Q 1 – Describe the different methods of asexual reproduction. Give examples.
Ans. Different methods of asexual reproduction are:
(a) Binary Fission: This process takes place in unicellular organisms. Parent cell elongates and gets divided into two identical daughter cells. Each daughter cell grows into an independent adult.
(b) Endospore Formation: In this method the spore wall is formed around a bacterial cell to form an endospore. This endospore germinates to form an active bacterium under favourable conditions.
(c) Fragmentation: In this process, body of the organism breaks up into two parts. Then each part grows into a new filament thus forming two organisms from a single one.
(d) Spore Formation: The spores are tiny spherical unicellular structures protected by thick wall. The spores are stored in a hard outer covering and this is called sporangium. Under favourable conditions the hard cover breaks and spores spread for germination.
(e) Budding: In yeast, new organisms are produced by the bud formation from the parent organism. After growing to full size, the bud gets detached and forms a new independent individual.
(f) Vegetative propagation: When vegetative parts of a plant like stems, leaves and root etc., give rise to new ones, it is.called vegetative propagation.
Q 2 – Explain what you understand by sexual reproduction.
Ans..Sexual reproduction means involvement of two parents in the process of reproduction. It is found mainly in higher plants where male gamete and female gamete fuse to form a zygote. These zygotes develop into individuals which are not identical. Off springs inherit the characteristics of both the parents. In sexual reproduction both parents survive after the process of reproduction.
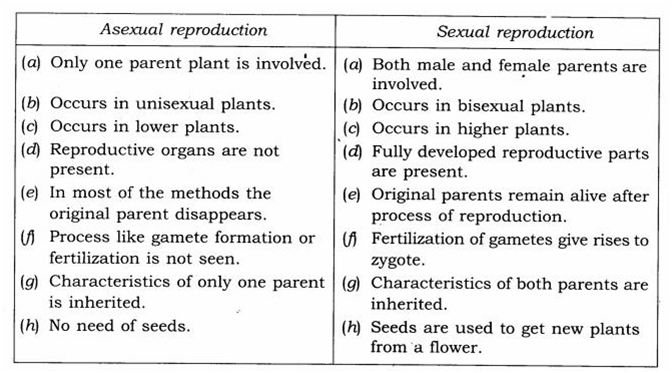
Q 3 – State the main difference between asexual and sexual reproduction.
Ans.
Q 4 – Sketch the reproductive parts of a flower.
Ans.

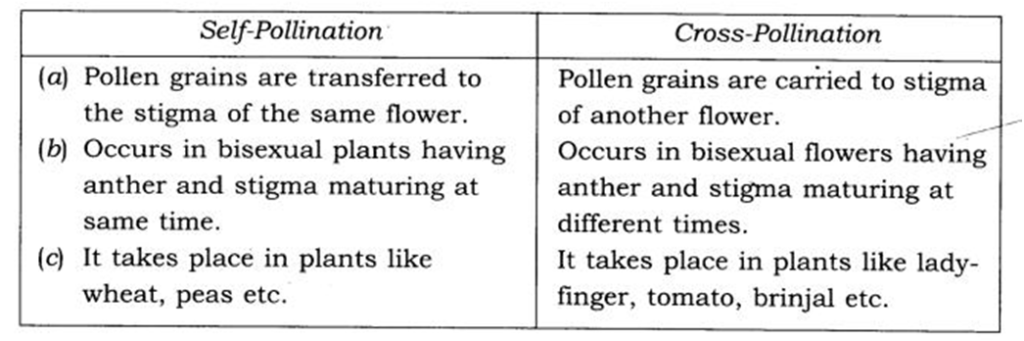
Q 5 – Explain the difference between self-pollination and cross-pollination
Ans.
Q 6 – How does the process of fertilization take place in flowers?
Ans. When the pollen grain reaches the stigma of a same species flower, it starts growing out into the pollen tube of the stigma. This tube continues to grow inside the style till it reaches the ovule. Male cells are released into the ovule for the fertilization with the female egg cell and thus the zygote is formed. After this process of fertilization, the ovary develops into fruit and ovule into seeds.
Q 7 – Describe the various ways by which seeds are dispersed.
