Q 1 – Which of the following is a secondary activity?
(a) Coal mining industry
(b) Tourism industry
(c) Fishing
(d) Agriculture
Ans. (b) Tourism industry
Q 2 – Which of the following is a private sector industry?
(a) Hindustan Aeronautics Limited
(b) Tata Iron and Steel Industry
(c) Steel Authority of India
(d) National Thermal Power Corporation
Ans. (b) Tata Iron and Steel Industry
Q 3 – Which factors affect the location of industry ?
(a) Land
(b) Labour
(c) Capital
(d) All of these
Ans. (d) All of these
Q 4 – What does an industrial system consists of?
(a) Inputs
(b) Processes
(c) Output
(d) All of these
Ans. (d) All of these
Q 5 – Which metal is often called the backbone of modern industry?
(a) Steel
(b) Gold
(c) Silver
(d) Aluminium
Ans. (a) Steel
Q 6 – Which among the following is the largest lake?
(a) Huran
(b) Superior
(c) Ontario
(d) Michigan
Ans. (b) Superior
Q 7 – ITI is the full form of –
(a) Indian Training Institute
(b) Institute of Technology of India
(c) Indian Telephone Industry
(d) Industrial Technology Institute
Ans. (c) Indian Telephone Industry
Q 8 – Which is not the quality of clothes?
(a) Muslin
(b) Chintzes
(c) Calicos
(d) Osaka
Ans. (d) Osaka
Q 9 – With limited capital, a food processing unit is set up in a particular village in Gujarat. This unit generates employment to that particular village. Name the type of classification of industry under which this food processing unit will come under.
(a) Forest based industry
(b) Agro based industry
(c) Small Scale industry
(d) Large Scale industry
Ans. (c) Small Scale industry
Q 10 – Which of the following can be considered as an example of the economic activity extraction of minerals from the industry sector?
(a) Tourism industry
(b) Iron and Steel industry
(c) Banking industry
(d) Coal mining industry
Ans. (d) Coal mining industry
Q 11 – Joint sector Industries are owned and operated by the state and individuals or a group of individuals. From the given list fo industries, which one can be called a Joint Sector industry?
(a) Iron and Steel industry
(b) Tata Group of Companies
(c) Reliance Industries
(d) Maruti Udyog Limited
Ans. (d) Maruti Udyog Limited
Q 12 – In the light of various factors that influence industrial location, some industries have a tendency to grow close to each other. Name such areas.
(a) Industrial Structures
(b) Industrial Regions
(c) Industrial Systems
(d) Industrial Organisms
Ans. (b) Industrial Regions
Q 13 – To which category of industry (based on raw materials) does Iron made from iron ore belong to?
(a) Marine based
(b) Forest based
(c) Agro based
(d) Mineral based
Ans. (d) Mineral based
Q 14 – Name the classification of industries on the basis of raw material used by them.
Ans.The industries classified on the basis of raw materials used by them are6
- Agro-based industries
- Mineral-based industries
- Marine based industries
- Forest-based industries
Q 15 – Why was Sakchi chosen to set up the steel plant? Give reasons.
Ans. Sakchi was chosen to set up the steel plant for several reasons because:
- the place was only 32 km away from Kalimati station on the Bengal-Nagpur railway line.
- It was close to the iron ore, coal and manganese deposits as well as to Kolkata, which provided a large market.
- TISCO gets coal from Jharia coalfields, and iron ore, limestone, dolomite and manganese from Odisha and Chattisgarh.
- The Kharkai and Subarnarekha rivers ensured sufficient water supply. Government initiatives provided adequate capital for its later development.
Q 16 – How is the steel used by other industries as raw materials?
Ans. Steel is used by other industries as raw material in many ways.
- Steel is tough and it can be easily shaped, cut, or made into wire.
- Special alloys of steel can be made by adding small amount of other metals such as aluminium, nickel and copper.
