Q 1 – Suggest one traditional way of storing water from ancient time.
Ans. In ancient times, people used to make Bawris to store water.
Q 2 – What is the source of water in each of the following?
(a) Wells
(b) Ground
(c) Atmosphere
Ans. (a) The source of water in wells is groundwater.
(b) The source of water on ground is rain.
(c) The source of water in atmosphere is evaporation.
Q 3 – The earth Tooks blue from space. Explain why?
Ans. The major surface area (71%) of the earth is covered with water. This imparts blue colour to the earth.
Q 4 – Some slogans has been given for the conservation of water. What does the slogan ‘Jal hai to kal hai’ means?
Ans. This means if you have water, you can think of future, i.e. no life is possible without water.
Q 5 – Reservoir of dam helps us to manage water. How?
Ans. The reservoir of dam or river can release water at our will. We can divert the flow of water at desired places where it is really needed and we can manage water resource effectively.
Q 6 – The excessive use of water leads to a severe problem. Write the problem.
Ans. The excessive use of water leads to water scarcity in an area.
Q 7 – How much of the earth’s surface is covered with water?
Ans. About two-third of the earth’s surface is covered with water.
Q 8 – Mention the year which is celebrated as international year of freshwater?
Ans. The year 2003 was celebrated as International year of freshwater.
Q 9 – State the consequences, if plants do not get enough water.
Ans. The plants will wilt and ultimately dry up in lack of water.
Q 10 – Mention the source of groundwater.
Ans. Rainwater and water from the other sources like rivers, ponds, etc are the source of groundwater.
Q 11 – From where do the workers get water for construction?
Ans. Workers get water from the underground water.
Q 12 – Can we keep on drawing water from under the ground? How will it affect the water table?
Ans. No, we cannot keep on drawing water.
It causes the depletion of water table.
Q 13 – State the percentage of actual amount of water available for human use.
Ans. The actual amount of water available for human use is very little, i.e. approx 0.0006 % of all water found on the earth.
Q 14 – If wells dug to get groundwater, then it dry up after sometime, what initiative should be taken to get water from it again?
Ans. In the above condition, the groundwater get recharged through the process of infiltration. It replenishes the groundwater.
Q 15 – Water circulates through the water cycle in the three forms. Name them.
Ans. Water circulates through the water cycle in the three forms, i.e. solid, liquid and gas.
Q 16 – As our population increases, we need more water for drinking, washing and other purposes. Does this affect the water table? Explain.
Ans. Yes, rising population leads to an increase in consumption and at the same time, a decrease in the seepage of water into the . ground leads to the depletion of water table.
Q 17 – The substance Wis necessary for the normal growth and development of all types of plants and animals. An acute scarcity of substance Whas an ill effect on plants which can hinder the natural process Xin plants causing a severe shortage of /leading to famine. It may also lead the shortage of Zwhich is essential for breathing and respiration. What could W, X, Yand Zbe?
Ans. W- Water, X- Photosynthesis
Y-Food, Z-Oxygen
Q 18 – Explain how the traditional use of groundwater is different from the present use.
Ans. Traditionally in ancient times, people made bawris to collect rainwater in the old buildings. We still use these structures and are reviving them to harness rainwater.
Q 19 – Planting trees help groundwater conservation. Explain how.
Ans. Plants lose water in the form of water vapour by the process of transpiration. So, forests contribute a lot of water vapours formation which make clouds.
Thus, plants help to revive water cycle.
Q 20 – List the reasons for lowering of water table in cities.
Ans. Water drawn from underground water gets replenished by seepage of rainwater. The water table does not get affected as long as we draw the same amount of water as is replenished by natural resources like rain.
However, there are number of factors which cause depletion of water table at a very fast rate which is really a matter of concern for everyone of us. Increase in population, industrial and agricultural activities are some common factors affecting water table. Scanty rainfall, deforestation and decrease in the effective area for seepage of water may also deplete the water table.
Q 21 – Place the following statements in a proper order to form a meaningful paragraph.
(a) Which in turn decreases the seepage of rainwater into the ground.
(b) This decreases the open areas like parks and playgrounds.
(c) Increasing population create demand for construction of houses, shops, offices, roads and pavements.
(d) This results in depletion of water table and creates scarcity of more water.
Ans. Increasing population create demand for construction of houses, shops, offices, roads and pavements (c). This decreases the open areas like parks and playgrounds (b) which inturn decreases the seepage of rainwater into the ground (a). This results in depletion of water table and creates scarcity of more water (d).
Q 22 – Given below are three states of water in a beaker. These states are inter-convertible. Name the process forward and backforth labelled A, B, C, D, which cause these conversions.
