Q 1. Who proposed the two kingdom classification?
Ans. Carolus Linnaeus.
Q 2. What is biodiversity?
Ans. The variety of life forms including plants, animals and microscopic organisms which inhabit this earth constitute biodiversity.
Q 3. What is classification?
Ans. The grouping of organisms on the basis of their similarities and differences is called classification.
Q 4. What is the taxonomy?
Ans. The branch of science which deals with the classification of organisms is called taxonomy.
Q 5. Who proposed the five kingdom system of classification?
Ans. R.H. Whittaker.
Q 6. Name the fundamental unit of classification.
Or
Which is the lowermost category in the hierarchy of classification?
Ans. Species.
Q 7. Give one point of difference between gymnosperms and angiosperms.
Ans. The seeds of gymnosperms are naked whereas the seeds of angiosperms are enclosed within a fruit.
Q 8. Name the largest phylum of kingdom Animalia.
Ans. Arthropoda.
Q 9. Name the class to which the sea horse belongs.
Ans. Sea horse belongs to class Pisces.
Q 10. Which group of plants is referred to as vascular cryptogams?
Ans. Pteridophytes.
Q 11. Which phylum in animial kingdom consists of pseudocoelomate organisms?
Ans. Nematoda
Q 12. Which group of organisms are called as the ‘Amphibians of plant kingdom*?
Ans. Bryophytes
Q 13. Name the two classes of angiosperms with one example of each.
Ans. The two classes are –
- Monocots: Wheat
- Dicots: Pea
Q 14. Name the division of cryptogams to which algae belong.
Ans. Thallophyta
Q 15 . Which is the highest unit of classification?
Ans. Kingdom
Q 16 . What is the characteristic feature due to which echinoderms are named?
Ans. Spiny skin (Echino- spiny; derm-skin)
Q 17 . Name the group which comprises of bacteria and blue green algae.
Ans. Monera
Q 18 . Name an organism which is called saprophyte. Why is it called so?
Ans. Yeast. It is called so as it feeds on dead and decaying matter to obtain its nutrition.
Q 19 . Identify the kingdom in which the organisms do not have a well-defined nucleus and are not able to show multicellular designs.
Ans. Monera
Q 20 . Give reason, why blue green algae are classified along with bacteria and placed in the kingdom Monera.
Ans. As the blue green algae are unicellular prokaryotes like bacteria.
Q 21 . Mention any one characteristic feature of saprophytes.
Ans. The saprophytes feed on dead and decaying organic matter.
Q 22 . Write one point of difference between monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plants.
Ans. Monocots are plants which bear single cotyledon in their seeds. Dicots are the plants which bear two cotyledons in their seeds.
Q 23 . Poriferans have hole or pores all over the body that lead to a system that helps in circulating water to bring in food and oxygen. Name the system.
Ans. The system is called as the canal system.
Q 24 . State the phylum to which liver fluke and Planaria belong.
Ans. Phylum Platyhelminthes
Q 25 . Write the type of body cavity and symmetry possessed by nematodes.
Ans;. Body cavity is pseudocoelom and symmetry is bilateral symmetry.
Q 26 . Name one mammal that lays eggs.
Ans. Platypus
Q 27 . Name the substance which Coelomic cavity of arthropods is filled with. What type of symmetry do they have?
Ans. Coelomic cavity of arthropods is filled with blood. They show bilateral symmetry.
Q 28 . Name the phylum to which centipede and prawn belong.
Ans. Phylum Arthropoda
Q 29 . Echinoderms are marine animals. What is their skeleton made up of?
Ans. Their skeleton is made up of calcium carbonate.
Q 30 . Name one reptile with a four chambered heart.
Ans. Crocodile
Q 31 . Shyam knew the correct scientific name of mango but did not follow the convention while writing it and wrote it as Mangifera Indica. Rewrite the scientific name as per the convention.
Ans. Mangifera indica
Q 32 . Which mode of nutrition is found in blue-green algae?
Ans. Autotrophic mode of nutrition is found in blue-green algae, i.e., they can synthesise their own food.
Q 33 . How can we say that classification of organisms is closely related to their evolution?
Ans, We can say that classification of organisms is closely related to their evolution because the simple organisms have a primitive body design as they appeared earlier whereas the complex organisms have more advanced body designs as they are more recent. This shows that during the course of evolution more complex body designs were formed from simpler ones.
Q 34 . What is the difference between algae and fungi?
Ans.
Algae:
- Have chlorophyll.
