Q 1 – Draw in your notebook the symbols to represent the following components of electrical circuits: connecting wires, switch in the ‘OFF’ position, bulb, cell, switch in the ‘ON’ position and battery.
Ans.

Q 2 – The bulb in the circuit shown in fig. 14.13 does not glow. Can you identify the problem? Make necessary changes in the circuit to make the bulb glow.‘
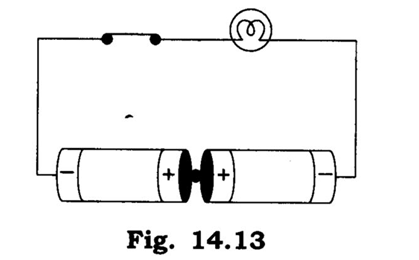
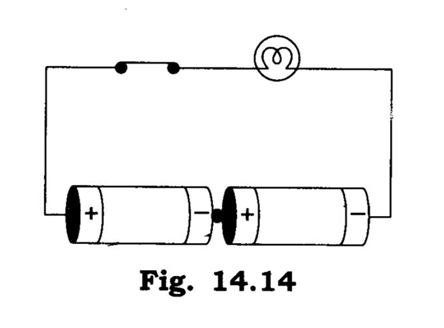
Ans. Problem in this circuit is the combination of two cells. In the circuit positive terminal of one cell should be connected with negative terminal of other to make the bulb glow
Q 3 – Name any two effects of electric current.
Ans. Electric current has the following effect :
(i) Electric current can give rise to heating and lighting.
(ii) Electric current can convert a straight conductor into a temporary magnet.
Q 4 – When the current is switched on through a wire, a compass needle kept nearby gets deflected from its north-south position. Explain.
Ans. When current is passed through the wire, it deflects the compass near it from its north-south position like a magnet. This is called magnetic effect of the current. As we know that needle of the compass is made up of a thin magnet. When this needle comes in contact with another magnet then the like poles of the magnet repel each other and opposite poles attract each other. So the deflection is seen in the needle. In this case the wire behaves like a magnet and causes deflection in needle of the compass.
Q 5 – Will the compass needle show deflection when the switch in the circuit shown by fig. 14.15 is closed?
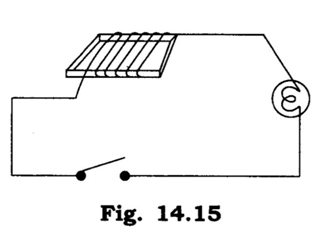
Ans. No, because there is no source of electric current in this circuit, i.e., there is no battery.
Q 6 – Do you think an electromagnet can be used for separating plastic bags from a garbage heap?
Ans. No, the plastic bags do not get attracted by the magnet, so they cannot be separated by an electromagnet. Plastic bags are not magnetic materials, only magnetic materials like iron can be attracted by the magnet.
Q 7 – An electrician is carrying out some repairs in your house. He wants to replace a fuse by a piece of wire. Would you agree? Give reasons for your response.
Ans. No, we would not agree to allow to replace the fuse by a wire. Wires in the fuses are of specific melting points. So wd should always use ISI marked fuses in our houses to prevent short circuits.
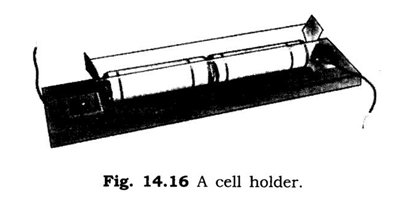
Q 8 – Zubeda made an electric circuit using a cell holder shown in fig. 14.16, a switch and a bulb. When she put the switch in the ‘ON’ position, the bulb did not glow. Help Zubeda in identifying the possible defects in the circuit
.
Ans. It is important to put the cells in right series. The positive terminal of the first cell should be connected with negative terminal of the second cell. The switch should be closed properly and bulb should not be fused. If Zubeda will check these then the bulb will certainly glow.
Q 9 – In the circuit shown in fig. 14.17.
Ans.
