(From Q 1 to Q 15 carry 1 mark each)
Q 1 – The numerical ratio of displacement to distance for a moving object is:
(a) Always less than 1
(b) Equal or less than 1
(c) Always more than 1
(d) Equal to 1 or more than one
(b) Equal or less than 1
Q 2 – Four cars A, B, C and D are moving on a leveled, straight road. Their distance time graphs are shown in the figure below. Which of the following is the correct statement regarding the motion of these cars?
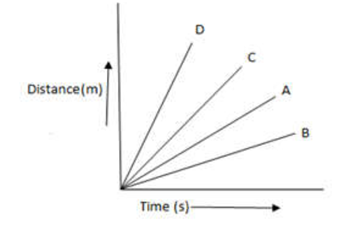
(a) Car A is faster than car D
(b) Car B is the slowest
(c) Car D is faster than car C
(d) Car B is the Faster than C
(b) Car B is the slowest
Q 3 – The term cell was given by
(a) Robert Hooke
(b) Tatum
(c) Schwann
(d) De Bary
(a) Robert Hooke
Q 4 – Which of the following are examples of prokaryotes?
(a) Algae
(b) Fungi
(c) Bacteria
(d) Protozoa
(a) Algae
Q 5 – Xylem and phloem are examples of
(a) epidermal tissue
(b) simple tissue
(c) protective tissue
(d) complex tissue
(d) complex tissue
Q 6 – The flexibility in plants is due to a tissue called
(a) chlorenchyma
(b) parenchyma
(c) sclerenchyma
(d) collenchymas
(d) collenchymas
Q 7 – Which of the following statement is not correct for an object moving along a straight path in an accelerated motion?
(a) Its speed keeps changing
(b) Its velocity always changes
(c) It always goes away from the earth
(d) A force is always acting on it
(c) It always goes away from the earth
Q 8 – A water tanker filled up to 2/3 of its height is moving with a uniform speed. On sudden application of the brake, the water in the tank would
(a) move backward
(b) move forward
(c) be unaffected
(d) rise upwards
(b) move forward
Q 9 – A mixture of common salt, sulphur, sand and iron filings is shaken with carbon disulphide and filtered through a filter paper. The filtrate is evaporated to dryness in a china dish. What will be left in the dish after evaporation?
a) Sand
b) Sulphur
c) Iron filings
d) Common salt
b) Sulphur
Q 10 – Select the correct order of evaporation for water, alcohol, petrol and kerosene oil:
(a) Water > alcohol > kerosene oil > petrol
(b) Alcohol > petrol > water > kerosene oil
(c) Petrol > alcohol > water > kerosene oil
(d) Petrol > alcohol > kerosene oil > water
(d) Petrol > alcohol > kerosene oil > water
Q 11 – Physical properties of a mixture:
a) Vary with the amount of substance
b) Depend on the volume of the substance
c) Depend on the organization of the substance
d) Vary depending upon its components
d) Vary depending upon its components
Q 12 – Name the non-metal which shiny.
Iodine
In each of the following questions, a statement of Assertion is given and a corresponding statement of Reason is given just below it. Out of the given statements, mark the correct answer as:
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Q 13 – Assertion : If the net external force on the body is zero, then its acceleration is zero.
Reason : Acceleration does not depend on force.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
Q 14 – Assertion : A rocket works on the principle of conservation of linear momentum.
Reason : For two bodies system when there is a change in momentum of one body, the same change occurs in the momentum of the second body but in the opposite
direction.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Q 15 – Assertion : Mass is a measure of inertia of the body in linear motion.
Reason : Greater the mass, greater is the force required to change its state of rest or
motion.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Q 16 – Fill in the blanks:
(а) Evaporation of a liquid at room temperature leads to a ________ effect.
(b) At room temperature the forces of attraction between the particles of solid
substances are __________ than those which exist in the gaseous state.
(c) A mixture of chloroform and water taken in a separating funnel is mixed and left
undisturbed for some time. The upper layer in the separating funnel will be of ________
and the lower layer will be that of _________
(d) A mixture of two or more miscible liquids, for which the difference in the boiling
points is less than 25 K can be separated by the process called __________
(e) _______ gives flexibility in plants.