- Autotrophic mode of nutrition.
- Cell wall made of cellulose.
- Food stored in the form of starch.
- Examples: Chlamydomonas, Spirogyra, Ulo-thrix
Fungi:
- Lack chlorophyll.
- Heterotrophic mode of nutrition.
- Cell wall made of chitin.
- Food stored in the form of glycogen.
- Examples: Rhizopus, Agaricus, Yeast
Q 35 . Pick the odd one out and justify your choice by giving reasons:
(a) Moss, Fern, Pinus, Spirogyra
(b) Sea cucumber, Octopus, Feather star, Star fish
Ans. (a) The odd one out in this case is Pinus as it is a phanerogams having covered reproductive parts whereas the other three are cryptogams which bear hidden reproductive organs.
(b) The odd one out in this case is Octopus as it belongs to phylum Mollusca while others are the members of phylum Echinodermata.
Q 36 . Why were fungi and bacteria considered as plants even though they do not have chlorophyll?
Ans. Fungi and bacteria were considered as plants as they have cell wall which is a characteristic feature of the plants. So, some earlier classification systems included them under plants.
Q 37 . Why do bryophytes and pteridophytes grow in moist and shady places?
Ans, Bryophytes and pteridophytes grow in moist and shady places as they need water for their reproduction. Male gametes are carried towards the female gamete by water in order to bring about fertilisation in them.
Q 38 . Which divisions of the plant kingdom are called cryptogams? Why are they called so?
Ans. Thallophyta, Bryophyla and Pteridophyta are considered as cryptogams. They are called so because they bear hidden and inconspicuous reproductive orgAnswer:
Q 39 . Characteristics of some organisms are given. Identify their group and give one example of each.
(а) Single celled, eukaryotic and photosynthetic
(b) The body is divided into segments, may be unisexual or hermaphrodite
Ans. (a) Protista: Euglena
(b) Annelida: Earthworm
Q 40 . How do saprophytes get their food? Give one example of saprophyte.
Ans. Saprophytes derive their nutrition from the dead and decaying materials. For example, Agaricus (Mushroom), Rhizopus (Bread mould), Yeast etc.
Q 41 . What are phanerogams? How are they classified?
Ans. The phanerogams are the plants which produce seeds and have a well differentiated body with true roots, stem and leaves. They are advanced members of kingdom Plantae. It includes gymnosperms and angiosperms.
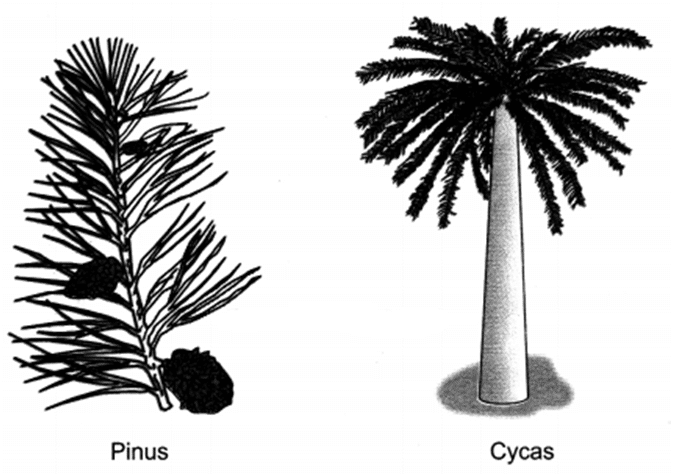
Q 42 . What are gymnosperms? Give two examples.
Ans. The plants which bear naked seeds which are not enclosed in fruit are called gymnosperms. For example, Cycas, Pinus, etc.
Q 43 . Write two peculiar characters of sponges.
Ans. The two peculiar features of sponges are:
(i) They have pores called ostia all over their body and a single large opening at the top, called osculum which helps to develop a canal system for water movement.
(ii) They have a skeleton made up of calcareous or siliceous spicules or spongin fibres which gives strength and support.
Q 44 . Classify the following in their respective phylum/class: Jellyfish, earthworm, cockroach, rat
Ans.
- Jellyfish: Phylum Coelenterata
- Earthworm: Phylum Annelida
- Cockroach: Phylum Arthropoda
- Rat: Phylum Vertebrata, Class: Mammalia
Q 45 . What are the two peculiar features of phylum Echinodermata?
Ans. The phylum Echinodermata has organisms which have
- spiny skin
- water vascular system
Q 46 . What are the three germ layers present in the organisms? What are the two groups of organisms on the basis of germ layers?
