Q 1 –When was Human Resource Development Ministry formed in India at central level of Government?
(a) In 1990
(b) In 1985
(c) In 2004
(d) In 2009
Ans. (b) In 1985
Q 2 – The highest density of the population in the world is in
(a) Europe
(b) South America
(c) South central Asia
(d) none of these
Ans. (c) South central Asia
Q 3 – The population of the world is
(a) 77 billions
(b) 7.0 billions
(c) 0.77 billions
(d) 0.077 billions
Ans. (b) 7.0 billions
Q 4 – How have USA and Australia gained in respect of population growth?
(a) By immigration
(b) By tourism
(c) By both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Ans. (a) By immigration
Q 5 – Which country has high population growth rate?
(a) Pakistan
(b) Kenya
(c) India
(d) China
Ans. : (b) Kenya
Q 6 – Human resources differ from one another in respect of
(a) educational level
(b) age
(c) sex
(d) all of these
Ans. (d) all of these
Q 7 – Using resources carefully, judicially & giving them time to get renewed is called _________
(a) Resource Development
(b) Sustainable Conservation
(c) Sustainable Development
(d) Resource Conservation
Ans. (d) Resource Conservation
Q 8 – The number of deaths per 1,000 people refer to
(a) Migration
(b) Birth Rate
(c) Death rate
(d) Population change
Ans. (c) Death rate
Q 9 – Pick out the apt definition for population distribution.
(a) The way in which people live in the villages
(b) The way in which people live in urban areas
(c) The way in which the skilled human resources are utilized in a country
(d) The way in which people are spread across the earth surface
Ans. (d) The way in which people are spread across the earth surface
Q 10 – Land covers only about _________ percent of the total area of the earth’s surface
(a) 20
(b) 25
(c) 30
(d) 35
Ans. (c) 30
Q 11 – Cite an example where religious or cultural activities tend to attract more people
(a) Mumbai
(b) Sahara
(c) Osaka
(d) Jerusalem
Ans. (d) Jerusalem
Q 12 – Which of the following statements are false with respect to thinly populated areas?
(a) Usually the high altitude areas and extremely cold zones are sparsely populated.
(b) Climate here is inhospitable
(c) Very few people live in the equatorial forests.
(d) These regions enjoy an equable climate where there is adequate rainfall.
Ans. (d) These regions enjoy an equable climate where there is adequate rainfall.
Q 13 – A few important statements with respect to the Human Resources are given below. Pick out the one that is not True
(a) The numbers and characteristics of human resources do not change.
(b) Human resource is the ultimate resource
(c) Human resources like other resources are not equally distributed
(d) Human resources differ in educational levels, age and sex
Ans. (a) The numbers and characteristics of human resources do not change.
Q 14 – When was Human Resource Development Ministry formed in India at central level of Government?
(a) In 1990
(b) In 1985
(c) In 2004
(d) In 2009
Ans. (b) In 1985
Q 15 – In India, in how many years once is Census is taken?
(a) 25
(b) 15
(c) 20
(d) 10
Ans. (d) 10
Q 16 – What is meant by population composition?
Ans. Population composition refers to the structure of the population
The composition of population helps us to know how many are males or females, which
age group they belong to, how educated they are and what type of occupations they are
employed in, what their income levels and health conditions are.
Q 17 – Why is population growth slowing in United Kingdom?
Ans. In United Kingdom, population growth is slowing because of both low death and
low birth rates.
Q 18 – Human resources are not equally distributed over the world. Why?
Ans. Human resources like other resources are not equally distributed over the world. They differ in their educational levels, age and sex. Their numbers and characteristics also keep changing
Q 19 – Why some countries like Kenya have high population growth rates?
Ans. Some countries like Kenya have high population growth rates. They had both
high birth rates and death rates. Now, with improving health care, death rates have fallen,
but birth rates still remain high leading to high growth rates.
Q 20 – What is an age-sex pyramid?
Ans. A population pyramid, also called an “age-sex pyramid”, is a graphical
illustration that shows the distribution of various age groups in a population, which forms
the shape of a pyramid when the population is growing
Q 21 – What does the shape of a population pyramid of Japan indicate?
Or
Describe the population pyramid of Japan
Ans. In countries like Japan, low birth rates make the pyramid narrow at the base. Decreased death rates allow numbers of people to reach old age.
Q 22 – What are the factors affecting population change?
Or
What are the main causes of population change explain in brief?
Or
What are the main elements of population change?
Or
What are the main components of population change?
Ans. The major factors affecting population are birth, death and migration. Birth rate is the number of live births per 1,000 people. Death rate is the number of deaths per 1,000 people. Migration is the movement of people in and out of an area.
Q 23 – Why did world population rise from 1800 onwards?
