Laws of Chemical Combination
Chemical Reactions
- In a chemical reaction, two or more molecules interact to produce new compounds and are called reactants, whereas the newly formed compounds are called products.
- In a chemical reaction, a chemical change must occur, which is generally observed with physical changes like precipitation, heat production, colour change, etc.
Law of conservation of mass
- According to the law of conservation of mass, matter can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. It remains conserved.
- Mass of reactants will be equal to the mass of products.
Law of constant proportions
- A pure chemical compound contains the same elements combined together in a fixed proportion by mass is given by the law of definite proportions.
- For e.g., If we take water from a river or from an ocean, both have oxygen and hydrogen in the same proportion.
The elements are present in chemical compounds in a predetermined mass ratio. The “law of constant proportions” is this. This “law of constant proportions” is also known as the “Proust’s law” or the “law of defined proportions.” For instance, the oxygen and hydrogen content in pure water is always 1:8.
Atoms
An atom is the defining structure of an element, which cannot be broken by any chemical means.
The atomic symbol has three parts:-
- The symbol X: the usual element symbol
- The atomic number A: equal to the number of protons
- The mass number Z: equal to the total number of protons and neutrons in an element.
Atomic Radius
This distance between an atom’s nucleus and outer electron shell. The atomic radius is calculated by measuring the distance between the nuclei of two identical atoms bonded together. Half this distance is the atomic radius.
According to Dalton’s atomic theory, atoms, which are indestructible and indivisible building blocks, make up all substances. Unlike other elements, which have atoms of different sizes and weights, an element’s atoms have all the same size and mass.
Dalton proposed that the concept of atoms could be used to explain the laws of conservation of mass and definite proportions. He proposed that atoms, which he described as “solid, massy, hard, impenetrable, moving particle(s),” are the smallest, indivisible units of matter.
- The matter is made up of indivisible particles known as atoms.
- The properties of all the atoms of a given element are the same, including mass. This can also be stated as all the atoms of an element have identical mass and chemical properties; atoms of different elements have different masses and chemical properties.
- Atoms of different elements combine in fixed ratios to form compounds.
- Atoms are neither created nor destroyed. The formation of new products (compounds) results from the rearrangement of existing atoms (reactants) in a chemical reaction.
- The relative number and kinds of atoms are constant in a given compound.
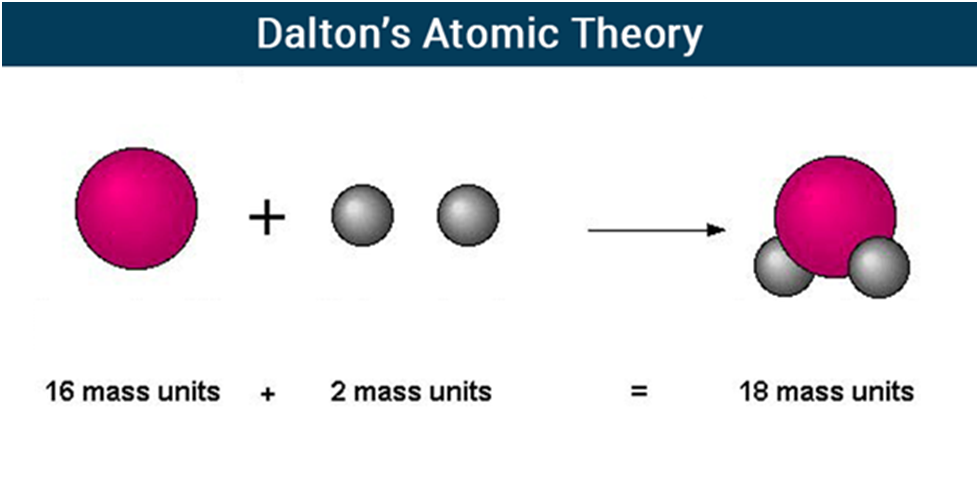
Dalton’s Atomic Theory
Atomic Mass
Atomic mass and atomic mass unit
- Atomic mass is the total of the masses of the electrons, neutrons, and protons in an atom, or in a group of atoms, the average mass.
- Mass of an atomic particle is called the atomic mass.