(f) Phloem transport from _______ and _______ to other parts of the plant.
(g) Transporting channels of the cell _______
(a) cooling
(b) stronger
(c) Water, Chloroform
(d) Sublimation
(e) Collenchyma
(f) Food; leaf
(g) Endoplasmic reticulum
Q 17 – What is solubility ?
The maximum amount of solute that can dissolve in a known quantity of solvent at a certain temperature is its solubility.
Q 18 – What is meant by resultant force ? explain with example.
When there is more than one force acting upon the same body. The different forces are altogether replaced by a single force. This force is called resultant force.
Example –
If three forces 50 N , 40 N and 35 N are acting on a body simultaneously. 30N is opposite the direction of the other two. Calculate the resultant force.
Solution
As per the formula we will place the quantities.
(50 N + 40 N) – 35 N
90 N – 35 N
= 55 N
Q 19 – Why does a fall on a hard concrete floor hurt more than a fall on matteress ?
When you jump onto the concrete surface, your feet are brought to rest almost instantaneously because the rate of change of momentum is very high. Hence, you get injured due to a large force on your body on account of the hard floor.
But, when you jump on sand, you come to rest in a longer period of time. So, the change in momentum takes place in longer interval of time. Hence, a small force is exerted on your body and you don’t get injured.
Q 20 – Who proposed the cell theory? explain the theory ?
- Matthias Schleiden, a German botanist, and Theodor Schwann, a British Zoologist formulated the cell theory in the mid-nineteenth century.
- In 1838 Schleiden was the first to state that cells are building blocks of plants.
- These discoveries led to the formulation of cell theory.
- But the cell theory failed to explain how the new cell arises from pre-existing cells.
- In 1855, Rudolf Virchow, a German physiologist, stated that ‘Omnis cellula e cellula’ means that new cell arises from pre-existing cells.
Cell theory postulates:
- The cell is the structural and functional unit of life.
- All living organisms are made of cells.
- All cells arise from pre-existing cells expanded by Rudolf Virchow in 1858.
Q 21 – Explain how a karate player can break a pile of tiles with a single blow of his hand.
A karate player can break a pile of tiles with a single blow because he strikes the pile with his hand very fast. In doing so, the large momentum of his hand is reduced to zero in a very short time. This exerts a large force on the pile of tiles which is sufficient to break them apart.
Q 22 – Define unsaturated and saturated solution.
Unsaturated solution: The solution is unsaturated when it can still dissolve more solute.
Saturated solution: The solution is saturated when it can not dissolve further more solute.
Q 23 – Calculate the mass of sodium sulphate required to prepare its 20% (mass percent) solution in 100g of water?
Let the mass of sodium sulphate which is required to prepare this solution be 𝑥 grams.
So,
20 = [𝑥/(𝑥 + 100)] × 100
20/100 = [𝑥/𝑥 + 100]
1/5 = 𝑥/𝑥 + 100
𝑥 + 100/5 = 𝑥
𝑥 + 100 = 5𝑥
5𝑥 – 𝑥 = 100
4𝑥 = 100
𝑥 = 100/4
𝑥 = 25
Thus, 25g of sodium sulphate is required.
Q 24 – Define homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures.
A homogeneous mixture has the same uniform appearance and composition throughout. Many homogeneous mixtures are commonly referred to as solutions.
A heterogeneous mixture consists of visibly different substances or phases. The three phases or states of matter are gas, liquid, and solid.
Q 25 – 36g of common salt is dissolved in 100 g of water at 396K to make a saturated solution. Find the concentration (mass by mass) of the solution at this temperature.
Q 26 – An element is sonorous and highly ductile. Under which category would you classify this element? What other characteristics do you expect the element to possess?
As the given element is sonorous and highly ductile, therefore, it is categorized as a metal. Some other expected characteristics are:
(i) It should possess metallic luster and can be polished.
(ii) It should be good conductors of heat and electricity.
(iii) It should be ductile.
(iv) It should be malleable.
