Q 1.Write S.I. unit of resistivity
Ans. Ohm-metre (Ωm)
Q 2.Name a device that helps to maintain a potential difference across a conductor
Ans. Cell or battery
Q 3.If a wire is increased to 4 times its original length, by what factor does the resistivity change?
Ans. Since the resistivity depends only on the material of the wire, and not its length, it will remain the same.
Q 4.Write relation between heat energy produced in a conductor when a potential difference V is applied across its terminals and a current I flows through for ‘t
Ans. Heat produced, H = VIt
Q 5.State difference between the wire used in the element of an electric heater and in a fuse wire.
Ans. The wire used in the element of electric heater has a high resistivity and have a high melting point, i.e. even at a high temperature element do not burn while fuse wire have a low melting point and high resistivity
Q 6.Two resistors of 10 Ω and 15 Ω are connected in series to a battery of 6 V. How can the values of current passing through them be compared?
Ans. In series, same current flows through each resistor. So, ratio of current is 1:1.
Q 7.How much current will an electric bulb draw from 220 V source if the resistance of the bulb is 1200Ω? If in place of bulb, a heater of resistance 100 Ω is connected to the sources, calculate the current drawn by it.

Q 8.Draw a schematic diagram of an electric circuit comprising of 3 cells and an electric bulb, ammeter, plug-key in the ON mode and another with same components but with two bulbs in parallel and a voltmeter across the combination
Ans.

Q 9.Out of the two wires X and Y shown below, which one has greater resistance? Justify your answer.

Ans. Wire ‘Y’ has greater resistance as it has more length than wire ‘X’. It is because resistance of wire is directly proportional to the length of wire.
Q 10.A 9Ω resistance is cut into three equal parts and connected in parallel. Find the equivalent resistance of the combination.

Q 11. (a) What do the following circuit symbols represent?
(b) The potential difference between the terminals of an electric heater is 60 V when it draws a current of 4 A from the source. Find the resistance of heater when in use.

Ans. (a) (i) Wires crossing without touching each other.
(ii) Rheostat/Variable resistor
(b) Given: V = 60 V, I = 4 A, R = ?
From Ohm’s law, V = IR
⇒ 60 = 4 × R
⇒ R = 15 Ω
Q 12.The charge possessed by an electron is 1.6 × 10 coulombs. Find the number of electrons that will flow per second to constitute a current of 1 ampere.

