Chapter- 5 The fundamental unit of life
Very Short Answers Questions
Q 1. Who discovered the cell?
(a) Robert Hooke
(b) Leeuwenhoek
(c) Robert Brown
(d) T. Schwann
Ans. (a) Robert Hooke
Q 2. Which of the following controls all biological activities of a cell?
(a) Protoplasm
(b) Cell wall
(c) Nucleus
(d) All of these
Ans. (c) Nucleus
Q 3. The cell wall of a plant cell is made up of:
(a) glucose
(b) fructose
(c) protein
(d) cellulose
Ans. (d) cellulose
Q 4. Which of the following is known as the ‘Power House’ of a cell?
(a) Nucleus
(b) Golgi Bodies
(c) Ribosome
(d) Mitochondria
Ans. (d) Mitochondria
Q 5. The basic unit of life is:
- (a) tissue
- (b) cell
- (c) both
- (d) none of them
Ans: (b) cell
Q 6. Which is the longest cell of the human body?
(a) Nerve cell
(b) Liver cell
(c) Kidney cell
(d) Cardiac cell
Ans. (a) Nerve cell
Q 7. Who proposed the “Black Reaction”?
(a) Benda
(b) Camillo Golgi
(c) Schleiden
(d) None of them
Ans. (b) Camillo Golgi
Q 8. Who discovered the nucleus in the cell?
(a) Leeuwenhoek
(b) Robert Brown
(c) Schleiden
(d) Robert Hooke
Ans. (b) Robert Brown
Q 9. Which out of the following is not a function of vacuole?
(a) Storage
(b) Providing turgidity and rigidity to the cell
(c) Waste excretion
(d) Locomotion
Ans. (d) Locomotion
Q 10. Lysosome arises from:
(a) endoplasmic reticulum
(b) Golgi apparatus
(c) nucleus
(d) mitochondria
Ans. (b) Golgi apparatus
Click Here:- Class 9 Important Questions and Answers Chapterwise
Q 11. Match the Column.
| A | B |
| 1. A method of plant breeding | (i) Protein factory |
| 2. Mitochondria | (ii) Cell wall |
| 3. Lysosome | (iii) Polyploidy |
| 4. Ribosome | (iv) Powerhouse of the cell |
| 5. Cellulose | (v) Suicidal bag |
Ans.
| A | B |
| 1. A method of plant breeding | (iii) Polyploidy |
| 2. Mitochondria | (iv) Powerhouse of the cell |
| 3. Lysosome | (v) Suicidal bag |
| 4. Ribosome | (i) Protein factory |
| 5. Cellulose | (ii) Cell wall |
Q 12. Which of the following can be made into crystal?
(a) A bacterium
(b) An Amoeba
(c) A virus
(d) A sperm
Ans. (c) A virus
Q 13. Which of these options are not a function of ribosomes?
(i) It helps in manufacture of protein molecules.
(ii) It helps in manufacture of enzymes.
(iii) It helps in manufacture of hormones.
(iv) It helps in manufacture of starch molecules.
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (iv) and (i)
Ans. (c) (iii) and (iv)
Q 14. Following are a few definitions of osmosis:
Read carefully and select the correct definition.
(a) Movement of water molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration through a semi-permeable membrane.
(b) Movement of solvent molecules from its higher concentration to lower concentration.
(c) Movement of solvent molecules from higher concentration to lower concentration of solution through a permeable membrane.
(d) Movement of solute molecules from lower concentration to higher concentration of solution through a semi permeable membrane.
Ans. (a) Movement of water molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration through a semi-permeable membrane.
Q 15. Plasmolysis in a plant cell is defined as
(a) breakdown (lysis) of plasma membrane in hypertonic medium
(b) shrinkage of cytoplasm in hypertonic medium
(c) shrinkage of nucleoplasm
(d) none of them
Ans. (b) shrinkage of cytoplasm in hypertonic medium
Q16. Find out the false sentence.
(a) Nucleus is involved with the formation of lysosomes.
(b) Nucleus, mitochondria and plastid have DNA, hence they are able to make their own structural proteins.
(c) Mitochondria is said to be the power house of the cell as ATP is generated in them.
(d) Cytoplasm is called as protoplasm.
