Q 1. Name the planet nearest to the Sun.
Ans. Mercury
Q 2. What is the speed of light?
Ans. 300000 km per second (3 x 108 m/s).
Q 3. Which is the brightest planet in the night sky?
Ans. Venus
Q 4. Name the star which is nearest to our solar system.
Ans. Alpha centuari
Q 5. Which planets do not have satellite of their own?
Ans. Venus and Mercury
Q 6. How many planets are there in our solar system?
Ans. Eight
Q 7. Which planet is called Red planet?
Ans. Mars
Q 8. Why Earth appears blue from space?
Ans. Due to presence of water Earth appears blue from space.
Q 9. What is the other name of Orion?
Ans. Hunter
Q 10. Which planet is least dense among all?
Ans. Saturn
Q 11. Do stars emit light only during night time?
Ans. No, they emit light all the time.
Q 12. Name the unit which is used to measure astronomical distances?
Ans. Light year
Q 13. What is asteroid?
Ans. Asteroid is a small rocky body orbiting the sun or found between the orbit of Mars or Jupiter.
Q 14. Which is the other name of constellation Great Bear?
Ans. Saptarishi
Q 15. What is Sun?
Ans. Sun is a star.
Q 16. What are meteors?
Ans. Meteors are bright streaks of light in the sky produced by the entry of a small meteoroids into the Earth’s atmosphere. They are also called the ‘shooting stars’.
Q 17. What is a satellite?
Ans. A satellite is defined as a heavenly body that moves around another heavenly body along its own orbit.
Q 18. What is artificial satellite? Give examples.
Ans. Satellites that are made by man are called artificial satellites. Example, INSAT, IRS EDUSAT, etc.
Q 19. What are meteorites?
Ans. The meteors which are so large that they do not evaporate completely before reaching the earth’s surface are called meteorites.
Q 20. What are comets?
Ans. Comets are the members of our solar system. They revolve around the sun in highly elliptical orbit as a bright head with a long tail.
Q 21. Why the Sun is also called as star?
Ans. The Sun is also called as star because it has its own source of energy and it continuously emits light and heat.
Q 22. What is the solar system? Explain.
Ans. The sun along with the eight planets, the moons, and other heavenly bodies form the solar system. Our solar system is a part of the milky way galaxy. The sun is at the centre of the solar system around which all other planets rotate. Except Mercury and Venus, remaining six planets have their natural satellite revolving around them in a particular orbit. In our solar system, Earth is the only planet having life. This is due to the hostile conditions available in it. Sun is the ultimate source of energy for sustenance of life on the Earth.
Q 23. What makes life possible on planet Earth?
Ans. Some special environmental conditions responsible for the existence and continuation of life on the Earth are:
- Right distance from the Sun
- Right temperature range
- Presence of water
- Presence of oxygen and hostile atmosphere
- Presence of a blanket of ozone
Q 24. Write few lines about every planet of the solar system.
Ans. There are total eight planets in our solar system which are as follows:
- Mercury: Mercury is the planet which is nearest to the sun. It is the smallest planet of the solar system. It has no satellite of its own.
- Venus: Venus is the second planet in our solar system. It is the brightest planet in the night sky.
It has no moon or satellite of its own. - Earth: It is the third planet of the solar system and is the only planet on which life exists. It has only one moon.
- Mars: The fourth planet of our solar system is Mars. It is also called the red planet. Mars has two satellites.
- Jupiter: It has large number of satellites and it is the largest planet of our solar system.
- Saturn: Saturn appears yellowish in colour. It contains beautiful rings which are not visible with naked eyes.
- Uranus: It is the seventh planet of our solar system. It is the second outermost planet of solar „ system.
- Neptune: It is the last planet of our solar system.
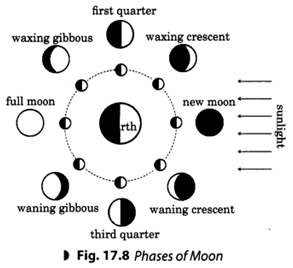
Q 25. Explain why do we see phases of moon.
Ans. The moon does not have its own light. We see the moon because the sunlight falling on it gets reflected toward us. thus, we see only that part of the moon which reflects light keeps on changing daily. This happens because the moon revolves around the earth along with this moon also revolves around the sun. Therefore, we see phases of the moon.
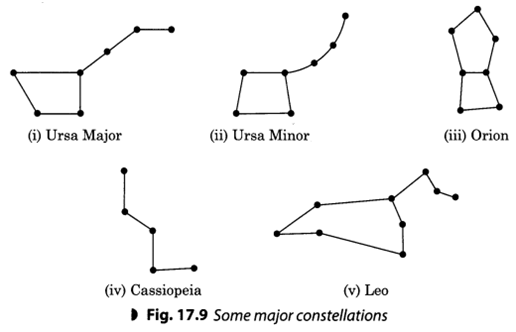
Q 26. What is constellations? Name and explain some major constellations.
Ans. The groups of stars that make an imaginary shape in the night sky are called constellations (nakshatras). They are usually named after mythological characters, people, animals and object they resemble in shape. There are 88 constellations known so far.