- Alloys give steel unusual hardness, toughness or ability to resist rust.
- Steel is often called the backbone of modern industry.
Q 17 – How is the classification of industries done on the basis of raw materials size and ownership? Explain.
Ans. Industries are classified on the basis of raw materials, size and ownership:
1. Raw materials: Industries may be agro-based, mineral-based, marine-based and forest-based depending on the type of raw materials used by them.
- Agro-based industries: These industries use plant and animal-based products as their raw materials.
- Mineral-based industries: These industries use mineral ores as their raw materials, and the products of these industries feed other industries.
- Marine based industries: They use the products from the sea and oceans as raw materials.
- Forest-based industries: It utilises forest produce as raw materials.
2. Size: It refers to the amount of capital invested, number of people employed and the volume of production.
Based on size, industries can be classified into small scale and large scale industries.
- Small scale industry: Cottage or household industries are a type of small scale industry where the products are manufactured by hand, by the artisans. These industries use lesser amount of capital and technology as compared to large scale industry.
- Large scale industry: These are industries that produce large volumes of products. Investment of capital is higher and the technology used is superior in large scale industries.
3. Ownership: Industries can be classified into private sector, state-owned or public sector, joint sector and cooperative sector.
- Private-sector industries: These are owned and operated by individuals or a group of individuals.
- Public sector industries: These are owned and operated by the government.
- Joint sector industries: These are owned and operated by the state and individuals or a group of individuals.
- Cooperative sector industries: The are owned and operated by the producers or suppliers of raw materials, workers or both.
Look at the picture given below and answer the following questions:
Q 18 – Picture-1
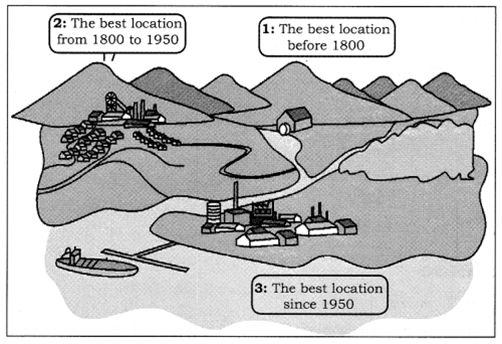
(i) What does the above picture show?
(ii) Where was the iron and steel industry located before 1800 A.D.?
Ans. (i) It shows the changing location of iron and steel industry.
(ii) Before 1800 A.D. iron and steel industry was located where raw materials, power supply and running water were easily available.
Q 19 – Picture-2
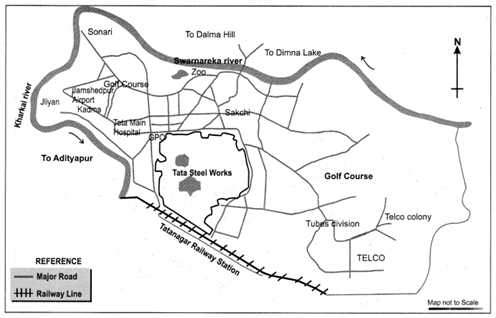
(i) Name the major railway station shown in the figure.
(ii) What does the picture show?
Ans. (i) Tatanagar railway station.
(ii) It shows the location of iron and steel industry in Jamshedpur.
Q 20 – Give two examples of the following in the space provided.
Ans. (i) Raw Materials: cotton and iron
(ii) End product: shirt and car
(iii) Tertiary Activities: banking and transport
(iv) Agro-based Industries: Food processing and leather industries
(v) Cottage Industries: Basket weaving and pottery
(vi) Co-operatives: Anand Milk Union Limited and Sudha Dairy
Q 21 – Discuss the Bhopal disaster.
Or
What was the cause of the Bhopal gas tragedy?
Or
What were the effects of the Bhopal gas tragedy?