Ans. (a) Nucleus is involved with the formation of lysosomes.
Q17. Which cell organelle plays a crucial role in detoxifring many poisons and drugs in a cell?
(a) Golgi apparatus
(b) Lysosomes
(c) Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
(d) Vacuoles
Ans. (c) Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Q 18. The proteins and lipids, essential for building the cell membrane, are manufactured by
(a) rough endoplasmic reticulum
(b) golgi apparatus
(c) plasma membrane
(d) mitochondria
Ans. (a) rough endoplasmic reticulum
Q 19. The cell organelle involved in forming complex sugars from simple sugars are
(a) endoplasmic reticulum
(b) ribosomes
(c) plastids
(d) golgi apparatus
Ans.
(d) golgi apparatus
Q 20. Amoeba acquires its food through a process, termed
(a) exocytosis
(b) endocytosis
(c) plasmolysis
(d) exocytosis and endocytosis both
Ans. (b) endocytosis
Q 22. Silver nitrate solution is used to study
(a) endoplasmic reticulum
(b) golgi apparatus
(c) nucleus
(d) mitochondria
Ans. (b) golgi apparatus
Q 23. Lipid molecules in the cell are synthesised by
(a) smooth endoplasmic reticulum
(b) rough endoplasmic reticulum
(c) golgi apparatus
(d) plastids
Ans. (a) smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Q 24. Describe the microscopic structure of the cell.
Ans. The cork cells were the first cells to be observed. They were composed of box-like compartments, forming a honeycomb structure. Cell organelles are found embedded in the cytoplasm. These are smaller in size and bounded by plasma membrane.
Q 25. How can you calculate the magnification of a microscope?
Ans. Magnification of a microscope is calculated by multiplying the powers of eyepiece and objective lenses.
Mathematically, M = P1 × P2, where Pi is the power of eyepiece and P2 is the power of objective.
Q 26. What is a cell wall and how is it formed?
Ans. Cell wall is non-living and freely permeable rigid structure bounding the plant cell. It is secreted by the cell itself for the protection of its plasma membrane and cytoplasm.
Q 27. Why were the scientists not able to observe most of the cell organelles before 1940?
Ans. Before 1940, scientists could view the cell only under a light microscope. The invention of the electron microscope in 1940 enabled the scientists to observe the cell in greater detail.
Q 28. There would be no plant life if chloroplasts did not exist. Justify.
Ans. Chloroplasts contain the pigment chlorophyll which is responsible for food preparation in plants by the process of photosynthesis . Hence, if there were no chloroplasts then there would not have been any plant life.
Q 29. Why is the Golgi apparatus called the secretary organelle of the cell?
Ans. This is because it packages material synthesised in the ER and dispatches it to intracellular (plasma membrane and lysosomes) and extracellular (cell surface) targets.
Q 30. Why are peroxisomes mostly found in kidney and liver cells?
Ans. Peroxisomes contain various oxidative enzymes which detoxify the toxic material. Since the blood carries various toxic substances to kidney and liver, a large number of peroxisomes are present in them to oxidize the toxic material.
Q 31. What do you mean by plasmodesmata?
Ans. Due to the presence of cell wall the exchange of materials between the plap.t cells is not possible. Therefore, protoplasts of plant cells are connected by cytoplasmic channels through their walls which are called as plasmodesmata. These channels are used for the exchange of the material between two cells.
Q 32. Why do the animal cells not have cell wall?
Ans. Animals do not have rigid walls because cell walls are incompatible with the way in which an animal moves and grow. The flaccid cell membrane provides the animal cell freedom of mobility and formation of different tissues which is not present in plants.
Q 33. How are chromatin, chromatid and chromosomes related to each other?
Ans. Chromatin is a thin thread-like structure which is composed of DNA (deoxy ribonucleic acid) and proteins to form a rod-like chromatid. Two similar chromatids attach to a centromere to form a chromosome.
Q 34. How is bacterial cell different from onion peel?
Ans.
| Bacterial cell | Onion peel |
| 1. Size is small (1-10 mm). 2. Nucleus is absent. 3. It is a prokaryotic cell. | 1. Size is larger (5-100 mm). 2. Nucleus is present. 3. It is a eukaryotic cell. |
Q 35. Differentiate between diffusion and osmosis.