Ans. The three germ layers are ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm. The groups are diploblastic and triploblastic.
Q 47. How are vertebrates different from the other chordates?
Ans. The notochord is present at any stage of their life cycle in the case of chordates. In the vertebrates the notochord gets replaced by the vertebral column.
Q 48 . How are pteridophytes are different form Phanerogams? Give one example for each group.
Ans. Pteridophytes have hidden, inconspicuous reproductive organs example ferns.
Phanerogams have well differentiated reproductive organs which are not hidden, example rose, apple.
Q 49 . (a) Given below are few plant species. Identify the divisions to which they belong and write the major characteristic of each division.
(i) Spirogyra
(ii) Deodar
(iii) Moss
(b) What is the mode of nutrition for all of them?
Ans.
(i) Thallophyta: Plant body is not well differentiated
(ii) Gymnosperms: have naked seeds
(iii) Bryophyta: have rhizoids for absorption of water, have stem-like and leaf-like structures.
(iv) All of them are autotrophic organisms.
Q 50 . What do you understand by the term ‘naked embryo’? Name any two divisions in kingdom Plantae that have naked embryo. Give one example of each division.
Ans. Naked embryo is the term which refers to an embryo which is not borne inside the seed. The pteridophytes and gymnosperms bear naked embryo. For example, Ferns and horsetail are pteridophytes. Pinus and Cycas are gymnosperms.
Q 51 . Write the difference between Gymnosperms and Angiosperms giving example of each type.
Or
What are gymnosperms? Give two characteristics.
Ans.
Gymnosperm:
- Bear naked seeds.
- Are woody, evergreen, perennials.
- Examples: Pinus and Cycas
Angiosperm:
- Bear seeds enclosed in fruit.
- Can be woody, non-woody annual, biennial or perennials.
- Examples: Mango, Neem
Q 52 . Thallophyta, bryophyta and pteridophyta are classified as cryptogams whereas gymnosperms and angiosperms are classified as phanerogams, why?
Ans. Due to the presence of hidden and inconspicuous reproductive organs, thallophyta, bryophyta and pteridophyta are called as cryptogams. Gymnosperms and angiosperms are phanerogams as they have well developed and distinct reproductive organs, flowers, fruits and seeds.
Q 53 . State reasons for the following:
(а) Platyhelminthes are called so.
(b) Birds have hollow bones.
Ans.
(a) Platyhelminthes are called so because they have a dorsoventrally flattened body.
(b) Presence of hollow bones is an adaptation in birds which helps them to keep low body weight which is helpful in flight.
Q 54 . Identify the phylum of animals by the given characteristics and give an example of each.
(a) The coelomic cavity is blood-filled and the animals have jointed legs.
(b) The animals are called as flatworms and are either free living or parasitic
Ans.
(a) Phylum arthropoda: eg., cockroach, butterfly, spider, etc.
(b) Phylum Platyhelminthes: Planaria, liver fluke, tapeworm, etc.
Q 55 . Write one point of difference between the following:
(а) Bilateral symmetry and radial symmetry
(b) Annelids and Nematodes
Ans. (a) Bilateral symmetry – Body can be divided into two exact halves from one plane only.
Radial symmetry – Body can be divided into equal halves from any plane.
(b) Annelids – Have true coelom
Nematodes – Have pseudocoelom.
Q 56 . Label a, b, c and d, given in the figure below. Give the function of (b).
Ans.

(a) Dorsal fin
(b) Caudal fin
(c) Pelvic fin
(d) Pectoral fin
Function of Caudal fins: Caudal fins help in streamlined movement in water.
