as reflectors in torches, vehicle headlights and in searchlights.
Reason: When an object is placed beyond the centre of curvature of a concave mirror, the image formed is real and inverted.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
(e) Both A and R are false.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Q 31 – The defect of vision in which the person is able to see distant objects distinctly but cannot see nearby objects clearly are called
(a) Long-sightedness
(b) Far-sightedness
(c) Hypermetropia
(d) All of the above
(d) All of the above
Q 32 – Eye lens is:
(a) converging
(b) diverging
(c) convex and concave
(d) none of these
(a) converging
Q 33 – Which of the following phenomena contributes significantly to the reddish appearance of the sun at sunrise or sunset?
(a) Dispersion of light
(b) Scattering of light
(c) Total internal reflection of light
(d) Reflection of light from the earth
(b) Scattering of light
Q 34 – A person uses a convex lens of focal length 20 cm in spectacles, the power of the lens will be:
(a) –5 D
(b) +5 D
(c) +2 D
(d) –2 D
(b) +5 D
Q 35 – The defect of myopia can be corrected by using
(a) Concave lens
(b) Convex lens
(c) Either concave or convex
(d) A complicated combination of lenses.
(a) Concave lens
Q 36 – The animal which does not have eyes that look sideways is:
(a) Horse
(b) Chicken
(c) Lion
(d) Cow
(c) Lion
Q 37 – With both eyes open, a person’s field of view is about:
(a) 90°
(b) 150°
(c) 180°
(d) 360°
(c) 180°
Q 38 – The bluish colour of water in the deep sea is due to
(a) the presence of algae and other plants found in water
(b) reflection of the sky in the water
(c) scattering of light
(d) absorption of light by the sea
(c) scattering of light
Q 39 – Having two eyes gives a person:
(a) deeper field of view
(b) coloured field of view
(c) rear field of view
(d) wider field of view
(d) wider field of view
Q 40 – The animals of prey have:
(a) two eyes at the front
(b) two eyes at the back
(c) two eyes on the sides
(d) one eye at the front and one on the side
(c) two eyes on the sides
Q 41 – When light rays enter the eye, most of the refraction occurs at the
(a) crystalline lens
(b) the outer surface of the cornea
(c) iris
(d) pupil
(b) outer surface of the cornea
Q 42 – The animals called predators to have:
(a) both the eyes on the sides
(b) one eye on the side and one at the front
(c) one eye on the front and one at the back
(d) both the eyes at the front
(d) both the eyes at the front
Q 43 – The focal length of the eye lens increases when eye muscles
(a) are relaxed and the lens becomes thinner
(b) contract and lens becomes thicker
(c) are relaxed and the lens becomes thicker
(d) contract and lens becomes thinner
(a) are relaxed and the lens becomes thinner
Q 44 – Which of the following colour of white light has the least wavelength?
(a) red
(b) orange
(c) violet
(d) blue
(c) violet
Q 45 – Which of the following colour of white light has the maximum wavelength?
(a) red
(b) orange
(c) violet
(d) blue
(a) red
Q 46 – Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) A person with myopia can see distant objects clearly.
(b) A person with hypermetropia can see nearby objects clearly.
(c) A person with myopia can see nearby objects clearly.
(d) A person with hypermetropia cannot see distant objects clearly.
(a) A person with myopia can see distant objects clearly.
Q 47 – Due to atmospheric refraction of sunlight, the time from sunrise to sunset is lengthened by about:
(a) 6 minutes
(b) 2 minutes
(c) 4 minutes
(d) 5 minutes
(c) 4 minutes
Q 48 – A student traces the path of a ray through a glass prism for four different values of angle of incidence. On analysing the diagrams he is likely to conclude that the emergent ray
(a) is always parallel to the incident ray.
(b) is always perpendicular to the incident ray.
(c) is always parallel to the refracted ray.
(d) always bends at an angle to the direction of the incident ray.
(d) always bends at an angle to the direction of the incident ray.
Q 49 – Bifocal lens is used in
(a) myopia
(b) lever
(c) Cataract
(d) Presbyopia
(d) Presbyopia
Q 50 – Crystalline lens of people at old age becomes milky and cloudy. This condition is called
(a) myopia
(b) lever
(c) cataract
(d) presbyopia
(c) cataract
Q 51 – A student is observing the diagram showing the path of a ray of light passing through a glass prism. He would find that for all angles of incidence the ray of light bends:
(а) towards the normal, while entering into the prism and away from the normal while emerging out of the prism.
(b) away from the normal while entering into the prism and towards the normal while emerging out of the prism.
(c) away from the normal while entering as well as while emerging out of the prism.
(d) towards the normal while entering as well as while emerging out of the prism.