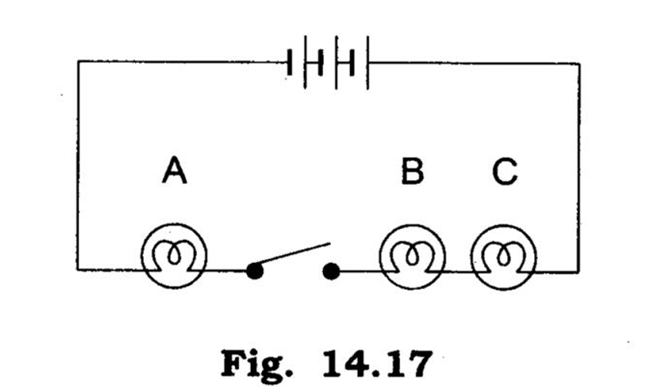
Q 10 – Would any of the bulb glow when the switch is in the ‘OFF’ position?
What will be the order in which the bulbs A, B and C will glow when the switch is moved to the ‘ON’ position?
Ans. No bulb will glow.
All bulbs will glow simultaneously.
Q 11 – What is a battery?
Ans. When two or more cells are joined together, it is called a battery.
Q 12 – Name the effects of electric current.
Ans.
- Heating effect
- Magnetic effect
- Chemical effect
Q 13 – What is a circuit diagram?
Ans. It is a symbolic representation of an electric circuit.
Q 14 – Which property of a conducting wire is utilised in making electric fuse?
Ans. Low melting point of the wire.
Q 15 – What happens if the filament of the bulb is broken?
Ans. The circuit would be incomplete and the bulb does not glow even if the switch is in the ‘ON’ position.
Q 16 – What is the use of a cell holder?
Ans. A cell holder is used to make battery of two or more cells.
Q 17 – How are the cells placed in the cell holder?
Ans. The cells are placed in the cell holder such that the positive terminal of one cell is connected to the negative terminal of the next cell.
Q 18 – Give two examples of the heating effect of current.
Ans.
(i) Electric kettle
(ii) Hair dryers
Q 19 – Why should we buy electric appliances with the ISI mark?
Ans. The ISI mark ensures that the appliance is safe and wastage of energy is minimum. So we should buy only electric appliances with the ISI mark.
Q 20 – Name the device used to protect damages to the circuit due to excessive flow of current
Ans. Electrical fuse or MCB.
Q 21 – What happens if by accident the current exceeds the safe limit?
Ans. The wires may become overheated and may cause fire.
Q 22 – What is a fuse?
Ans. A fuse is a safety device which prevents damages to electrical circuits and possible fires.
Q 23 – Who was the first person to notice the deflection of compass needle every time the current was passed through the wire?
Ans. Hans Christian Oersted.
Q 24 – What do the doctors use to take out small pieces of magnetic material accidently fallen in the eye?
Ans. Doctors use tiny electromagnets for this purpose.
Q 25 – Give one reason for short circuit.
Ans. Direct touching of wires with each other.
Q 26 – Why is an electric fuse required in all electrical appliances?
Ans. It is required to check excessive flow of electric current and save electrical appliances from further damage.
Q 27 – Why is it advisable not to touch a lighted electric bulb connected to the mains.
Ans. Lighted electric bulb connected to the mains may be very hot and can burn our hand badly.
Q 28 – Define a battery. Explain the arrangement of cells in a battery.
Ans. A battery is a combination of two or more cells in which cells are placed such that the positive terminal of one cell is connected to the negative terminal of the next cell. Many devices like torches, transistors, toys, TV remote controls, etc., use batteries. The cells are sometimes placed one after the other and sometimes side by side.
Q 29 – When does the current flow throughout the circuit? Explain.
Ans. When the switch is in the ‘ON’ position, and the positive terminal of the battery is connected to the negative terminal of the battery through wires then the circuit is said to be closed and the electric current flows throughout the circuit.
Q 30 – How many types of circuit are there? Describe.
Ans. There are two types of circuit
- closed circuit and
- open circuit.
(i) Closed-circuit: When the switch is in the ‘ON’ position and the circuit from the positive terminal of the battery to the negative terminal is complete then the circuit is said to be closed and the current flows throughout the circuit. Also the bulb glows in the closed circuit.