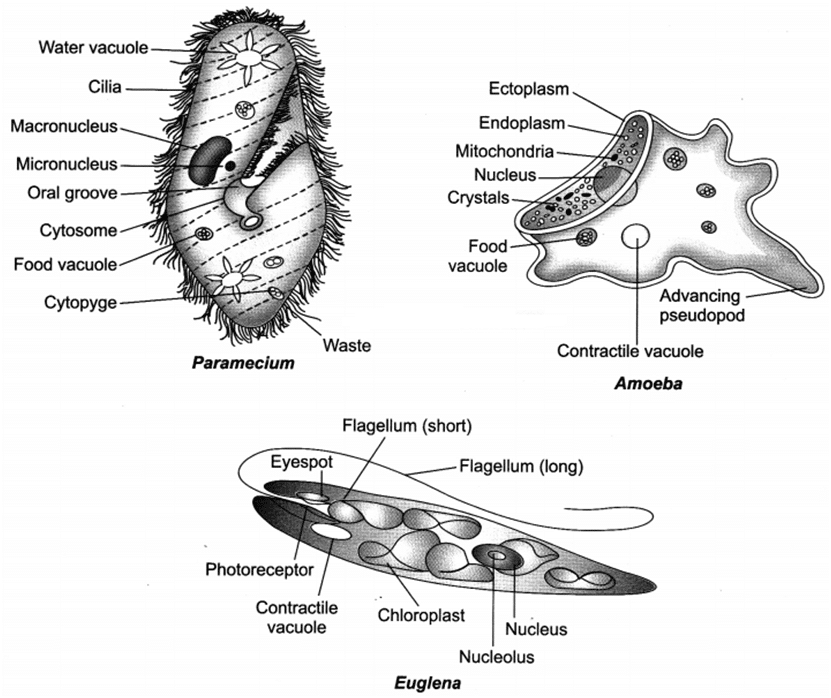
Q 57 . (a) Draw labelled diagrams of three protozoa.
(b) Euglena is a dual organism. Why?
Ans.
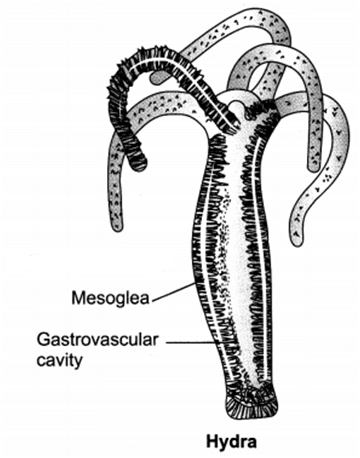
Q 58 . (i) Draw a neat labelled diagram of Hydra.
(ii) Label mesoglea and gastro-vascular cavity.
(iii) Name the group of animals it belongs to.
(iv) Name one species of this group that lives in colonies.
(i) and (ii)-See figure
Q 59 . Draw a neat diagram of Spirogyra and label the following parts:
(a) Outermost layer of the cell
(b) Organelle that performs the function of photosynthesis
(c) Jelly-like substance in the cell where all organelles are suspended.
(d) Dark coloured and dot-like structure generally present in the centre of the cell.
Ans.

Q 60 . Thallophyta, bryophyta and pteridophyta are called as ‘Cryptogams’. Gymnosperms and Angiosperms are called as ‘phanerogams’. Discuss why. Draw one example of Gymnosperm.
Ans.
Thallophyta, bryophyta and pteridophyta are called as ‘Cryptogams’ because they have hidden or inconspicuous reproductive organs. Spores are formed in them instead of seeds. Gymnosperms and Angiosperms are called as ‘phanerogams’ as they have well differentiated reproductive tissue/organs. Seed harbours the embryo and provides it nourishment too.
Q 61 . Define the terms and give one example of each
(a) Bilateral symmetry
(b) Coelom
(c) Triploblastic
Ans.
(a) If the organism can be divided exactly into two halves from one median plane only, the symmetry is called bilateral symmetry, example liver fluke.
(b) The internal body cavity present between visceral organs and body wall in which well developed organs can be accommodated is called as coelom, example butterfly.
(c) The organisms who have three embryonic layers are called as triploblastic organisms example star fish.

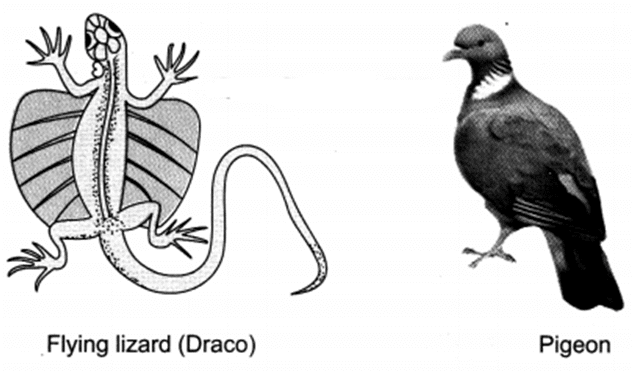
Q 62 . Differentiate between flying lizard and bird. Draw the diagram.
Ans. Flying lizard belongs to the group reptiles and is characterised as cold-blooded, body covered with scales and have three-chambered heart, while birds belong to group aves and are characterised as warm¬blooded, having feather covered body, forelimbs modified as wings and having four-chambered heart.