Q 1 – Define the term Agriculture.
Ans. Agriculture is the science and art of cultivation on the soil, raising crops and rearing livestock. It is also called farming.

Q 2 – What is meant by Horticulture?
Ans. Horticulture is the growing of vegetables, flowers and fruits for commercial use.

Q 3 – Define Viticulture.
Ans. Viticulture means the cultivation of grapes.

Q 4 – Where is the breeding of fish done in the process of Pisciculture?
Ans. Breeding of fish is done in specially constructed tanks and ponds.
Q 5 – Define commercial farming.
Ans. In commercial farming crops are grown and animals are reared for sale in market.
Q 6 – Who has discovered the coffee plant?
Ans. In about AD 850, Kaldi, an Arab goat-herder has discovered the coffee plant.
Q 7 – What type of climate and soil are required by coffee in its growth?
Ans. Coffee requires warm and wet climate and well-drained loamy soil.
Q 8 – What is also known as ‘Golden Fibre’?
Ans. Jute is also known as the ‘Golden Fibre’.

Q 9 – Define Agricultural Development.
Ans. Agricultural development refers to efforts made to increase farm production in order to meet the growing demand of increasing population.
Q 10 – Give some examples of Primary Activities.
Ans. Agriculture, fishing, gathering, etc.
Q 11 – Give some examples of secondary activities.
Ans. Manufacturing of steel, baking of bread and weaving of clothes, etc.
Q 12 – What should be the Meal condition for the growth of jute?
Ans. It requires high temperature, heavy rainfall, and humid climate.
Q 13 – What is Tea?
Ans. Tea is a beverage crop grown on plantations.
Q 14 – What is the quantity of labour required for the purpose of picking the leaves?
Ans. Labour in large quantity is required for the purpose of picking the leaves.
Q 15 – What is the ideal condition for the growth and plantation of Maize?
Ans. Maize requires moderate temperature, rainfall and lot of sunshine.
Q 16 – Which food crop is the stable diet of tropical and subtropical regions?
Ans. Rice.
Q 17 – Which food crop is also known as coarse grains?
Ans. Millets.
Q 18 – What does primitives farming include?
Ans. This includes shifting cultivation and nomadic herding.
Q 19 – Define the term Milpa.
Ans. In Mexico practice of shifting cultivation is known as Milpa.
Q 20 – Where is mixed farming practised?
Ans. Mixed farming is practised in Europe, eastern USA, Argentina, Southeast Australia, New Zealand and South Africa.
Q 21 – What are tertiary activities?
Ans. Tertiary activities are those which provide support to primary and secondary activities.
Q 22 – Where is nomadic herding practised?
Ans. Nomadic herding is practised in semi- arid and arid regions of Sahara, Central Asia and some parts of India.