Ans;. Following are the ways in which the seeds are dispersed:
(i) Some light seeds like that of madar, which are hairy, dry and small are carried away by the wind to different places.
(ii) Spiny seeds and fruits like that of xanthium and urena, stick to the clothes of passers by and animals. These seeds are carried away by these agents to different places.
(iii) In some plants having heavy seeds like that of coconut, water acts as the dispersing agents.
(iv) Some seeds are dispersed with the fruit burst like in case of balsam and castor.
Q 8 – Match items in Column I with those in Column II

Ans.

Q 9 – Fungus, moss and fern reproduces by a common method of asexual reproduction. Name the method.
Ans. Spore formation.
Q 10 – Boojho had the following parts of a rose plant-a leaf, roots, a branch, a flower, a bud and pollen grains. Which of them can be used to grow a new rose plant?
Ans. A branch.
Q 11 – What is zygote?
Ans. Zygote is a diploid cell formed from the fusion of male and male and female gametes.
Q 12 – By which method of asexual reproduction sweet potato reproduces?
Ans. Vegetative propagation.
Q 13 – n the vegetative propagation, the new plants are exact copies of the parent cell. Why?
Ans. Because they are produced from a single parent.
Q 14 – What are produced by plants as a result of sexual reproduction?
Ans. Seeds.
Q 15 – Which type of reproduction produces a new plant which is exact copy of the parent plant?
Ans. Vegetative propagation.
Q 16 – What is a bud?
Ans. A small bulb-like projection coming out from the yeast cell is called a bud.
Q 17 – Which part of the seed germinate into a small seedling?
Ans. Embryo.
Q 18 – How does a moss plant reproduce?
Ans. By means of spores.
Q 19 – Which type of bodies are spores?
Ans. Asexual reproductive bodies.
Q 20 – What type of flowers does Petunia have?
Ans. Bisexual flowers.
Q 21 – Where is the egg-formed?
Ans. In an ovule
Q 22 – What is sexual reproduction?
Ans. Reproduction in which both male and female gametes are involved is called sexual reproduction.
Q 23 – What produces male gamete?
Ans. Pollen grain produces male gamete.
Q 24 – What protects pollen grains from drying up?
Ans. A tough protective coat prevents them from drying up.
Q 25 – What are bisexual flowers?
Ans. The flowers that contain both stamens and pistil are bisexual flowers.
Q 26 – What are unisexual flowers?
Ans. The flowers which contain either only the pistil or only the stamens are called unisexual flowers.
Q 27 – Pollen grain can be carried away by wind or water. Why?
Ans. They are light.
Q 28 – Name two fruits which are fleshy and juicy.
Ans. Mango and apple
Q 29 – Name two hard fruits.
Ans. Almonds and walnuts
Q 30 – Name the agents of seed dispersal
Ans. Wind, water, animals and human beings.
Q 31 – How are seeds dispersed in the case of castor and balsam?
Ans. When the fruits of castor and balsam burst with sudden jerks, the seeds are dispersed.
Q 32 – Name two plants in which seeds are dispersed by animals
Ans. Xanthium and Urena.
Q 33 – How many types of reproduction are there in plants? Explain.
Ans. There are two types of reproduction in plants:
- Sexual reproduction
- Asexual reproduction
(i) Sexual reproduction; The mode of reproduction in which new plants are produced from seeds by involvement of both male and female gametes.
(ii) Asexual reproductions: In this mode of reproduction, new plants are produced without seeds by involvement of single parent.
Q 34 – Explain vegetative propagation.
Ans. It is a type of asexual reproduction i n which new plants are obtained from vegetative parts like roots, stems, leaves or buds of the parent plants. For example, sweet potato and Dahlia give rise to new plants by roots, roses by stems, etc.
Q 35 – How do cacti plants reproduce?
Ans. Cacti plants produce new plants from any part which get detached from the main plant body. Each detached part grow into a new plant. This is a type of asexual reproduction
Q 36 – Some plants reproduce by cutting. Explain.
Or
How does new plant produce by cutting?
Or
How does rose plants reproduce?