Ans. One of the worst industrial disasters of all time occurred in Bhopal on 3 December 1984 around 00:30 a.m. It was a technological accident in which highly poisonous Methyl Isocynate (MIC) gas along with Hydrogen Cyanide and other reaction products leaked out of the pesticide factory of Union Carbide. The official death toll was 3,598 in 1989. Thousands, who survived still suffer from one or many ailments like blindness, impaired immune system, gastrointestinal disorders etc.
Q 22 – Explain the factors favourable for the development of the IT industry in California.
Or
Discuss the locational advantages of Silicon Valley – California.
Ans. Locational advantages of Silicon Valley – California
- Close to some of the most advanced scientific and technological centres in the world.
- Pleasant climate with an attractive and a clean environment. Plenty of space for
development and future expansion. - Located close to major roads and airports.
- Good access to markets and skilled work force
Q 23 – Explain the factors favourable for the development of the IT industry in
Bangalore.
Or
Discuss the locational advantages of ‘Silicon plateau – Bangalore’
Ans. Locational advantages of ‘Silicon plateau – Bangalore’
- Bangalore has the largest number of educational institutions and IT colleges in India.
- The city was considered dust free with low rents and cost of living.
- The state government of Karnataka was the first to announce an IT Policy in 1992.
- The city has the largest and widest availability of skilled managers with work
experience.
Q 24 – What are the similarities between information technology industry in Bangalore
and California?
Ans. Similarities between information technology industry in Bangalore and California
- Presence of high quality educational institutions and advanced scientific and
technological centres. - Availability of skilled work force.
- Good access to markets.
- Pleasant climate with an attractive and a clean environment.
- Well developed and well connected.
Q 25 – Distinguish between agro-based and mineral based industry.
Ans. Difference between agro-based and mineral based industry
| Agro-based industry | Mineral based industry |
| Agro based industries use plant and animal based products as their raw materials. | Mineral based industries are primary industries that use mineral ores as their raw materials. |
| Example: Food processing, vegetable oil, cotton textile, dairy products and leather industries | Example: iron and steel industries. |
Q 26 – Distinguish between public sector and joint sector industry
Ans. Difference between public sector and joint sector industry
| Public sector industry | Joint sector industry |
| The public sector industries are owned and operated by the government. | Joint sector industries are owned and operated by the state and individuals or a group of individuals. |
| Example: Hindustan Aeronautics Limited, and Steel Authority of India Limited | Example: Maruti Udyog Limited |
Q 27 – Explain different aspects of the industrial system with an example.
Or
What consists an Industrial System? Explain with an example.
Or
What are the inputs processes and outputs of the textile industry?
Ans. An industrial system consists of inputs, processes and outputs. The inputs are the raw materials, labour and costs of land, transport, power and other infrastructure. The processes include a wide range of activities that convert the raw material into finished products. The outputs are the end product and the income earned from it. In case of the textile industry the inputs may be cotton, human labour, factory and transport cost. The processes include ginning, spinning, weaving, dyeing and printing. The output is the shirt we wear.
Q 28 – Why was sakchi chosen to set up the steel plant by TISCO?
Ans. Sakchi was chosen to set up the steel plant for several reasons
- This place was only 32 km away from Kalimati station on the Bengal-Nagpur railway
line. - It was close to the iron ore, coal and manganese deposits as well as to Kolkata, which
provided a large market. - TISCO, gets coal from Jharia coalfields, and iron ore, limestone, dolomite and
manganese from Orissa and Chhattisgarh. - The Kharkai and Subarnarekha rivers ensured sufficient water supply.
- Government initiatives provided adequate capital for its later development.
Q 29 – What are the factors responsible for the growth of iron and steel industry in Pittsburgh?
Ans. The steel industry at Pittsburgh enjoys locational advantages.
- Some of the raw material such as coal is available locally, while the iron ore comes from
the iron mines at Minnesota, about 1500 km from Pittsburgh. - Between these mines and Pittsburgh is one of the world’s best routes for shipping ore
cheaply – the famous Great Lakes waterway. - Trains carry the ore from the Great Lakes to the Pittsburgh area.