Q 23 – What is the main feature of plantation agriculture?
Ans. In plantation agriculture only a single crop is grown over a large area.
Q 24 – Why is mixed farming called so?
Ans. In mixed farming the land is used for growing crops as well as rearing livestock
Q 25 – Which two countries lead in the production of jute?
Ans. India and Bangladesh are the leading producers of jute
Q 26 – What is organic farming?
Ans. Organic farming is a type of farming in which organic manure and natural pesticides are used instead of chemicals. No genetic modification is done to increase the yield of the crop.
Q 27 – What weather conditions are required in the growing and harvesting seasons of wheat?
Ans. In the growing season wheat requires moderate temperature and rainfall and in the harvesting season it needs bright sunshine.
Q 28 – How does the Joe Horan grow com with full scientific ways?
Ans .
- Joe Horan, a farmer, grows corn on his field after making sure that soil and water resources meet the needs of this crop.
- Adequate measures are taken to control pests that can damage the crop.
- From time to time he sends the soil samples to soil testing laboratory to check whether the nutrients are sufficient or not.
- The results help Horan to plan a scientific fertiliser programme.
- His computer is linked to the satellite which gives him a precise picture of his field. This helps him to use chemical fertilisers and pesticides wherever they are required.
Q 29 – What is Agricultural Development and what is the ultimate aim of agricultural development?
Ans. Agricultural development refers to efforts made to increase farm production in order to meet the growing demand of increasing population. This can be achieved in many ways such as increasing the cropped area, the number of crops grown, improving irrigation facilities, use of fertilisers and high yielding variety of seeds. Mechanisation of agriculture is also another aspect of agricultural development. The ultimate aim of agricultural development is to increase food security.
Q 30 – How is rice a major food crop in category of crops grown to meet the requirement of the growing population?
Ans.
- Rice is the major food crop of the world.
- It is the staple diet of the tropical and sub-tropical regions.
- Rice needs high temperature, high humidity and rainfall.
- It grows best in alluvial clayey soil, which can retain water.
- China leads in the production of rice followed by India, Japan, Sri Lanka and Egypt.
- In favourable climatic conditions as in West Bengal and Bangladesh two or three crops are grown in a year.
Q 31 – What do the term plantations means and which are the major plantations in the tropical regions of the world?
Ans.
- Plantations are a type of commercial farming where single crop of tea, coffee, sugarcane, cashew, rubber, banana or cotton are grown.
- Large amount of labour and capital are required.
- The produce may be processed on the farm itself or in nearby factories.
- The development of a transport network is thus essential for such farming.
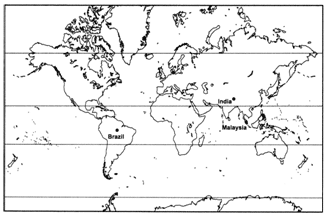
- Major plantations are found in the tropical regions of the world. Rubber in Malaysia, Coffee in Brazil, tea in India and Sri Lanka are some examples.
Q 32 – Name the 3 sectors of activities done by people.
Ans. The work or activities done by the people can be classified into 3 Sectors – Primary, secondary and tertiary
Q 33 – What are the activities under the secondary sector?
Ans. All activities connected with the manufacturing of goods with natural resources can be
classified under Secondary activities. Manufacturing of steel, baking of bread and weaving of cloth are examples of this sector of activities.
Q 34 – How was the word ‘agriculture, coined?
Ans. The word agriculture is the English adaptation of the Latin word ‘agricultura’. ‘Ager’ means field and ‘cultura’ means cultivation; in the strict sense ‘agricultura’ means “tillage of the soil.
Q 35 – What is meant by arable land?
Ans. Geographically, arable land is an agricultural term, meaning land that can be used for growing crops.
Q 36 – What are the different kinds of cultivation?
Ans. Agriculture, Sericulture, Pisciculture, Viticulture and Horticulture are the different kinds of cultivation.
- Agriculture is cultivation on the soil – growing crops and rearing livestock.
- Sericulture is rearing of silk worms to extract silk.
- Pisciculture is breeding of fish in specially constructed tanks and ponds.
- Viticulture is cultivation of grapes.
- Horticulture is growing vegetables, flowers and fruits for commercial use.
Q 37 – How is farming classified?
Ans. Farming can be broadly classified into 2 categories, namely Subsistence Farming and Commercial Farming.
Q 38 – Write a brief note on Intensive subsistence farming.
Ans.
- Subsistence farming is practised to meet the needs of the farmer’s family. Low levels of technology and household labour are used to produce a small output.
- In Intensive subsistence the farmer cultivates a small plot of land using simple tools and more labour.
- More than one crop is grown annually, on the same plot, as the climate is favourable and the soil is fertile. Rice is the main crop; other crops include wheat, maize, pulses and oilseeds.
- Intensive subsistence agriculture is prevalent in the thickly populated areas of the monsoon regions of south, southeast and east Asia.
Q 39 – What is Nomadic herding?
Ans.
- Nomadic herding is practised in the semi-arid and arid (dry) regions of Sahara, Central Asia and some parts of India, like Rajasthan and Jammu and Kashmir.
- In nomadic farming, herdsmen move from place to place with their animals for fodder and water, along a definite route.
- The nomads move from place to place due to the restraints of the climate and land.
- Sheep, camel, yak and goats are most commonly reared by the nomads.
- These animals provide milk, meat, wool, hides and other products to the herders and their families.
- In the drier parts of Asia, especially Southwest Asia, most rural people make a living by raising livestock. Many are nomads who move with their herds of animals over large territories, constantly seeking good supplies of grass and water.
- The people live simply and carry their tents and belongings with them. They rear animals such as goats, sheep, camels, and yaks.
Q 40 – What is the difference between Subsistence farming and Commercial farming?