Ans. Cutting is a process through which many plants are propagated through asexual reproduction. For example, rose plant is propagated through this process. A part of stem from the desired plant is cut. The cutting of the plant is buried in the soil. The cutting is watered every day. After some time the leaves and roots arise from the nodes of the cutting. With time the cutting develops into a new plant.
Q 37 – What is budding? Explain with an example.
Ans. The process of formation of an additional outgrowth, as bud, which gets detached from the parent cell to produce new individual is called budding. For example, the yeast grows asexually by process of budding. The small bulb like projection coming out from the yeast cell is called bud. It gradually grows and gets detached from the parent cell and forms a new yeast cell. Sometimes, another bud arises from the bud forming a chain of buds.
Q 38 – What is fragmentation? Give an example.
Ans. Fragmentation is one of the types of asexual reproduction. In this type, plants like Spirogyra, breaks up into two or more fragments or pieces. Each fragment develops into a new individual. When water and nutrients are available algae grow and multiply rapidly by fragmentation.
Q 39 – Explain reproduction through spore formation.
Ans. Reproduction through spore formation is a type of asexual reproduction. Spores are small spherical bodies covered with a protective coat. The coat protects the spore from unfavourable conditions. The coat burst and spore germinate into new plants when the conditions are favourable. The fungi on a bread piece grow from spore which are present in the air. Plants such as moss and fern also reproduce by means of spores
Q 40 – Define two types of flowers with examples.
Ans. Flowers are the reproductive parts of a plant. There are two types of flowers-
- unisexual and
- bisexual flowers.
The flowers which contain either only the pistil or only the stamens are called unisexual flowers, e.g., corn and papaya. On the other hand, the flowers which contain both stamens and pistil are called bisexual flowers, e.g., mustard and rose.
Q 41 – What is pollination?
Ans. The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of a flower is called pollination. Pollen grains are light so they can be carried by wind or water. Insects visit flowers and carry away pollen on their bodies. These are the agents which help in pollination.
Q 42 – What are the post fertilisation changes in a flower?
Ans. After fertilisation, the ovary grows into a fruit and other parts of the flower fall off. The ripened ovary is called fruit. The seeds develop from the ovules. The seed contains an embryo, which is formed from zygote due to fusion of male and female gametes. The embryo develops into future plant on getting favourable conditions.
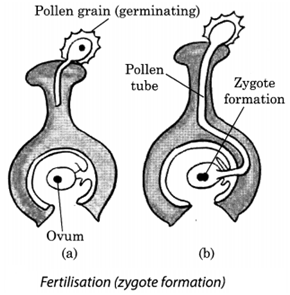
Q 43 – Explain zygote formation or fertilisation with the help of a diagram.
Ans. n sexual reproduction, a male and female gamete fuse to form a zygote. This process of fusion of gametes to form a zygote is called fertilisation (Fig. 12.16). The zygote develops into an embryo.
Q 44 – What are the advantages of vegetative propagation?
Ans. Plants produced by vegetative propagation take less time to grow and bear flowers and fruits earlier than those produced from seeds. The new plants are exact copies of the parent plant, as they are produced from a single parent.
Q 45 – Which is more advantageous for plants-self-pollination or cross-pollination? Give reasons for your answer.
Ans. Cross-pollination is more advantageous as it help the plant in having variation in offsprings, new varieties are formed, make plant to adapt to new changes in environmental conditions and diseases. It helps the plant to yield better.
Q 46 – What is brinjal, a vegetable or a fruit? Explain.
Ans. Brinjal is actually fruit of the plant which we take or consume as vegetable. Brinjal develops from the fertilised ovary of the flower and contains many seeds.
Q 47 – Write how the following seeds are dispersed.
(a) Seeds with wings
(b) Small and light seeds.
(c) Seeds with spines/hooks
Answer:
(a) Dispersed by wind
(b) Dispersed by wind
(c) Dispersed by animals
Q 48 – How plants are benefitted by seed dispersal?
Ans. Seed dispersal prevents compietition between the plant and its own seedlings for sunlight, water and minerals. It also enables plant to invade new habitats for wider distribution. Thus, seed dispersal provides suitable conditions for survival and growth of the plant.