Q 1. Why fingers appear blurred when we move our hand very fast in front of our eyes?
Ans. This is due to persistence of vision l/16th of a second.
Q 2. Why too little or too much light is bad for our eyes?
Ans. Too little or too much light is bad for eyes. Insufficient light causes eyestrain and headaches. Too much light, like that of the sun, a owerful lamp or a laser torch can injure the retina
Q 3. A book lying on a table in a room can be seen from all the parts of theroom. Give reason?
Ans. A book lying on a table in a room can be seen from all the parts of the room because the light is reflected by the book and it reaches our eye at any part of the room.
Q 4. Name the phenomenon shown in the figure.
Ans. Lateral inversion.
Q 5. What makes things visible?
Ans. When light reaches our eyes after striking an object, we are able to see an object.
Q 6. Which element is used at the back of plane mirror?
Ans. Silver
Q 7. The distance between the object and its image formed by a plane mirror appears to be 18 cm. What is the distance between mirror and the object?
Ans. 9 cm
Q 8. How is hypermetropia corrected?
Ans. It is corrected by using convex lens.
Q 9. How is myopia corrected?
Ans. It is corrected by using concave lens.
Q 10. A ray of light is incident on a mirror at an angle of 40°. What is the angle of reflect?
Ans. 40°
Q 11. Name a device which works on the principle of multiple reflection.
Ans. Periscope
Q 12. Can we see an object in the dark?
Ans. No
Q 13. What is the nature of the image formed by the plane mirror?
Ans. Virtual and erect
Q 14. Where is the image formed in a plane mirror?
Ans. Behind the mirror
Q 15. What is yellow spot?
Ans. It is highly light sensitive spot for seeing things with highest clearness.
Q 16. What do we call the image that cannot be obtained on a screen?
Ans. Virtual
Q 17. Name the scientist who studied that if a white light is passed through a prism, it splits into different colours.
Ans. Sir Issac Newton
Q 18. Name the liquid found between the cornea and lens.
Ans. Aqueous humour
Q 19. What is a mirror?
Ans. A piece of glass with a shiny metal-covered at back, that reflects light, producing an image of the object in front of it is known as mirror.
Q 20. How do we see various objects?
Ans. We see various objects due to reflection. As we know all surface reflect light, when light falls on any object, it reflects the light. The reflected light reaches our eyes and we are able to see the object.
Q 21. What is irregular reflection?
Ans. Irregular reflection is defined as the reflection of light from an uneven surface. In irregular reflection, the reflected beam is not parallel.
Q 22. List the characteristics of an image formed in a plane mirror.
Ans. he characteristics of an image formed in a plane mirror are:
- It is virtual.
- It is erect.
- It is of same size as the object.
Q 23. What is the far point and near point of the human eye with normal vision?
Ans. In optics, the farthest and closest point at which an object can be brought into focus by the eye are called far point and near point of the eye respectively. The far point of the human eye with normal vision is infinity. The near point of the human eye with normal vision is 25 cm.
Q 24. Differentiate between rod and cone cells.
Ans. Rods are the rod-shaped cells present in the retina of an eye which are sensitive to dim light whereas cones are the cone-shaped cells present in the retina of the eye which are sensitive to bright light.
Q 25. Explain the phenomenon of dispersion of light.
Ans. Dispersion is defined as the phenomenon of splitting of white light into different colours on passing through a transparent medium such as prism. When white light is passed through a prism, it splits into seven colours. It is observed that the colours are in the following order:
- Violet (V),
- Indigo (I),
- Blue (B),
- Green (G),
- Yellow (Y),
- Orange (O)
- Red (R).
The order of colours can be remembered by the acronym VIBGYOR. This coloured band is called spectrum of white light.
Q 26. Explain some common eye defects in human.
Ans. Some eye diseases are:
- Cataract: A cataract is a clouding of the lens in the eye leading to a decrease in vision. It can affect one or both eyes. Often it develops slowly. Symptoms may include faded colours, blurry vision, halos around light, trouble with bright lights, and trouble seeing at night. This may result in trouble driving, reading, or recognising faces. Cataracts are the cause of half of blindness and 33% of visual impairment worldwide. Cataract is treated by replacing the opaque lens with a new artificial lens.