(ii) Open circuit: When the switch is in the ‘OFF’ position or the filament of the bulb is broken, the circuit is incomplete and it is said to be an open circuit. No current flows through any part of the circuit.
Q 31 – Why are wires of different materials and different lengths and thicknesses used?
Ans. The amount of heat produced in a wire depends on its material, length and thickness. Thus for different requirements, the wires of different lengths and thickness and materials are used.
Q 32 – What type of wire is used for making electric fuses?
Ans. Wires made of some special materials that melt quickly and break when large electric currents are passed through them are used for making electric fuses. For example, alloy of lead and tin.
Q 33 – What is an electromagnet?
Ans. A coil that behaves like a magnet when electric current is passed through it and loses its magnetism when the supply of electricity is broken is called an electromagnet. It is a temporary magnet made by coiling wire around an iron core; when current flows in the coil the iron behaves as a magnet. Electromagnets can be made very strong and can lift heavy loads.
Q 34 – Explain the working of an electric bell with diagram.
Ans. t consists of a coil of wire wound on an iron piece. The coil acts as an electromagnet. An iron strip with a hammer at one end is kept close to the electromagnet. There is a contact screw near the iron strip.
Q 35 – When does an electric short circuit occur? What harm can it do?
Ans. When the plastic covering of both live wire and neutral wire removes due to wear and tear, these two wires come in contact with each other. Since, the resistance of neutral wire is very low, excessive current flow through the wire in a short time which heats the wire to a great extent. This can result in fires. Another reason of short circuiting is connection of many devices to a single socket. This can also lead to excessive flow of current
Q 36 – What do you mean by overloading of an electric circuit? State two measures to avoid overloading.
Ans. The current flowing in domestic wiring at a particular time depends on the power ratings of the appliances which are being used. When a number of appliances are switched on at the same time, they take out an extremely large amount of current. This is called ‘overloading the circuit’. Now due to an extremely large amount of current flowing through them, the copper wires of household get heated to a very high degree and a fire may be started.
Two measures to avoid overloading are following:
- Too many appliances should not be connected to a single socket.
- Many electrical appliances of high power rating should not be run at the same time
Q 37 – Explain construction of a simple electromagnet with a labelled diagram.
Ans. An electromagnet act on the principle of magnetic effect of the current. The coil of wire wound around an iron bar behaves like a magnet when electric current flows through it. When electric current is switched off, the coil generally loses its magnetism
To construct an electromagnet, take a big iron nail or a big iron screw. Take a long piece of insulated copper wire and wind quite a few turns around the nail. Connect the ends of the wire to the terminals of a battery through a switch as shown in Fig. 14.19.
Place some pins on or near the end of the nail. Now switch on the current. You will observe that pins cling to the nail. Now switch off the current. You will observe that pins no longer get attracted to the nail.
Q 38 – Why do birds do not get shock when they sit on high power live wire but we do?
Ans. As bird sit on only one wire, the circuit remains incomplete so they do not get shock.
Q 39 – Why are compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs) preferred over electric bulbs?
Ans. CFLs do not waste electricity as heat and thus consumes less energy whereas electric bulb along with light also give out heat
Q 40 – Why are MCB preferred over electric fuses?
Ans. Due to following reasons MCB are preferred over electric fuses:
- MCB is more sensitive to overcurrent than fuse.
- Restoration of electric supply is quick. Restoration can be done by just switching the operating knob to its ‘ON’ position
- Handling MCB is electrically more safe than fuse.
Q 41 – Can we use same fuse in a geyser and a television set or any other electrical appliances? Explain.
Ans. No, different electrical appliances need different amount of current. A geyser generally takes more voltage of current in comparison to a television. Therefore the fuse in these will be of different ratings.
Q 42 – Why we must cover plug pin holes which are within the reach of children with cellotape or a plastic cover when not in use?
Ans. Children are usually not aware of electrocution and they can put their fingers or other conducting material into the plug pin holes. To protect them from electric shock we must cover plug pin holes with cellotape or plastic cover.