Or
What was the main cause of population explosion?
Or
What has caused the population explosion?
Ans. In 1820, the world’s population reached one billion. A hundred and fifty years later, in the early 1970s, the world’s population reached 3 billion. This is often called population explosion. In 1999, less than 30 years later, the population doubled to 6 billion. The main reason for this growth was that with better food supplies and medicine, deaths were reducing, while the number of births still remained fairly high.
Q 24 – ‘Until the 1800s, the world’s population grew steadily but slowly.’ Why?
Ans. For an extremely long period of human history, until the 1800s, the world’s population grew steadily but slowly. Large numbers of babies were born, but they died early too. This was as there were no proper health facilities. Sufficient food was not available for all the people. Farmers were not able to produce enough to meet the food requirements of all the people. As a result the total increase in population was very low.
Q 25 – Discuss the role of any two factors influencing population change.
Ans. Birth rate and death rate are the natural causes of population change. Birth rate is the number of live births per 1,000 people. Death rate is the number of deaths per 1,000 people. When birth rate is more than death rate, population increases. When birth rate and death rate are same, population stays the same. When death rate is more than birth rate, population decreases. Thus, birth rate and death rate affect the balance of population.
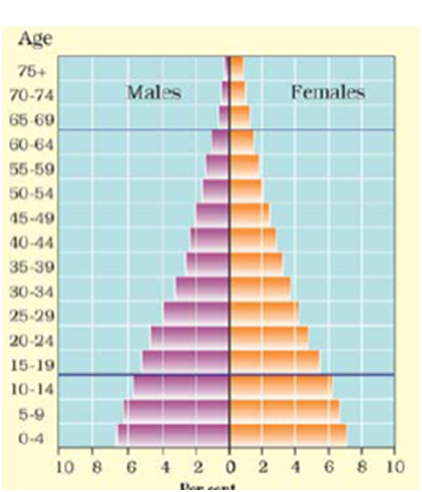
Q 26 – Discuss the population pyramid of Kenya.
Or
Why population pyramid of Kenya is broad at the base and narrow at the top?
Ans. The population pyramid of a country in which birth and death rates both are high is broad at the base and rapidly narrows towards the top. This is because although, many children are born, a large percentage of them die in their infancy, relatively few become adults and there are very few old people. This situation is represented by the pyramid shown for Kenya.

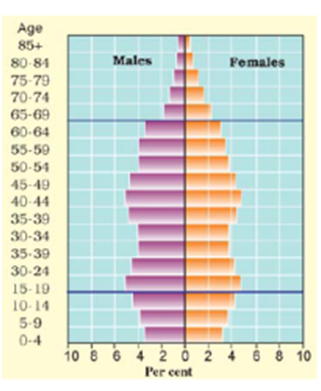
Q 27 – What does the shape of a population pyramid of India indicate?
Or
Describe the population pyramid of India.
Ans. In countries where death rates (especially amongst the very young) are decreasing, the pyramid is broad in the younger age groups, because more infants survive to adulthood. This can be seen in the pyramid for India. Such populations contain a relatively large number of young people and which means a strong and expanding labour force.
Q 28 – What are the causes for the uneven distribution of population in the world?
Ans. The distribution of population in the world is extremely uneven. Some areas are very crowded and some are sparely populated. The causes for the uneven distribution of population in the world are:
- Geographical Factors – Favourable topography and climate, fertile soil, availability of water and deposits of minerals are some of the factors that affect distribution of population.
- Social and cultural factors – Areas of better housing, education and health facilities are more densely populated. Places with religion or cultural significance attract people.
- Economic factors – Industrial areas provide employment opportunities. Large numbers of people are attracted to these areas.
Q 29 – Write a short note on distribution of population.
Ans. Distribution of population
- More than 90 per cent of the world’s population lives in about 10 per cent of the land surface.
- The distribution of population in the world is extremely uneven. Some areas are very crowded and some are sparely populated.
- Very few people live in high latitude areas, tropical deserts, high mountains and areas of equatorial forests. Many more people live north of the Equator than south of the Equator.
- Almost three-quarters of the world’s people live in two continents Asia and Africa.
Q 30 – What are population pyramids? How do they help in understanding about the population of a country?
Ans. Population pyramid is a graphical representation of population composition of a country. The shape of the population pyramid tells the story of the people living in that particular country. The numbers of children (below 15 years) are shown at the bottom and reflect the level of births. The size of the top shows the numbers of aged people (above 65 years) and reflects the number of deaths. The population pyramid also tells us how many dependents there are in a country. There are two groups of dependents — young dependents (aged below 15 years) and elderly dependents (aged over 65 years). Those of the working age are the economically active. The population pyramid of a country in which birth and death rates both are high is broad at the base and rapidly narrows towards the top.