- This is commonly expressed as per the international agreement in terms of a unified atomic mass unit (AMU).
- It can be best defined as 1/12 of the mass of a carbon-12 atom in its ground state.
Molecular mass
Molecular mass of an element is defined as the sum of the masses of the elements present in the molecule.
- Molecular mass is obtained by multiplying the atomic mass of an element with the number of atoms in the molecule and then adding the masses of all the elements in the molecule.
Molecule
The smallest identifiable unit into which a pure substance may be divided while retaining its composition and chemical properties is a molecule, which is a collection of two or more atoms.
Molecules of elements
A molecule is a collection of two or more chemically bound atoms, whether they are from the same element or another.
For example, when two hydrogen (H2) and one oxygen (O2) atoms interact, one water molecule is created.
Molecules of compounds
Salts and molecular compounds are the two categories into which compounds can be divided. Covalent bonds hold the atoms together in molecular molecules. Ionic bonds hold it together in salts. Every compound is composed of one of these two types of bonds.
Actually, a compound is a kind of molecule. The atoms that join together must be distinct from one another for the substance to qualify as a compound. O2, for instance, is a molecule, not a compound. Due to its atomic connection with another oxygen atom. NaCl, however, is a compound since it is made up of two distinct atoms that are chemically bound together.
Mole Concept
Mole concept & Avogadro Number
- In a substance, the amount of entities present for e.g. atoms, molecules, ions, is defined as a mole. A mole of any substance is 6.022×1023 molecules.
- Mole concept is one of the most convenient ways of expressing the amount of reactants and product in the reaction.
The value of Avogadro’s number is approximately 6.022×1023. The definition of Avogadro’s number is that it tells us the number of particles in 1 mole (or mol) of a substance. These particles could be electrons or molecules or atoms.
Molar Mass
Molar mass
A substance is something which has mass and occupies space. The molar mass/molecular weight is actually the sum of the total mass in grams of the atoms present to make up a molecule per mole. The unit of molar mass is grams/mole.
Atomic Valency
Molecules and Atomicity
A molecule is defined as the smallest unit of a compound that contains the chemical properties of the compound.
- The atomicity of an element is the number of atoms in one molecule of the element.
- For e.g:- Hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, chlorine, iodine, bromine all have two atoms in each of their molecules. So, the atomicity of hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, chlorine, iodine, bromine is two each.
Structure of atom
- Atom is made of three particles; electron, proton and neutron.
- The centre of the atom is called the nucleus. The nucleus of an atom contains the whole mass of an atom.
- Electrons in an atom are arranged in shells/orbitals.
Valency
Valence electrons are those electrons which are present in the outermost orbit of the atom.
- The capacity of an atom to lose, gain or share valence electrons in order to complete its octet determines the valency of the atom.
Writing Chemical Formulae
Compounds
- When two or more elements chemically combine in a fixed ratio by mass, the obtained product is known as a compound.
- Compounds are substances consisting of two or more different types of elements in a fixed ratio of its atoms.
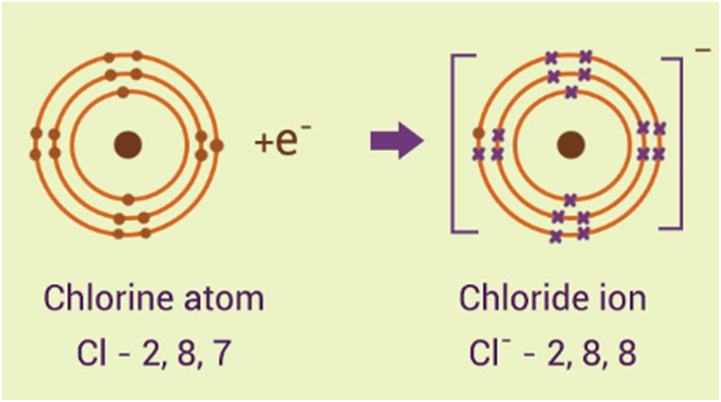
Ions
- An ion is defined as an atom or molecule which has gained or lost one or more of its valence electrons, giving it a net positive or negative charge.