Ans.
| Diffusion | Osmosis |
| 1. It occurs in any medium. 2. Diffusing molecules may be solid, liquid or gaseous solutes. 3. Semipermeable membrane is not required. | 1. It occurs in liquid medium only. 2. It involves movement of solvent molecules only. 3. Semipermeable membrane is required. |
Q 36. Differentiate between rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum. How is endoplasmic reticulum importantfor membrane biogenesis ?
Ans.
| Rough endoplasmic reticulum | Smooth endoplasmic reticulum |
| 1. They have ribosomes attached on their surfaces. 2. RER manufactures proteins and transports them to various places. | 1. They do not have ribosomes attached on their surfaces. 2. SER helps in manufacturing lipids and transports them to various places. |
Endoplasmic reticulum act as main site for synthesis of protein and lipids which are needed for the biogenesis of plasma membrane.
Q 37. What is membrane biogenesis? How is plasma membrane formed during this process?
Ans. The process of plasma membrane formation is called membrane biogenesis.
Following organelles are involved in this process:
The proteins and lipids are first synthesised in rough endoplasmic reticulum and the smooth endoplasmic reticulum, respectively. These are then transported to the Golgi complex for their modification. After modification, these are transported to the cell surface through vesicles which bud off from Golgi complex to fuse with cell membrane and form a part of the membrane.
Q 38. Write the name of different plant parts in which chromoplast, chloroplast and
leucoplast are present.
Ans.
- Chromoplasts are present in flowers, fruits or any other coloured part of the plant (other than green part).
- Chloroplasts are present in leaves and stem of plant (green part).
- Leucoplasts are present anywhere in plant as they are colourless and store food.
Q 39. What is cell division? Give the types of cell division.
Ans. Cell division is a process of formation of two or more daughter cells of its own type from the mother cell.
These are similar in structure and function.
Cell division occurs in three ways:
- Amitosis
- Mitosis
- Meiosis
In each case, division of nucleus (Karyokinesis) occurs before the division of
cytoplasm (Cytokinesis).
Q 40. What are the functional differences between a plasma membrane and cell wall?
Ans.
| Plasma membrane | Cell wall |
| 1. It holds cellular contents and controls passage of materials in and out of cell. | 1. It gives protection, strength and rigidity to the cell. |
| 2. It is semi permeable in nature and allows entry of selected molecules into the cell. | 2. It is completely permeable in nature. |
| 3. It is not elastic. | 3. It is elastic and controls the cell’s turgidity preventing its bursting. |
Q 41. How will absence of any one of the cell organelle affect the cell’s working?
Ans. Functions of all the organelles are inter-linked to each other and ultimately to the working of the cell. So, if even a single link is missing, the cell ultimately suffers and dies. For example, DNA from the nucleus passes the information for protein formation to the ribosomes which send the proteins to Golgi complex and ER for
modification and transport.
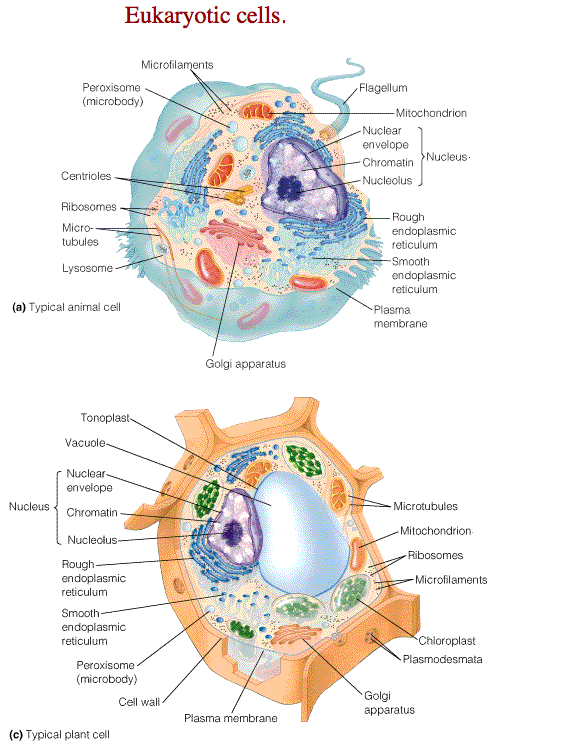
Q 42. Draw a neat diagram of plant cell and label any three parts which differentiate it from animal cell.