(v) It should have high tensile strength.
(vi) It should have high densities and melting point/boiling point too.
(vii) It should be complex (except for sodium and potassium which are soft metals).
(viii) It should be solid at room temperature (except mercury, which is liquid at room temperature).
While the characteristics of non-metals are:
(i) Non-metals are neither malleable nor ductile and do not conduct electricity.
(ii) Metalloids show some properties of metals and some other properties of non-metals.
Q 27 – Using second law of motion, derive the relation between force and acceleration.
According to the second law of motion
F=change in momentum per unit time
F=∆p/∆t…………………(i)
As we know p=mv
So change in momentum (∆p)=∆(mv)
∆p=m∆v……………….. (ii)
(since mass is constant and only velocity changes)
Also acceleration a = change in velocity per unit of time
a=∆v/∆t…………………(iii)
Using (i) & (ii)
F=m∆v/∆t
Using (iii)
F=ma
Q 28 – Which method can be used to separate a mixture of naphthalene and common salt?
Sublimation is the method of separating naphthalene from common salt.
Q 29 – What mass of potassium nitrate would be needed to produce a saturated solution of potassium nitrate in 150 grams of water at 313 K if its solubility is 62g at 313K.
Solution of potassium nitrate in 50 g at 313 K
Q 30 – The given velocity-time graph shows the motion of a cyclist. Find
(i) its acceleration
(ii) its velocity and
(iii) the distance covered by the cyclist in 15 seconds
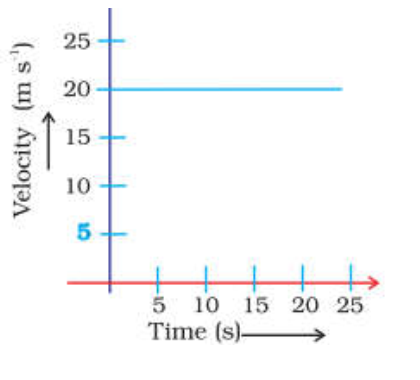
(i) its acceleration
Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity with respect to time. As velocity is constant, acceleration is 0 m/s2.
(ii) its velocity
The meaning of velocity of an object can be defined as the rate of change of the object’s position with respect to a frame of reference and time.
Here Velocity is constant hence v = 20 m/s
(iii) the distance covered by the cyclist in 15 seconds
Distance covered by the cyclist in 15 s = Area under v – t graph during that time interval
s = v x t
s = 20 x 15
s = 300 m
Q 31 – (a) How much momentum will an object of mass 10 kg transfer to the floor if it falls from a height of 5 m (g = 10 m/s²)
(b) A ball moving at a constant speed 10m/s, hits normally on a wall (mass of ball is 50 g) and rebounds with same speed. The change in momentum is
V =
Q 32 – A boy of mass 40 kg jumps out of a boat of 200 kg on the bank, with a velocity of 2m/s. If the momentum is conserved. With what velocity the boat will move backwards?
Using momentum conservation,
m1u1 + m2u2 = m1v1 + m2v2
m1 = mass of boy & m2 = mass of boat
m1 = 40 kg ,v1 = 3 m/s u1 = 0 , u2 = 0
⇒ 40 × 0 + m2 × 0 = 40 × 3 + m2 × v2
⇒ 0 + 0 = 120 + momentum of boat
0 = momentum of boat + 120
momentum of boat = −120 kgm/s
Q 33 – A car is travelling at 20 km/h, it speeds up to 60 km/h in 6 seconds. What is its acceleration?
Q 34 – A car accelerates from 72 km/h to 90 km/h in 20 seconds. Calculate :
(a) the acceleration produced in the car
(b) distance covered by the car in that time.
Q 35 – Write the characteristics of cell?
Basic characteristics of a cell are as follows:
(i) Cell is structural and functional unit of all living beings.
(ii) Cells can replicate independently.
(iii) Cells perform all the life sustaining activities by themselves.
Q 36 – Which organelle serves as a channel for transport of materials between cytoplasm and nucleus?
The organelle which serves as a Channel for transportation of material between cytoplasm and nucleus is the Endoplasmic Reticulum.