- A negatively charged particle is called an anion, and a positively charged particle is called a cation.
Ionic compounds: chemical formula
Each constituent element in a chemical formula is identified by its chemical symbol, along with the relative number of atoms that make up each element. These ratios are used in empirical equations to start with a key element and then assign atom counts for the remaining elements in the compound in relation to the key element.
- Ionic compounds are chemical compounds in which ions are held together by specialised bonds called ionic bonds.
- An Ionic compound always contains an equal amount of positive and negative charge.
- For example: In Calcium chloride, the ionic bond is formed by oppositely charged calcium and chloride ions.
Calcium atom loses 2 electrons and attains the electronic configuration of the nearest noble gas (Ar). By

doing so, it gains a net charge of +2
The two Chlorine atoms take one electron each, thus gaining a charge of -1 (each) and attain the electronic configuration of the nearest noble gas (Ar).
Law of definite proportion: Proposed by Louis Proust (1799).
A chemical compound always consists of the same elements combined together in
the same ratio by mass, irrespective of the method of preparation or the source
from where it is taken.
Example:
• One molecule of compound water always contains same ratio of Hydrogen and Oxygen by mass.
i.e.
H2O= 2 : 16 = 1 : 8
• Similarly one molecule of carbon dioxide always contains same ratio of carbon and oxygen by mass.
i.e.
Co2 = 12:32 =3:8
Dalton’s Atomic Theory: According to Dalton’s atomic theory, all matter, whether an
element, a compound or a mixture is composed of small particles called atoms. The
postulates of this theory may be stated as follows:
i. All matter is made of very tiny particles called atoms.
ii. Atoms are indivisible particles, which cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical
reaction.
iii. Atoms of a given element are identical in mass and chemical properties.
iv. Atoms of different elements have different masses and chemical properties.
v. Atoms combine in the ratio of small whole numbers to form compounds.
vi. The relative number and kinds of atoms are constant in a given compound.
Drawbacks:
i. Atom is no longer considered as the smallest indivisible particle. Atom has three sub
atomic particles electrons, protons and neutrons.
ii. Atoms of similar element may have different masses and are called isotopes. Eg.
Three isotopes of hydrogen are 11H, 12H and 13H.
iii. Atoms of different element may have same masses and are called isobars. Eg. 18 40Ar
and 2040Ca.
iv. The ratio in which the different atoms combine to form compound may be fixed and
integral but may not be simple
Atoms, Molecules, ions & Chemical Formula:
a. Atom: An atom is the smallest particle of an element which can take part in a chemical reaction. It may or may not exist freely. Each atom of an element shows all the properties of the element.
Atomic Mass
• The mass of one atom is called as atomic mass.
• One atomic mass unit is a mass unit equal to exactly one-twelfth (1/12th) the mass of one atom of carbon-12.
• Relative atomic masses of all elements have been found with respect to an atom of carbon-12.
• Relative atomic masses is defined as the no. of times an element is heavier than one-twelfth (1/12th) the mass of one atom of carbon-12.
• So, Atomic mass of atom is measured in amu. amu is written as ‘u’ unified mass as per latest IUPAC recommendations.
• Scientists initially took 1/16 of the mass of an atom of naturally occurring oxygen as the unit. This was considered relevant due to two reasons:
• Oxygen reacted with a large number of elements and formed compounds.
• This atomic mass unit gave masses of most of the elements as whole numbers.
b. Molecule: A molecule is a group of two or more atoms chemically bonded together.
The smallest particle of matter (element or compound) which can exist in a free state. The
properties of a substance are the properties of its molecules.
• MOLECULES OF ELEMENT (Homoatomic Molecules): The molecules of an
element are constituted by the same type of atoms. Eg. H2, O2, N2, Cl2 etc.
• MOLECULES OF COMPOUND (Heteroatomic Molecules): Atoms of different elements join together in definite proportions to form molecules of compounds. Eg.CO, HCl, Co2, NO2 etc.
• ATOMICITY: The number of atoms contained in a molecule of a substance (element or compound) is called its atomicity.
- Monoatomic molecules: All noble gases He, Ne and Ar etc.
- Diatomic molecules: H2, O2, N2, Cl2, CO, HCl.