- The Ohio, the Monogahela and Allegheny rivers provide adequate water supply.
Q 30 – Distinguish between small scale and large scale industries
Ans. Difference between small scale and large scale industries.
| Small scale industries | Large scale industries |
| 1. Most of the work is done by manpower, small machines and tools. | 1. The work is done mostly by larger machines and laborers. |
| 2. These industries employ less capital. | 2. These industries employ more capital. |
| 3. Silk weaving and food processing industries are small scale industries | 3. Production of automobiles and heavy machinery are large scale industries |
Q 31 –. What factors led to the establishment of cotton textile industry in Osaka?
or
Why cotton & textile industry developed in Osaka?
Or
Explain the locational advantages that Osaka has for the development of the cotton textile industry
Ans. The textile industry developed in Osaka due to several geographical factors.
- The extensive plain around Osaka ensured that land was easily available for the growth of cotton mills.
- Warm humid climate is well suited to spinning and weaving.
- The river Yodo provides sufficient water for the mills. Labour is easily available.
- Location of port facilitates import of raw cotton and for exporting textiles
Q 32 – Write the properties and significance of steel.
Ans. Steel is tough and it can easily be shaped, cut, or made into wire. Alloys give steel unusual hardness, toughness, or ability to resist rust.
- Steel is often called the backbone of modern industry. Ships, trains, trucks, and autos are made largely of steel.
- Even the safety pins and the needles we use are made from steel.
Oil wells are drilled with steel machinery. - Steel pipelines transport oil.
- Minerals are mined with steel equipment.
- Farm machines are mostly steel.
- Large buildings have steel framework.
Q 33 – Describe briefly the classification of industries on basis of raw material used.
Or
How are industries classified on the basis of raw material used?
Or
Explain classification of industry on the basis of raw material.
Ans. Industries may be agro based, mineral based, marine based and forest based depending on the type of raw materials they use.
- Agro based industries use plant and animal based products as their raw materials. Example: Food processing, vegetable oil, cotton textile, dairy products and leather industries.
- Mineral based industries are primary industries that use mineral ores as their raw materials. The products of these industries feed other industries. Example: Iron and Steel industry.
- Marine based industries use products from the sea and oceans as raw materials.
Example: Industries processing sea food or manufacturing fish oil. - Forest based industries utilise forest produce as raw materials. Example: pulp and paper, pharmaceuticals and furniture industries
Q 34 – Describe briefly the classification of industries on basis of ownership.
Or
How are industries classified on the basis of ownership?
Or
Explain classification of industry on the basis of ownership.
Ans. Industries can be classified into private sector, state owned or public sector, joint sector and cooperative sector.
- Private sector industries are owned and operated by individuals or a group of individuals.
- The public sector industries are owned and operated by the government, such as Hindustan Aeronautics Limited and Steel Authority of India Limited.
- Joint sector industries are owned and operated by the state and individuals or a group of individuals. Maruti Udyog Limited is an example of joint sector industry.
- Co-operative sector industries are owned and operated by the producers or suppliers of raw materials, workers or both. Anand Milk Union Limited and Sudha Dairy are a success stories of a co-operative venture.
Q 35 – Discuss the locational advantages for the development of the cotton textile industry in Ahmedabad.
Ans. Favourable locational factors were responsible for the development of the textile industry in Ahmedabad.
- Ahmedabad is situated in the heart of a cotton growing area. This ensures easy availability of raw material.
- The humid climate is ideal for spinning and weaving. The flat terrain and easy availability of land is suitable for the establishment of the mills.
- The densely populated states of Gujarat and Maharashtra provide both skilled and semi-skilled labour.
- Well developed road and railway network permits easy transportation of textiles to different parts of the country, thus providing easy access to the market.
- Mumbai port nearby facilitates import of machinery and export of cotton textiles.