Q 1 – What is reproduction?
Ans. Reproduction is the biological process by which new individual organisms are produced from their parents
Q 2 – What is sexual reproduction?
Ans. Reproduction which involves the fusion of male and female gametes is known as sexual reproduction.
Q 3 – What is fertilisation?
Ans. The fusion of ova and sperm is called fertilization.
Q 4 – What is asexual reproduction?
Ans. The mode of reproduction in which only a single parent is involved.
Q 5 – Which mode of reproduction does take place in human beings?
Ans. Sexual reproduction
Q 6 – How many partners are involved in sexual reproduction?
Ans. Two (Parents)
Q 7 – Name two animals in which asexual reproduction takes place.
Ans. Hydra and yeast
Q 8 – Name the reproductive organs of males.
Ans. A pair of testes, two sperm ducts, and a penis.
Q 9 – Name the reproductive organs of female.
Ans. A pair of ovaries, oviducts, and uterus.
Q 10 – Name the modes of reproduction.
Ans.
- Sexual reproduction
- Asexual reproduction.
Q 11 – What is male gamete or sperm?
Ans. The reproductive cell produced by male reproductive organs is called male gamete or sperm.
Q 12 – What is female gamete or ova?
Ans. The reproductive cell produced by female reproductive organs is called the female gamete or ova.
Q 13 – Which organ produces eggs or ovum?
Ans. A pair of ovary.
Q 14 – Explain two modes of reproduction with examples.
Ans. There are two modes of reproduction:
- Sexual reproduction: This type of reproduction takes place by fusion of male and female gametes; e.g., Human beings, mammals like cow, buffalo, etc.
- Asexual reproduction: This mode of reproduction involves only a single parent; e.g., Hydra, Amoeba, yeast, etc.
Q 15 – Explain the process of fertilization in brief.
Ans. Fusion of the male and female gamete, i.e., sperm and egg are called fertilization. During fertilization, the nuclei of the sperm and the egg fuse to form a single nucleus resulting in the formation of a fertilized egg or zygote.
Q 16 – What is internal fertilisation? Explain briefly.
Ans. Fertilization which takes place inside the female body is called internal fertilization. In this, a smaller number of ova or eggs are produced. Offsprings have a high chance of survival. It occurs mostly in mam¬mals; e.g., in human beings, cows, buffalo, etc.
Q 16 – In which organ fertilization takes place in female?
Ans. Fallopian tube
Q 18 – How is an embryo developed?
Ans. Fertilization results in the formation of a zygote. The zygote divides repeatedly to give rise to a ball of cells which then begin to form groups that develop into different tissues and organs of the body. This developing structure is called an embryo. It gets embedded in the wall of the uterus for further development.
Q 19 – Explain what is foetus.
Ans. The embryo continues to develop in the uterus. It gradually develops different body parts such as hands, legs, head, eyes, etc. The stage of the embryo in which all the body parts can be identified is called a fetus. After its development is complete, the mother gives birth to the baby.
Q 20 – What are viviparous and oviparous animals?
Ans. The animals which give birth to young ones are called viviparous animals and those which lay eggs are called oviparous animals. For example, Mammals including human beings are viviparous animals, and hens, lizards, all birds, etc., are oviparous animals.
Q 21 – What are sperm and ovum? Explain.
Ans. The male gamete is called sperm. It is produced by the male reproductive organ, the testes. Structurally, it consists of a head attached to a long tail. The tail helps the sperm to move around. The head bears a small nucleus.
Ovum is the female gamete. They are also called eggs. They are produced by the female reproductive organ. They consist of larger nuclei. Both sperm and ovum are reproductive cells and contain single cells.
Q 22 – Explain briefly the life cycle of a frog.
Ans. There are mainly three distinct stages in the life cycle of a frog, i.e., egg → tadpole (larva) → adult. Tadpoles look different from the adults. After some time tadpoles are converted into adult frogs.
Q 23 – What do you mean by reproduction? Describe various modes of reproduction.
Ans. Reproduction is an important process that is responsible for the continuity of life on the planet earth. In this process, an individual produces young ones of the same species. It helps in increasing the population of the same species on the earth, generation after generation. This is the fundamental feature that ensures the existence of all life forms on the earth. There are two modes of reproduction:
- Sexual reproduction: In this type of reproduction, both male and female parents are involved and they produce different gametes called male gametes or sperms and female gametes or ova (egg) respectively. Both fuse to form zygote which finally develops into foetus. For example, mammals including human beings higher invertebrates and all vertebrates undergo sexual reproduction.
- Asexual reproduction: In this type of reproduction, only single parent is involved and gametes or sex cells are not produced. Budding, binary fission, etc., are different methods of asexual reproduc¬tion. Lower organisms like Hydra, Amoeba, yeast, etc., undergo asexual reproduction.