- Myopia: Near-sightedness or myopia, is the most common refractive error of the eye. Myopia occurs when the eyeball is too long, relative to the focusing power of the cornea and lens of the eye. This causes light rays to focus at a point in front of the retina, rather than directly on its surface. It can be corrected using spectacles made of concave lens.
- Hypermetropia: Hypermetropia or long-sightedness occurs when eyeball is too short or the cornea or crystalline lens does not refract the light enough. This lead to formation of the image of a nearby object behind the retina. A hypermetropic person may have blurred vision when looking at objects close to them, and clearer vision when looking at objects in the distance. By placing a convex (plus powered) lens in front of a hypermetropic eye, the image is moved forward and focuses correctly on the retina.
Q 27. What is power of accommodation?
Ans. The process by which the ciliary muscles change the focal length of an eye lens to focus distant or near objects clearly on the retina is called power of accommodation.
Q 28. While playing, something entered into Somya’s eye. She immediately washed her eye with cold water. But as the irritation persisted, she immediately reported to her class teacher. Her class teacher took her to an eye doctor.
- What should be done if some foreign particles enter your eyes?
- Why is it not advised to rub your eyes when there is an eye irritation due to foreign particles?
- Do you think Somya was right in her action?
- What value of Somya is seen here?
Ans.
- We must do the following things:
- Restrict eye movement
- Shut the eyelid
- Do not rub eyes
- Try to clean it with splash of clear water
- Contact eye doctor immediately.
Foreign object may cause abrasions or scratches on our cornea or rubbing. It may also cause bleeding of cornea.
Yes.
She is intelligent, knowledgeable and aware of such kind of small accidents.
Q 29. Make your own mirror. Take a glass strip or glass slab, clean it and put it on a white sheet of paper. See yourself in the glass. Next put the glass slab on a black sheet of paper. Again look into the glass. In which case do you see yourself better and why?
Ans. We can see ourselves better in the case we put the glass slab on white paper because white sheet reflects more light as compared to black sheet.
Q 30. Write a short note on Braille system.
Ans.
The most popular resource for visually challenged persons is Braille. Braille system was developed by Louis Braille. He himself was a visually challenged person. There is Braille code for common languages, mathematics and scientific notation. Many Indian languages can be read using the Braille system.
- Braille system has 63 dot patterns or characters. Each character represents a letter, a combination of letters, a common word or a grammatical sign. Dots are arranged in cells of two vertical rows of three dots each. Patterns of dots to represent some English letters and some common words are shown in Fig. 16.26.

- These patterns when embossed on Braille sheets help visually challenged persons to recognise words by touching. To make them easier to touch, the dots are raised slightly.
- Visually challenged people learn the Braille system by beginning with letters, then special characters and letter combinations. Methods depend upon recognition by touching. Each character has to be memorised. Braille texts can be produced by hand or by machine. Typewriter-like devices and printing machines have now been developed.
Q 31. Write a note on ‘The Human Eye’.
Ans. Eye ia a sense organ that enables us to see the world around us. It is roughly spherical in shape.

- The first part that is bulged outward is called ‘cornea. It protects the eye.
- Behind the cornea, the coloured part of the eye, iris is present. It controls the size of the pupil.
- Pupil is a small opening in the cornea which allows the light to enter the eye.
- Behind the iris, eye lens is present which is a convex lens. It focus the image on retina, by bending the light rays.
- Retina is the inner back surface of the eye which acts as a screen to form image. It is sensitive to light.
- The sensation of the image formed on the retina is carried to the brain by the optic nerve.
- Optic nerve is connection between the eye and the.
Q 32. Write the ways to protect your eyes.
Ans. Eyes are very delicate organ that enable us to see this colourful world. Thus, we must protect our eyes and take proper care of them.
Following are the ways to protect the eye:
- Always sit straight while reading or writing.
- Never read while walking or lying down.
- Wash your eyes frequently with clean water.
- Never read in the dim or too much bright light.
- Never rub your eyes with hands.
- Never bring the book too close to your eyes.