(а) towards the normal while entering into the prism and away from the normal while emerging out of the prism.
Q 52 – A dark muscular membrane that controls the size of the pupil
(a) eye
(b) iris
(c) cornea
(d) retina
(b) iris
Q 53 – Which of the following phenomenon contributes significantly to the reddish appearance of the sun at sunrise or sunset?
(a) Dispersion of light
(b) Scattering of light
(c) Total internal Reflection
(d) Reflection of light from the earth
(b) Scattering of light
Q 54 – Least distance of distinct vision for a normal eye is
(a) 25 cm
(b) 50 cm
(c) 75 cm
(d) infinity
(a) 25 cm
Q 55 – In the following diagram, the path of a ray of light passing through a glass prism is shown:
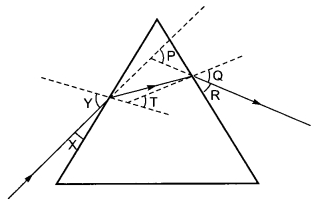
(a) X, R and T
(b) Y, Q and T
(c) X, Q and P
(d) Y, Q and P
(d) Y, Q and P
Q 56 – The black opening between the aqueous humour and the lens is called
(a) retina
(b) iris
(c) cornea
(d) pupil
(d) pupil
Q 57 – The splitting of light into its component colours is called
(a) Spectrum
(b) Dispersion
(c) Tyndall effect
(d) Refraction
(b) Dispersion
Q 58 – The medical condition in which the lens of the eye of a person becomes progressively cloudy resulting in blurred vision is called
(a) myopia
(b) hypermetropia
(c) presbyopia
(d) cataract
(d) cataract
Q 59 – After tracing the path of a ray of light through a glass prism a student marked the angle of incidence (∠i), angle of refraction (∠r), angle of emergence (∠e) and the angle of deviation (∠D) as shown in the diagram. The correctly marked angles are:
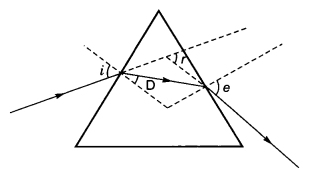
(a) ∠I and ∠r
(b) ∠I and ∠e
(c) ∠i, ∠e and ∠D
(d) ∠i, ∠r and ∠e
(b) ∠i and ∠e
Q 60 – Stars appears to be twinkling because of
(a) atmospheric refraction
(b) reflection
(c) Tyndall effect
(d) spectrum
(a) atmospheric refraction
Q 61 – In an experiment to trace the path of a ray of light through a glass prism for different values of angle of incidence a student would find that the emergent ray:
(a) is parallel to the incident ray
(b) is perpendicular to the incident ray
(c) is parallel to the refracted ray
(d) bends at an angle to the direction of the incident ray
Q 62 – The splitting of white light into its component colours is called
(a) refraction
(b) reflation
(c) dispersion
(d) Tyndall effect
(c) dispersion
Q 63 – Myopia may arise due to
(a) excessive curvature of the eye lens
(b) elongation of the eyeball
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these
(c) both (a) and (b)
Q 64 – The defect of vision in which a person cannot see the distant objects clearly but can see nearby objects clearly is called
(a) myopia
(b) hypermetropia
(c) presbyopia
(d) bifocal eye
(a) myopia
Q 65 – Reason behind advance sunrise and delayed sunset
(a) atmospheric refraction
(b) total internal reflection
(c) dispersion
(d) reflection
(a) atmospheric refraction
Q 66 – The change in focal length of an eye lens is caused by the action of the
(a) Pupil
(b) Retina
(c) Ciliary muscles
(d) Iris
(c) Ciliary muscles
Q 67 – Type of lens used in the correction of myopia
(a) convex lens
(b) concave lens
(c) reflecting lens
(d) bifocal lens
(b) concave lens
Q 68 – Type of lens used in the correction of hypermetropia
(a) concave lens
(b) reflecting lens
(c) bifocal lens
(d) convex lens
(d) convex lens
Q 69 – The muscular diaphragm that controls the size of the pupil is
(a) cornea
(b) ciliary muscles
(c) iris
(d) retina
(c) iris
Q 70 – While performing the experiment to trace the path of a ray of light passing through a glass prism, four students marked the incident ray and the emergent ray in their diagrams in the manner shown below.
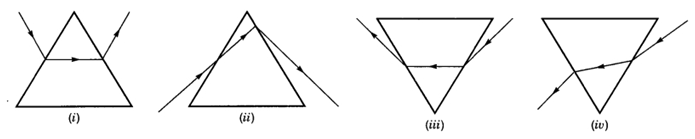
The correct path of the rays has been shown by:
(a) I
(b) II
(c) III
(d) IV
(c) III