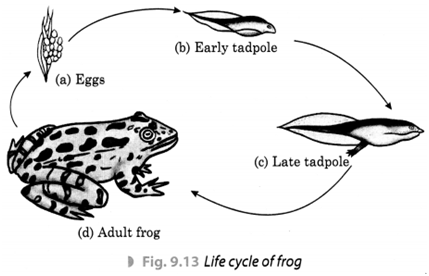
Q 24 – What do you mean by metamorphosis? How does metamorphosis take place in frogs? Explain with a diagram.
Ans. The transformation of the larva into an adult through drastic (sudden or abrupt) changes is called metamorphosis. For example, a moth emerging out of the cocoon, an adult frog from a tadpole, etc., undergo metamorphosis.
The frog undergoes three stages during its life cycle in which eggs laid down by frogs transform into tadpoles (larva) and finally into an adult following the process of metamorphosis. The following diagram clearly shows this process.
Q 25 – What is cloning? Explain how the first cloned mammal was born.
Ans. Cloning is the production of an exact or a true copy of a cell, any other living part, or a complete organism by asexual reproduction. Cloning of an animal was successfully performed for the first time by Ian Wilmut and his colleagues at the Roslin Institute in Edinburgh, Scotland. They cloned the sheep named Dolly on July 5, 1996.

In the process of cloning Dolly, a cell was collected from the mammary gland of a female Finn Dorsett sheep [Fig. 9.17(a)]. Meanwhile, an egg was obtained from a Scottish blackface ewe [Fig. 9.17(b)]. The nucleus was removed from the egg. Then, the nucleus of the mammary gland cell from the Finn Dorsett sheep was inserted into the egg of the Scottish blackface ewe whose nucleus had been removed. This egg was implanted into the Scottish blackface ewe. The egg developed normally and finally, Dolly was born. Cloning of Dolly was a successful attempt. However, many clones often die soon after birth. Sometimes cloning also leads to certain abnormalities among clones. Unfortunately, Dolly died on 14th February 2003 due to certain lung disease.
Q 26 – What is a fertilised egg called?
Ans. Zygote
Q 26 – Name the male gamete.
Ans. Sperm
Q 27 – What are the two methods of asexual reproduction?
Ans.
- Budding
- Binary fission
Q 28 – Name two animals that undergo internal fertilization.
Ans. Human being and cow
Q 29 – What type of reproduction is cloning?
Ans. Asexual reproduction
Q 30 – What is IVF technique of reproduction?
Ans. It is fertilization outside the body.
Q 31 – How are test-tube babies born?
Ans. Test tube babies are born through the IVF technique.
Q 32 – Explain the short life cycle of the silkworm.
Ans. The life cycle of the silkworm is completed in four stages.
Egg → Larva or Caterpillar→ Pupa → Adult
In silkworms, the caterpillar or pupa looks very different from the adult moth.
Q 33 – Describe the male reproductive organs with the help of a labelled diagram.
Ans. The male reproductive organs mainly consist of a pair of testes, two sperm ducts (vas deferens), and a penis. Male gametes called sperms are produced by the testes. Though the sperms are very small in size, each has a head, a middle piece, and a tail. It is unicelled with all the usual cell components. Figure 9.14 shows the male reproductive organs in humans.
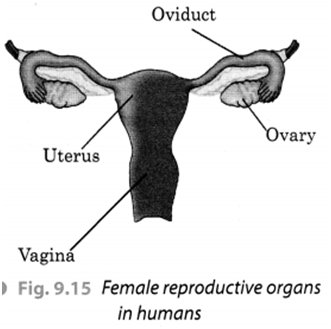
Q 34 – Describe female reproductive organs with the help of a labeled diagram.
Ans. The female reproductive organs mainly consist of a pair of ovaries, oviducts or fallopian tubes, uterus, and vagina. The female gametes called ova or eggs are produced by the ovary. In human beings, a single matured egg is released into the oviduct by one of the ovaries every month. The uterus is the part inside which the embryo grows and develops finally into a baby. An egg or ovum is a single cell. The vagina is the part that receives the penis during copulation. The following diagram shows these organs clearly.
Q 35 – Explain with a diagram the development of an embryo.
Ans. An embryo is developed in the process of fertilization. Fertilization results in the formation of zygote which begins to develop into an embryo

The zygote divides repeatedly to give rise to a ball of cell (Refer Fig. 9.7(b)) which further begin to form groups that develop into different tissues and organs of the body. This developing structure is called an embryo. The embryo gets embedded in the wall of the uterus for further development [Refer Fig. 9.7(c)]. The embryo continues to develop in the uterus. It gradually develops different body parts. This developing stage of embryo is called foetu (Fig. 9.16).