Q 13.Why is an electric bulb filled with argon and nitrogen gas?
Ans. An electric bulb is filled with argon and nitrogen gas because they do not react with the hot tungsten filament and hence, prolong the life of the filament of the electric bulb.
Q 14.Explain the role of fuse in series with any electrical appliance in an electric circuit. Why should a fuse with defined rating for an electric circuit not be replaced by one with a larger rating?
Ans. Fuse wire is a safety device connected in series with the live wire of circuit. It has high resistivity and low melting point. It melts when a sudden urge of large current passes through it and disconnects the entire circuit from the electrical supply. But, in case if we use a larger rating instead of a defined rating, then it will not protect the circuit as high current will easily pass through it and it will not melt.
Q 15.The wattage of a bulb is 24 W when it is connected to a 12 V battery. Calculate its effective wattage if it operates on a 6 V battery (Neglect the change in resistance due to unequal heating of the filament in the two cases).
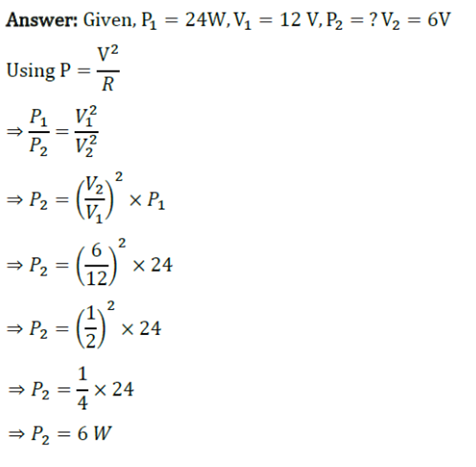
Q 16.In an experiment to study the relation between the potential difference across a resistor and the current through it, a student recorded the following observations:
| Potenital Difference (V) | 1.0 | 2.2 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 6.4 |
| Current (A) | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.6 |
On examine the above observations, the teacher asked the student to reject one set of readings as the values were out of agreement with the rest. Which one of the above sets of readings can be rejected? Calculate the mean value of resistance of the resistor based on the remaining four sets of readings.
Q 17.How is heating effect of electric current used in an electric bulb?
Ans. Electric bulb works on the principle of heating effect of electric current. When electric current passes through a very thin, high resistance tungsten filament of an electric bulb, the filament becomes white hot and emits light.
Q 18.Explain why, the filaments of electric bulbs are made of tungsten.
Ans. The filaments of electric bulbs are made of tungsten because it has a very high resistance. Due to its high resistance, heat produced is high and it becomes white-hot emitting light. Also due to its high melting point (3380° C), it can be kept white hot without melting.
Q 19.A current of 4 A flows through a 12V car headlight bulb for 10 minutes. How much energy transfer occurs during this time?
Ans.
Given : I = 4 A, V = 12 V, t = 10 min = 600 s
Energy transferred = VIt = 12 × 4 × 600 = 28800 J.
Q 20.An electric current of 4.0 A flows through a 12 Ω resistor. What is the rate at which heat energy is produced in the resistor?
Ans. Given: I = 4 A, R = 12 Ω
Rate of production of heat energy, P = I2R = 42 × 12 = 192 W.
Q 21.Calculate the energy transferred by a 5 A current flowing through a resistor of 2 Ω for 30 minutes.
Ans. Here, I = 5 A, R = 2 Ω, t = 30 min = 1800 s
Energy transferred = I2Rt = (5)2 × 2 × 1800 = 9 × 104 J.
Q 22.What is the shape of the graph obtained by plotting potential difference applied across a conductor against the current flowing through it?
Ans. Straight line.
Q 23.Give reason why metals are good conductors, whereas non-metals are bad conductors of electricity.
Ans.
- Metals contain free electrons which help in the conduction of electric charge and hence current
- Resistivity of metals is higher
Q 24.Why are copper and aluminium wires usually employed for electricity transmission?
Ans. Copper and aluminium have low resistivities. When electricity is transmitted through copper and aluminium wires, the power losses in the form of heat are very small.
Q 25.Differentiate between Resistance and Resistivity.
Ans. Resistance:
- It is the opposition provided by the atoms of a conductor to the flow of electrons.
- SI unit of resistance is Ω (Ohm).
- Resistance depends on length, area of cross section, material and temperature of conductor.
Resistivity:
- It is the resistance of the conductor of that substance of unit length and unit area of cross section.
- SI unit of Resistivity of Ωm (Ohm-meter).
- Resistivity of substance depends only on the material of substance.
Q 26.Distinguish between resistances in series and resistances in parallel.
Ans. Resistances in series:
- If a number of resistances are connected in such a way that the same current flows through each resistance, then the arrangement is called resistances in series.
- The current across each resistance is same.
- The equivalent resistance in series combination is greater than the individual resistances.
- This combination decreases the current.in the circuit.
Resistances in parallel:
- If a number of resistances are connected between two common points in such a way that the potential differences across each of them is the same, then the arrangement is called resistances in parallel.
- The voltage across each resistance is same.
- The equivalent resistance in parallel combination is smaller than each of the individual resistances.
- This combination increases the current in the circuit.
Q 27.Nichrome wire is used for making the Ideating elements of electrical appliances like iron, geyser, etc. Give reasons.
Ans.
- Nichrome has a very high resistance due to which it produces a lot of heat on passing current.
- It does not undergo oxidation easily even at high temperature due to which it can be kept red hot.
Q 28.What is an electric circuit? Distinguish between an open and a closed circuit.
Ans. Electric circuit: A continuous and closed path of electric current is called an electric circuit.
Open circuit: A discontinuous circuit through which no current can flow.
Closed circuit: A circuit without interruption, providing a continuous path through which a current can flow.
Q 29.With the help of a diagram, derive the formula for the equivalent resistance of three resistances connected in series.
Ans. (i) If a number of resistances are connected in such a way that the same current flows through each resistance, then the arrangement is called ‘Resistances in Series’.

(ii) Let R1, R2 and R3 be three resistances connected in a series combination and let R be their equivalent resistance.
Let V1, V2 and V3 be the potential difference across the resistances R1, R2 and R3 respectively. Let ‘V’ be the potential differences across the combination. Let ‘I’ be the current flowing through each resistance.
(iii) According to Ohm’s law,
V = IR
Hence, V1 = IR1; V2 = IR2; V3 = IR3
Ans.
(iv) For series combination of resistances,
V = V1 + V2 + V3
IRs = IR1 + IR2 + IR3
IRs = I (R1 + R2 + R3)
Rs = R1 + R2 + R3
Hence, the equivalent resistance in series (Rs) is equal to the sum of the individual resistances.
Q 30.What is the better way of connecting lights and other electrical appliances in domestic wiring? Why?
Ans. The better way of connecting lights and other electrical appliances in domestic wiring is parallel connection because of the following advantages:
- In parallel circuit, if one appliance stops working due to some defect, then all other appliances keep working normally.
- In parallel circuit, each electrical appliance has its own switch due to which it can be turned on or off, without affecting other appliances.
- In parallel circuit, each electrical appliance gets the same voltage (220 V) as that of the power supply line.
- In parallel circuit, the overall resistance of the domestic circuit is reduced due to which the current from the power supply is high.
If, in Figure R1 = 10 ohms, R2 = 40 ohms, R3, = 30 ohms, R4 = 20 ohms, Rg = 60 ohms and a 12 volt battery is connected to the arrangement, calculate: (a) the total resistance and (b) the total current flowing in the circuit.