Some major constellations are:
- Ursa Major (Great Bear): It is one of the most well known constellations and the third largest one. It looks like a big dipper. It is visible in the northern hemisphere. It has groups of seven relatively bright star.
- Ursa Minor (Little Bear): It is ladle shape similar to Ursa Major. It also consists of seven stars. At the end of the Little Bear’s tail is the pole star. It is the nearest bright star to the north celestial Pole.
- Orion (Hunter): It has seven prominent stars. The three middle stars represent the belt of hunter and four stars form a quadrilateral.
- Cassiopeia: It is a constellation in the northern sky that looks like a distorted letter W or M. It is visible during the winter in the early hours of night.
- Leo: Leo contains several bright stars making it one of the most easily recognisable constellations in the night sky. It is visible in both Northern and Southern hemispheres.
Q 27. A star is ten light years away from the Earth. Suppose it brightens up suddenly today. After how much time shall we see this change?
Ans. We shall see this change after ten years only because this change which occurred today will reach to our eyes through space after ten years only
Q 28. Why meteors are not visible during daytime?
Ans. The brightness of the streak of light formed by meteors are extremely less compared to that of the sun. Thus, meteors are not visible during daytime.
Q 29. If the moon emits light of its own, then would it still have phases?
Ans. The moon does not have its own light. It shines due to the reflected light of the sun. Therefore, phases are formed. If the moon emits its own light then no shadows will be formed and hence as a result no phases will be formed.
Q 30. Why do we always see the same side of moon?
Ans. The period of rotation of the moon on its own axis is equal to the period of its revolution around the earth. So, we always see the same side of moon.
Q 31. If the distance between Earth and Sun becomes half of its present distance, what is likely to happen to life? Justify your answer.
Ans. If the distance between the Earth and the Sun becomes half, then temperature of Earth will increase to alarming levels. Water on the Earth will evaporate leaving it dry. Most of the plants will die. Thus, ultimately ending all the life on the Earth.
Q 32. Most people blame stars and planets in their horoscope for being unsuccessful in their lives. Rohan is one of them. He believes that positioning of Saturn in wrong place in his horoscope is the reason of his bad performance in studies.
- What are the heavenly bodies?
- Do you really think that these heavenly bodies play an important role in our failure or success?
- Have you ever heard these kind of things regarding your failure, success or before doing any auspi-cious work? From whom?
- What value of Rohan is shown here?
Ans.
- A natural celestial object, visible in the sky, such as a star, planet, natural satellite, asteroid, comet, moon or sun is known as heavenly body.
- No.
- Yes, I have often heard these kind of things from my grandparents, parents and priest.
- Rohan is very superstitious, lazy as rather than studying he is blaming planets, orthodox, etc.
Q 33. What are some unique characteristics of Saturn?
Ans. Saturn appears yellowish in colour. It has a well-developed system of rings around it. These rings are not visible with the naked eye. We can observe them with a small telescope. It also has a large number of satellites. One interesting thing about Saturn is that it is the least dense among all the lanets. Its density is less than that of water.
Q 34. Draw a diagram of Cassiopeia constellation to show the position of main stars in it.
Ans.

Q 35. Draw a diagram to show the position of main stars in Leo Major constellation.
Ans.

Q 36. How is the surface of the moon?
Ans. The moon is a fascinating object for poets and story-tellers. But when astronauts landed on the moon, they found that the moon’s surface is dusty and barren. There are many craters of different sizes. It also has a large number of steep and high mountains. Some of these are as high as the highest mountains on the Earth .
Q 37. What factors make life possible on Earth?
Ans. The Earth is the only planet in the solar system on which life is known to exist. Some special environmental conditions are responsible for the existence and continuation of life on the Earth. These include just the right distance from the Sun, so that it has the right temperature range, the presence of water and suitable atmosphere and a blanket of ozone.
Q 38. What is meant by the phases of the Moon? Why phases of the moon occur?
Or
Why does the moon change its shape every day?
Ans. The various shapes of the bright part of the moon as seen during a month are called phases of the moon. The moon does not produce its own light, whereas the Sun and other stars do. We see the moon because the sunlight falling on it gets reflected towards us. We, therefore, see only that part of the moon, from which the light of the Sun is reflected towards us. This is how phases of the moon occur.
Q 39. Why is it difficult to observe the planet Mercury?
Ans. The planet mercury is nearest to the Sun. It is the smallest planet of our solar system. Because Mercury is very close to the Sun, it is very difficult to observe it, as most of the time it is hidden in the glare of the Sun. However, it can be observed just before sunrise or just after sunset, near the horizon. So it is visible only at places where trees or buildings do not obstruct the view of the horizon.
Q 40. Do all the stars in the sky move? Explain.
Ans. No, all the stars in the sky does not move. The earth rotates on its axis from west to east. Therefore, all the stars in the sky seem to move from east to west. The pole star appears to be stationary from the Earth, because it is situated close to the direction of the axis of rotation of the Earth.‘