Q 37 – What is membrane biogenesis? How is plasma membrane formed during this process?
The process of plasma membrane formation is known as membrane biogenesis. The plasma membrane is made up of lipids and proteins which are made by Smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum respectively
Plasma membrane also has glycolysis and glycoproteins which are made in golgi apparatus via modification of lipids and proteins received by golgi apparatus from smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum.
Q 38 – What type of tissue is found at the shoot apex? Name one more part of plant body where this type of tissue is found.
The Apical meristem is found in the shoot apex ,root apex and the tip of the leaves. It helps in the increase of the plant’s length.
Q 39 – Why vacuoles are absent in the cells of meristematic tissue?
i) The vacuole is a cell organelle used to store waste materials, store nutrients, excess salts etc.
ii) Usually big and more in number in mature cells.
iii) Meristematic cells are mainly concerned with cell division.
iv) Their primary function is mitosis. They do not have any waste material to store so vacuoles are usually absent in the meristematic cells.
Q 40 – Which chemical is deposited at the corners of cells of collenchyma?
Pectin and cellulose are deposited at the corner of cells in collenchyma.
Q 41 – Why do surgeons often spray some ether on the skin before performing minor surgery?
Ether is volatile liquid.
It absorbs heat energy from the body and evaporates rapidly such that the temperature of the area becomes so cool and the area becomes numb.
This reduces pain while performing surgery.
Q 42 – With proper explanation, explain whether the following statements are true or false?
(a) Sublimation occurs only when the solid is heated.
(b) A lighter gas can move downwards and a heavier gas can move upwards.
(c) Interconversion of matter is a constant temperature process.
(a) Statement is wrong. Sublimation may occur on its own or by heating, e.g., camphor, naphthalene, iodine, etc., sublime slowly at room temperature.
(b) Statement is true. Diffusion occurs against the law of gravitation. Therefore, lighter gases can also diffuse downwards and the heavier gases can also diffuse upwards. However rate of diffusion of lighter gases is faster than those of heavier gases.
(c) Statement is true. During interconversion of state of matter from solid to liquid or from liquid to gas, it tends to reach its melting point or boiling point. At this point, the temperature remains constant unit it has changed in another state.
Q 43 – Explain
(a) How do we swim?
(b) Why does a gun recoil?
(c) It is difficult to walk on sand or ice.
(d) The motion of rocket.
(e) Why does a fireman struggle to hold a hose-pipe?
(a) While swimming, a swimmer pushes the water backward with his hands (i.e., he applies force in the backward direction, which is known as action.) The reaction offered by the water to the swimmer pushes him forward.
(b) Recoiling of a gun: When a bullet is fired from a gun, it exerts a forward force on the bullet and the bullet exerts an equal (in magnitude) and opposite (in direction) force on the gun. Due to the high mass of the gun, it moves a little distance backward and gives a backward jerk to the shoulder of the gunman.
(c) It is difficult to walk on sand or ice: When our feet press the sandy ground in the backward direction, the sand gets pushed away and as a result, we get only a small reaction (forward) from the sandy ground making it difficult to walk.
(d) Rocket propulsion Before firing the rocket, the total linear momentum of the system is zero because the rocket is in the state of rest. When it is fired, chemical fuels inside the rocket are burnt and the hot gases are passed through a nozzle with great speed. According to the law of conservation of linear momentum, the total linear momentum after firing must be equal to zero. As the hot gases gain linear momentum to the rear on leaving the rocket, the rocket acquires equal linear momentum in the upward i.e., opposite direction.
(e) A fireman has to make a great effort to hold a hose-pipe to throw a stream of water on the fire to extinguish it. This is because the stream of water rushing through the hose-pipe in the forward direction with a large speed exerts a large force on the hose-pipe in the backward direction which is known as the reaction force. This reaction force tends to move the hose-pipe in the backward direction. Therefore, a fireman struggles to hold the hose-pipe strongly to keep it at rest.
Q 44 – Average velocity can be zero but average speed cannot if an object has moved some distance. Justify your answer.