Ans.
Q 43. Draw a neat labelled diagram of an animal cell. [NCERT Exemplar]
Ans.
Q 44. Draw a labelled diagram of mitochondria. Write the functions of mitochondria.
Ans.
Functions of mitochondria:
The mitochondria are the main sites for cellular respiration, the process in which the cell converts sugars and oxygen into ATP. ATP is used by various bodies as a source of energy to perform functions.
Q 45. What is active transport? Differentiate between active and passive transport.
Ans. The process in which the molecules are moved uphill against the concentration gradient. Active transport always involves the expenditure of energy because the materials are pumped against the concentration gradient.
| Active transport | Passive transport |
| 1. It involves movement of molecules against the concentration gradient. 2. It requires energy in the form of ATP molecules. 3. It is a rapid movement. 4. Movement of large molecules occur by active transport. | 1. It involves movement of molecules along the concentration gradient. 2. No energy is required. 3. It is a slow movement. 4. Only small molecules or water molecules are transported passively |
Q 46. Illustrate only a plant cell as seen under electron microscope. How is it different from animal cell?
Ans. Major differences found in Plant cells and Animal cells are:
- Plant cells have chloroplasts
- Plant cells have large vacuoles.
- Plant cells have cell walls.
Q 47. In brief state what happens when:
(a) dry apricots are left for sometime in pure water and later transferred to sugar solution?
(b) a red blood cell is kept in concentrated saline solution?
(c) the plasma membrane of a cell breaks down?
(d) rheo leaves are boiled in water ¦rst and then a drop of sugar syrup is put on it?
(e) golgi apparatus is removed from the cell? [NCERT Exemplar]
Ans. (a) The apricots swell due to osmosis initially and when transferred to sugar solution shrink again due to exosmosis.
(b) RBCs shrink due to exosmosis.
(c) It would lead to scattering of cell organelles and there will be no functioning of the organs.
(d) There will be no change in cell shape or size because the cells are dead due to boiling.
(e) Function of Golgi apparatus is packing, storing and transfer of protein. It would affect the functioning of cell.
Q 48. Describe an activity to demonstrate endosmosis and exosmosis. Draw a diagram also.
Ans. Put dried raisins or apricots in plain water and leave them for some time. Then place them into a concentrated solution of sugar or salt.
You will observe the following:
(a) Each of the raisins or apricots gains water and swells when placed in water.
Reason: The raisins or apricots swell up as water moves inside them from outside because the water concentration is less inside the cell as compared to the solution outside. Hence, water moves inside the cell by endosmosis.
(b) However, when placed in the concentrated solution they lose water, and consequently shrink.
Reason: The raisins or apricots shrink as water moves outside from them because the water concentration is more inside the cell as compared to the solution outside. Hence, water moves out of the cell by exosmosis.
Q 49. Differentiate between diffusion and osmosis. Write any two examples where a living organism uses osmosis to absorb water.
Ans. Diffusion – The movement of a substance from a region of its high concentration to the region of its low concentration is called diffusion.
Osmosis – The spontaneous movement of water molecules from a region of its high concentration to the region of its low concentration through a selectively permeable membrane is called osmosis.
Examples where a living organism uses osmosis to absorb water are:
Roots of plants absorb water by osmosis.
Unicellular organisms like Amoeba absorb water by osmosis
Q 50. Differentiate between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell.
Ans. Prokaryotic cell:
- Organisms whose cells lack a well defined nuclear membrane.
- They lack membrane bound cell organelles.
- Size is generally small (1-10 pm).
- Have a single chromosome.
Eukaryotic cell:
- Organisms with cells having a well defined nuclear membrane.
- They have membrane bound cell organelles.
- Size is generally large (5-100 pm).
