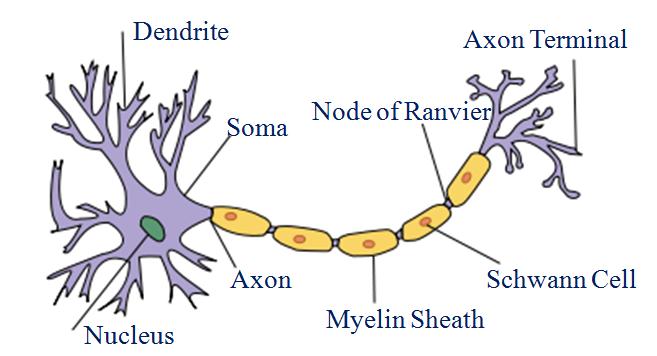
A neuron consists of a cell body with a nucleus and cytoplasm, from which long thin hair like parts arise. Each neuron has a single long part called the axon, and many small, short branched parts called dendrite. An individual nerve cell is called neuron, it may be up to a metre long.