- Triatomic molecules: O2, CO2, NO2.
- Polyatomic molecules: S8, p4, NH3
• Molecular Mass
• The molecular mass of a substance is the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms
in a molecule of the substance.
This is also expressed in terms of u.
Example: Molecular Mass of water (H2O) can be calculated as:
Molecular Mass= 1 x 2 + 16 = 18u
Formula Unit Mass:
• Formula unit mass is used for those substances whose constituent particles are ions.
• It is sum of the atomic masses of all atoms in a formula unit of a compound
Example: Formula Unit Mass of sodium chloride (NaCl) can be calculated as:
Formula Unit Mass = 23 + 35.5=58.5 u
Ions: An ion is a charged particle formed by loss or gain of electrons.
• Cation: Ion carrying positive charge is known as cation and is formed by loss of electrons.
Eg. H+ Ca2+, Fe3+ etc.
• Anion: Ion carrying negative charge is known as anion formed by gain of lectrons.
Eg. Cl-, O2-, N3- etc.
• Polyatomic ion: A group of atoms carrying a charge is as polyatomic ion.
Eg. NH4+ → Ammonium Ion; CO32- → Carbonate ion
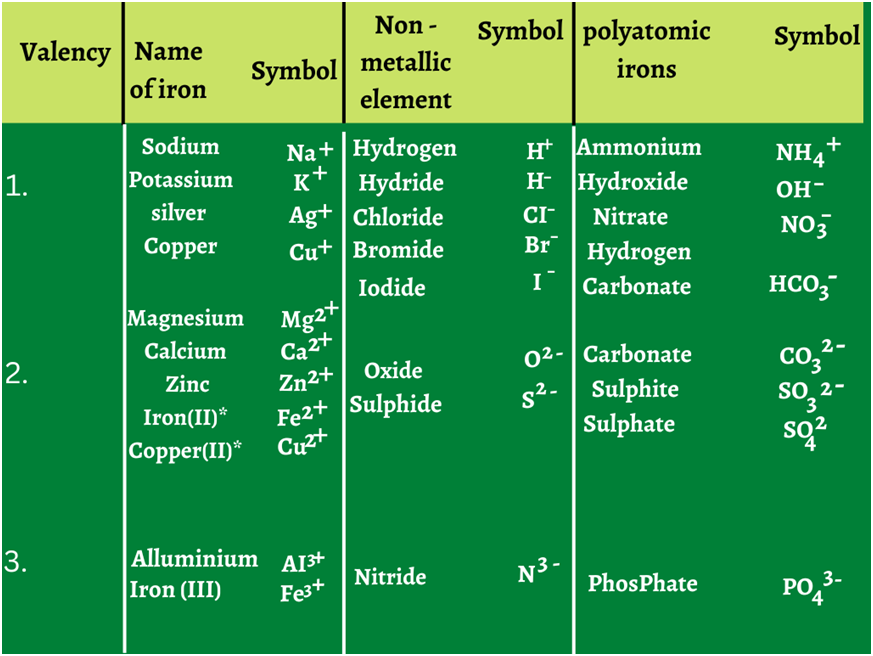
Valency: The number of electrons which an atom can lose, gain or share to form a
bond.
OR
It is the combining capacity of an atom of the element.
Chemical Formula: A chemical formula is a short method of representing
chemical elements and compounds.
The rules that you have to follow while writing a chemical formula are as follows:
• The valencies or charges on the ion must balance.
• When a compound consists of a metal and a non-metal, the name or symbol of the metal is written first. For example: calcium oxide (CaO), sodium chloride (NaCl), iron sulphide (FeS), copper oxide (CuO) etc., where oxygen, chlorine, sulphur are non-metals and are written on the right, whereas calcium, sodium, iron and copper are metals, and are written on the left.
• In compounds formed with polyatomic ions, the ion is enclosed in a bracket before writing the number to indicate the ratio. In case the number of polyatomic ion is one, the bracket is not required. For example, NaOH.
Criss- cross method of formula making: While writing the chemical formulae for compounds, we write the constituent elements and their valencies as shown below.
Then we must crossover the valencies of the combining atoms.