Ans.
(a) Let R’ be the equivalent resistance of R1 and R2. Then,
R’ = 8Ω
Let R” be the equivalent resistance of R3, R4 and R5. Then,

R” = 10 Ω
Total Resistance, R = R’ + R” = 8 + 10 = 18 Ω
(b) Current,
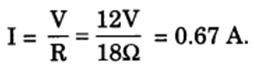
Q 31.Two lamps, one rated 60 W at 220 V and other 40 W a 220 V, are connected in parallel to an electric supply at 220 V.
(a) Draw the circuit diagram to show the connections.
(b) Calculate the current drawn from the electric supply.
(c) Calculate the total energy consumed by the two lamp together when they operate for one hour.
Ans.
(a) The required circuit diagram is shown below:

(b) Total power of the two lamps = 60 + 40 = 100 W
Applied Voltage, V = 220 V
Current drawn from the electric supply,

(c) Total energy consumed by the lamp in one hour = 60W × 1h + 40W × 1h = 100 Wh = 0.1 kWh.
Q 32.Two students perform experiments on series and parallel combinations of two given resistors R1 and R2 and plot the following V-I graphs.

Which of the graphs is (are) correctly labeled in terms of the words ‘Series and parallel’? justify your answer.
Ans.
In case of series combination, the effective resistance = R1 + R2 is more, hence slope of V – I graph will be more. It is otherwise in case of I – V graph. So, series and parallel are correctly marked in graph (ii).
Q 33.You are given three resistors of 10 Ω, 10 Ω, 20 Ω to a battery of emf 2.5 V, a key, an ammeter and a voltmeter. Draw a circuit diagram showing the correct connections of given components such that the voltmeter gives a reading of 2.0 V.
Ans.

Q 34.The electrical resistivity of few material is given below in ohm-metre. Which of these materials can be used for making elements of a heating device.
A 6.84 × 10-8 Ωm
B 1.60 × 10-8 Ωm
C 1.00 × 10-4 Ωm
D 2.50 × 1012 Ωm
E 4.40 × 10-5 Ωm
F 2.30 × 1017 Ωm
Ans. A material having highest value of resistivity is used for making element of heating devices; therefore, material C will be used. D and F are insulators since they have very high values of resistivity.
Q 35.Two electric bulbs A and B are marked 220 V, 60 W and 220 V, 100 W respectively. Which one of the two has greater resistance?
Ans. The resistance of a bulb is given by the expression R = V2/P. For the voltage, the bulb having a smaller power has more resistance. Therefore, the 60W, 220 V bulb has a greater resistance.
Q 36.A potential difference V is applied across a conductor of length l and diameter D. How is the resistance R of the conductor affected, when (i) V is halved (ii) l is halved and (iii) D is doubled. Justify your answer in each case.
Ans. The table below gives the variation:

Q 37.The applied potential difference across a given resistor is altered so that the heat produced per second increases by a factor of 16. By what factor the applied potential difference change.
Ans. The heat produced across a resistor is given by R = V2/P. It is proportional to the square of potential. Therefore, if the heat becomes 16 times the voltage must have been increased 4 times.
Q 38.The values of current I flowing in a given resistor for the corresponding values of potential difference V across the resistor are given below:
| I (amperes) | 0.5 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 |
| V (volts) | 1.6 | 3.4 | 6.7 | 10.2 | 13.2 |
Q 39.Plot a graph between V and I and calculate the resistance of the resistor.
Ans. The graph between V and I for the given data is shown below:

Resistance of the resistor,

Q 40.A piece of wire having resistance ‘R’ is cut into four equal parts.
(a) How does the resistance of each part compare with the original resistance?
(b) If the four parts are placed in parallel, how will be the resistance of the combination compare with the resistance of the original wire?
Ans.
(a) As R ∝ l, when the wire is cut into four equal pieces, the resistance of each part is R4
(b) When they are connected in parallel.


Q 41.Two resistance when connected in parallel give resultant value of 2 Ω. When connected in series, the value becomes 9 Ω. Calculate the value of each resistance.
Ans. Let R1 and R2 be the two resistances,
R1 + R2 = 9Ω …….(1)
When connected in parallel

Now (a – b)2 = (a + b)2 – 4ab
(R1 – R2)2 = (R1 + R2)2 – 4 R1R2 = 9 × 9 – 4 × 18
(R1 – R2)2 = 81 – 72 = 9 or R1 – R2 = 3
∴ R1 – R2 = 3 ………(2)
Solving eq. (i) and (ii), we gets
R1 + R2 = 9 or R1 – R2 = 3
2R1 = 12
∴ R1 = 6Ω
Putting the value of R1 in eq. (i), we get
R1 + R2 = 9 or R2 = 9 – R1 = 9 – 6
R2 = 3Ω