- Have more than one chromosome
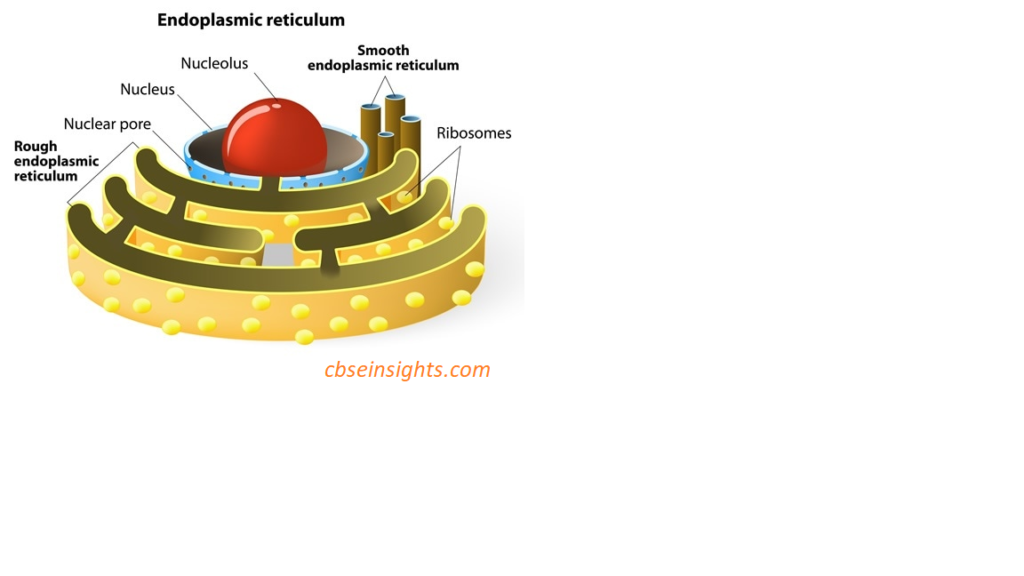
Q 51. What are the different types of endoplasmic reticulum? Write the functions of each.
Ans. There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum – Rough endoplasmic reticulum and Smooth endoplasmic reticulum. The functions of these are:
Rough endoplasmic reticulum –
- It looks rough as it has particles called Ribosomes attached to its surface.
- Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis.
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum –
- It helps in the manufacture of fat molecules, or lipids, important for cell function.
- Some proteins and lipids made by SER help in building the cell membrane and this process is known as membrane biogenesis.
- Helps in detoxifying many poisons and drugs in the liver cells of the group of vertebrates.
Q 52. Draw a neat and labelled diagram of a typical prokaryotic cell.
Ans.

Q 53. Explain in detail what do you know about the structure of the nucleus.
Ans.The nucleus was discovered by Robert Brown in 1831. The structure and the features of nucleus are:
It is a dark coloured, spherical or oval, dot-like structure near the centre of each cell.
It is the control centre of the cell as it controls all the activities of the cell.

It has a double layered covering called nuclear membrane.
The nuclear membrane has pores which allow the transfer of materials from inside the nucleus to the cytoplasm.
The nucleus plays a central role in cellular reproduction (process by which a single cell divides and forms two new cells).
Nucleus along with the environment directs the chemical activities of the cell to determine the way the cell will develop and the form it will exhibit at maturity.
Nuclear region of the cell may be poorly defined due to the absence of a nuclear membrane in some organisms like bacteria.
Such an undefined nuclear region containing only nucleic acids is called a nucleoid.
Q 54. How does Amoeba obtain its food?
Ans. Amoeba takes in food with the help of finger like extensions called pseudopodia by the process called endocytosis. Pseudopodia help to engulf the food which gets enclosed in a food vacuole. The complex particles of the food get broken down into simpler substances
inside the food vacuole and diffuse into the cytoplasm of Amoeba. The undigested food particles are removed from the cell by exocytosis.

Q 55. Draw a well labelled diagram of an eukaryotic nucleus. How is it different from a nucleoid?
Ans.
It is different from a nucleoid as it is a membrane bound organelle.
Q 56 . What will be the effect on the cell when:
(a) The cell is placed in a medium having lower water concentration.
(b) The cell is placed in a medium having higher water concentration.
(c) The cell is placed in a medium having water concentration which is equal to that inside the cell.
Ans. The consequences of the following conditions are:
(a) The cell having low water concentration than the surrounding medium will undergo endosmosis.
(b) The cell containing higher water concentration than the surrounding medium will undergo exosmosis.
(c) The cell having equal water concentration to its surrounding medium will not be affected as there won’t be any net movement of water into or outside the cell.