- Eat foods rich in vitamin A.
Q 33. Boojho planned an activity to observe an object A through pipes as shown in the given figure, so that he could see objects which he could not directly see.‘
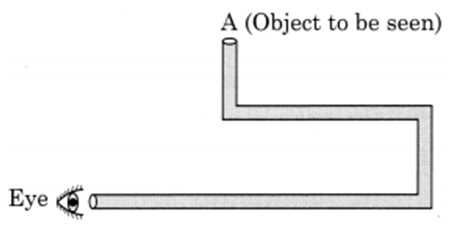
(a) How many mirrors should he use to see the object?
(b) Indicate the positions of the mirrors in the figure.
(c) What must be the angle with respect to the incident light at which he should place the mirrors?
(d) Indicate the direction of rays in the figure.
(e) If any of the mirrors is removed, will he be able to see the object?
Ans.
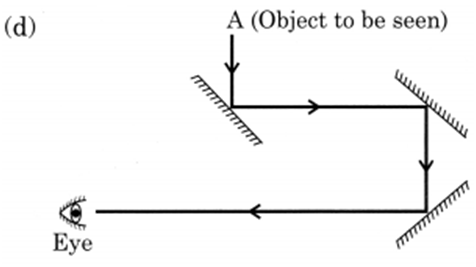
Q 34. What is cataract? How can the vision of a person having cataract be restored?
Ans. Sometimes, particularly in old age, eyesight becomes foggy. It is due to the eye lens becoming cloudy. When it happens, persons are said to have cataract. There is a loss of vision, sometimes extremely severe. It is possible to treat this defect. The opaque lens is removed and a new artificial lens is inserted. Modern technology has made this
procedure simpler and safer.
Q 35. Suppose you are in a dark room. Can you see objects in the room? Can you see objects outside the room? Explain
Ans. If we are in dark room, then it is not possible for us to see the objects in the room. However objects outside the room are visible to us. This is so, because eyes alone cannot see any object. It is only when light from an object enters our eyes that we see the object. The light may have been emitted by the object, or may have been reflected by it.
Q 36. How does eye adjust itself to deal with light of varying intensity?
Ans. The iris controls the amount of light entering into the eye by automatically adjusting the size of the pupil according to the intensity of the light that the eye receives. If the amount of light is high, the iris contracts the pupil and reduces the amount of light entering the eyes. If the amount of light is less, the iris expands the pupil so that more light can enter the eye and the things can be viewed clearly.
Q 37. Explain why, an owl can see well in the night but not during the day whereas an eagle can see well during day but not in the night?
Ans. A night bird (owl) can see very well in the night but not during the day. On the other hand, day light birds (kite, eagle) can see well during the day but not in the night. The Owl has a large cornea and a large pupil to allow more light in its eye. Also, it has on its retina a large number of rods and only a few cones. The day birds on the other hand, have more cones and fewer rods.
Q 38. What are the functions of the following parts of the eye? Iris, Eye-lens, Retina and Optic nerve?
Ans.
- Iris – Iris controls the size of the pupil. The iris is the part of that eye which gives it its distinctive colour.
- Eye-lens – The lens focuses light on the back of the eye, on a layer called retina.
Retina – Retina receives the light focused by the lens. Retina contains several nerve cells. Sensations felt by the nerve cells are then transmitted to the brain. - Optic nerve – The job of the optic nerve is to transfer visual information from the retina to the brain.
Q 39. Explain how you can take care of your eyes.
Ans. It is necessary that we take proper care of our eyes. If there is any problem we should go to an eye specialist. Have a regular checkup.
- If advised, we should use suitable spectacles.
- Too little or too much light is bad for our eyes. Insufficient light causes eyestrain and headaches. Too much light, like that of the sun, a powerful lamp or a laser torch can injure the retina.
- We should not look at the sun or a powerful light directly.
- We should not rub our eyes. If something gets into the eyes, we should splash the eyes
with a lot of clean water. If there is no improvement then we should consult a doctor. - We should wash our eyes frequently with clean water.
- We should always read at the normal distance for vision. We should not read by bringing our book too close to our eyes or keeping it too far.