List of the Lesson:
- Geography is a field of study is integrative, empirical and practicalIt studies each and every event on the earth over the space and time Human geography studies the relationship between man and nature Geo. can be studied through law making or descriptive There are two approaches of geography.
1. Systematic approach
2. Regional approach
Physical and human phenomena are described in metaphors using symbols from the human anatomy.
Human Geography:
- Human geography is the synthetic study of relationship between human societies and earth’s surface.
Nature of Human Geography
- Human Geography studies the inter-relationship between the physical environment and socio- cultural environment created by human beings through mutual interaction with each other.
- The elements like villages, cities, road-rail networks, etc and all other elements of material culture have been created by human beings using the resources provided by the physical environment. Thus, In the saying of Ellen Semple “Human geography is a study of changing relationship between unresting man and unstable earth”.
Naturalisation of Humans and Humanisation of Nature
- Humans interact with their physical environment with the help of technology. This indicates the level of cultural development.
- The interaction of primitive societies with the physical environment is termed as environmental determinism which is naturalisation of humans.
- With the development of technology, humans began to modify nature and created cultural landscape. This is called possiblism or humanisation of nature.
- A middle path of neo determinism was introduced by Griffith Taylor which means that neither is there a situation of absolute necessity (environmental determinism) nor is there a condition of absolute freedom (possibilism).
History of Human Geography
- The emergence of human geography started with the interaction, adaptation, adjustment and modification between the humans and the environment.
- Before the age of discovery, there was very little interaction between different societies but in the late 15th Century information about the unknown societies were made available now. Exploration by travellers expanded the area of human geography and interacted with different societies.
- With this, new approaches can across like welfare or humanistic school of thought, radical school of thought and behavioural school of thought.
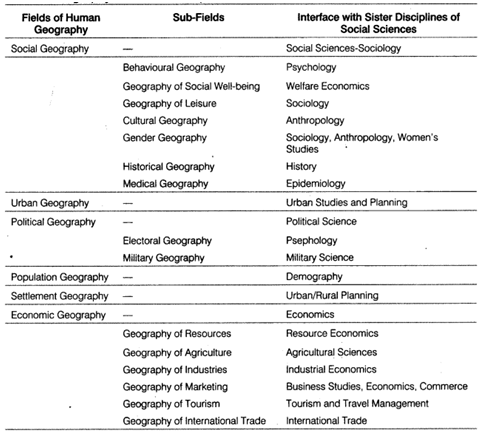
Field and Sub-fields of Human Geography
- Human geography is inter-disciplinary in nature and develops vast linkages with other sister disciplines in social sciences.
- The fields and sub-fields of human geography explains every aspect of all elements of human life on the surface of the earth.
Human Geography and Sister Disciplines of Social Sciences
Stages Through Corridories of Time
| PERIOD | APPROACHES | BROAD FEATURES |
| Colonial | Exploration & description | Imperialism and trade lead to discover many lands |
| Colonial | Regional analysis | Understanding of parts in totality would lead to understand the whole |
| 1930- interwar | aerial differentiation | Find the reasons for the uniqueness of a region |
| 1950-1960 | Spatial organization | Apply technology to study geography |
| 1970 | Emergence of humanistic, radical and behavioral school | Emergence of sociopolitical reality with the help of schools |
| 1990 | Post modernism | Generalization and apply of universal laws to understand geography |
Non-determinism/ Stop and go Determinism
1. Developed by Griffith Taylor
2. It is a middle path between environmental determinism and possibilism
3. The concept shows that neither is there a situation of absolute necessity nor is there a condition of absolute freedom. 4. Sustainable development is the main aim
5. The Neo determinism maintains balance between development and nature
- Human Geography Through the Corridors of Time Schools of human geography Welfare School Concerned with social well-being of the people:
(a) housing
(b) Health
(c) Education
Radical School:
- Concerned with causes of poverty, deprivation, and Social Inequality
- Behavioural School: Given the importance to lived experience, perception of space by Social categories