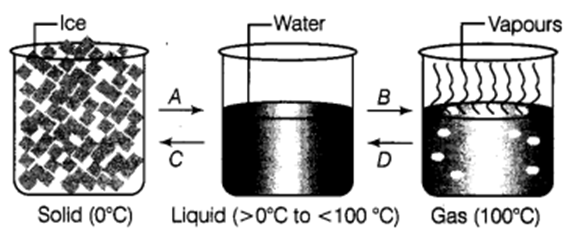
Ans.
A-Melting, 6-Boiling, C- Freezing,
D- Condensation
Q 23 – The water bearing layer of the earth called P is made up of two components O and R, in which R water collect under the ground. The top level of layer Pis called S. When too many tubewells are used in an area, the level of S in that area goes down. What are P, Q, R and S?
Ans.
P- Aquifer, Q- Soil, R- Permeable rocks,
S -Water table
Q 24 – How can you observe the three forms of water (a) in nature and (b) at home?
Ans.
The three forms of water
- in nature are snow (solid), water (liquid) and water vapour (gas).
- at home are ice (solid), water (liquid) and steam (gas).
Q 25 – Name some industries familiar to you. Make a list of the products obtained from these and used in our daily life. Discuss how the growing industrial activity is responsible for depletion of water table?
Ans. Following industries and their products pollute the water:
- Leather industries, e.g. shoes and other products.
- Chemical factories, e.g. fertilisers, different insect repellant sprays, etc.
- Petrochemical industries, e.g. petroleum and different fuels.
- Oil industries.
All the above industries release pollutants such as asbestos, lead, mercury, nitrates, sulphur, etc in different rivers, lakes and ponds which are polluting the water and hence is responsible for depletion of water table.
Q 26 – Mention three causes of water scarcity in our country.
Ans. The three causes of water scarcity in our country are
- Rapid urbanisation.
- Increased number of industries.
- Population explosion.
Q 27 – Certain pattern of the rainfall in our country leads to scarcity of water. Explain that pattern. Which part of the country gets rainfall twice a year?
Ans. We face shortage of water mainly because water is not evenly distributed by the nature on the earth. Some places such as North East India get so much rains, so that it gets flooded almost every year. On the other hand, Thar desert in Rajasthan may get rains rarely in the monsoon season. This uneven pattern of rains causes water scarcity in India at some places.
Q 28 – A number of problems can be faced due to shortage of water. List some of them.
Ans. The number of problems that can be faced due to shortage of water are as follows
- Less amount of pure drinking water will be available.
- Lack of equal distribution of water.
- Drought.
Q 29 – Some definitions are given which can be corrected by changing one word. Correct them.
(a) Aquifer is groundwater stored between layers of hard rock above the water table.
(b) The process of evaporation of water in the ground is called infiltration.
(c) The evaporation of water from oceans and its arrival back into oceans is called vapour cycle.
Ans.
(a) Aquifer is groundwater stored between layers of hard rock below the water table.
(b) The process of seeping of water in the ground is called infiltration.
(c) The evaporation of water from oceans and its arrival back into oceans is called water cycle.
Q 30 – Deforestation can be considered as a reason for depletion of the water table. Comment.
Ans. Large scale deforestation has occurred to accommodate the growing population, to grow food for them and to provide space for industries. Vegetation slows down the flow of rainwater on land and increases the absorption of water by the soil.
Cutting down of trees and destroying vegetation, therefore interferes with the natural process by which seeping takes place and the groundwater is recharged.
It finally results in the depletion of the water table
Q 31 – Give the main causes of water scarcity in our country.
Ans. The main causes of water scarcity in our country are
- Rapid urbanisation.
- Increased number of industries.
- Population explosion.
Q 32 – Shishir returned from school and found his mother busy in the kitchen. He noticed that she is making his favourite dosa. Shishir rushed to his mother as he was feeling hungry and found that the tap in the kitchen was leaking. He told his mother to replace it as leaking taps lead to the wastage of water. His mother smiled and ensured him to do the same.
(a) What is water management?
(b) Why should we save water?
(c) What values are shown by Shishir?
Ans. (a) Minimum wastage of water is called water management.
(b) We should save water to prevent water crisis.
(c) Shishir is sincere, responsible and has capability of applying knowledge practically.
Q 33 – All the rain that falls over an area is not utilised. Do you agree? Explain.
Ans. Precipitation (rain) is a natural process and is a part of natural water cycle. It replenishes all the natural resources of water like ponds, lakes, river and finally oceans and seas too.
When we say utilisation of rainwater, we mean that rain in a particular area.
Yes, it is not properly utilised as most of the water is run off as surface water to the rivers and goes to oceans.
We can harness/harvest this water to local waterbodies like ponds, lakes and groundwater by proper planning as it is being done in some districts of Rajasthan successfully.