Ans. An commercial Farming crops are grown and animals are reared for sale in the market, that is, for commercial purposes, while in Subsistence farming crops are grown mainly for the farmer’s family needs.
Q 41 – What are the 3 categories of Commercial farming?
Ans. The three categories of Commercial farming are Commercial Grain Farming; Mixed Farming and Plantation Agriculture.
Q 42 – What is mixed cropping or mixed farming?
Ans. Mixed cropping involves the simultaneous growing of two or more crops intermingled on the same land. Mixed farming is the combining of two independent agricultural enterprises on the same farm. A typical case of mixed farming is the combination of crop enterprise with dairy farming, that is, crop cultivation with livestock farming. Mixed farming may be treated as a special case of diversified farming. This particular combination of enterprises, support each other and add to the farmer’s profitability.
Q 43 – What are the advantages in mixed cropping?
Ans. The advantages in mixed cropping are ……
1. Greater stability of yield over different seasons
2. Better use of growth resources
3. Better control of weeds, pests, and diseases
4. One crop may provide physical support to another one
5. One crop provides shelter to the other crop
6. Erosion control through providing continuous leaf cover over the ground surface.
7. Benefit to small farmers of limited means.
Q 44 – How can one increase agricultural production?
Ans. Agricultural production can be increased by increasing area under cultivation and by increasing the number of crops grown in a year. Agricultural production can be also be increased by improving irrigational facilities and using fertilizers. Use high yielding variety of seeds and machinery in cultivation increase crop yield.
Q 45 – Write a note on Munna Lal and his farm – land.
Ans. Munna Lal’s farmland is fertile and he grows two crops in a year – wheat or rice and pulses. He purchases high yielding varieties of seeds from the market every alternate year. He rents a tractor for ploughing his field and irrigates it from a tube-well near his farm for which he pays a rent. Munna Lal also has two buffaloes and a few hens and he sells the milk in the cooperative store located in the nearby town. All the members of the family help him in various farm activities.
Munna Lal takes the advice of government agricultural officers and officers in the co-operative society regarding farming methods and on the type of fodder for his animals, safety measures to protect the health of the livestock. Sometimes, he takes credit from a bank or the agricultural co-operative society to buy seeds and farm implements. As Munna Lal does not have the facilities to store his crop he sells it in the local mandi at a nominal rate.
Q 46 – Describe the climate conditions required for the proper cultivation of rice. Mention the main regions of its production.
Ans. Rice is a major food crop in tropical and sub-tropical parts of the world. Its cultivation needs high temperature, high humidity and rainfall. Its growth is best in alluvial clayey soils, since they have water retention capacity. China and India are the leading producers in the world. In favourable climatic conditions, even two to three crops are grown in a year.
Q 47 – Describe various types of economic activities. Give examples.
Ans. The three types of economic activities are primary, secondary and tertiary.
• Primary Activities: Those activities which involve direct extraction and production of natural resources are called primary activities. Examples: agriculture, fishing, mining.
• Secondary Activities: Those activities which are concerned with the processing of natural resources are called secondary activities. Examples: manufacturing of finished products.
• Tertiary Activities: Those activities which fall neither in the primary category nor the secondary category are called tertiary activities. They form a support to primary and secondary activities. Examples: selling goods, advertising and banking.
Q 48 – How is Nomadic farming practised? What does the reared animal provide the herders and their family?
Ans. Nomadic herding is practised in the semi-arid and arid regions of Sahara, Central Asia and some parts of India, like Rajasthan and Jammu and Kashmir. In this type of farming, herdsmen move from place to place with their animals for fodder and water, along defined routes.
This type of movement arises in response to climatic constraints and terrain, sheep, camel, yak and goats are most commonly reared. They provide milk, meat, wool hides and other products to the herders and their families.
Q 49 – What do you understand by agricultural development?
Ans. Agricultural development refers to efforts made to increase production in farms so as to meet the ever growing demand of the population. The activities that come under this development are increasing the cropped area, growing more crops, improving irrigation, using fertilisers, sowing HYV (high-yielding variety) of seeds and by promoting mechanisation. Mechanisation ensures that little labour is done by the farmers; instead machines are used to provide efficiency.
Q 50 – Write in brief about intensive subsistence farming.
Ans. Intensive subsistence farming is a type of farming in which the farmer cultivates a small plot of land using simple tools and more labour. Climate with large number of days with sunshine and fertile soils permit growing of more than one crop annually on the same small plot. Rice is the main crop grown by farmers under this method.
Other crops are wheat, maize, pulses and oilseeds. Intensive-farming is prevalent in the thickly populated areas of the monsoon regions of south, southeast and east Asia.
Q 51 – Describe commercial farming and its types in detail.
Ans. Commercial farming is the practice in which crops are grown exclusively for commercial purpose, i.e. for sale in the market. A large area is cultivated and huge capital is involved unlike subsistence farming. Machines are used to a large extent. Commercial grain farming is a class of commercial farming. Crops like wheat and maize are grown for commercial purpose. The temperate grasslands of North America, Europe and Asia are some common areas where it is seen.
Mixed farming is another type of commercial farming. The land is used for growing food and fodder crops and rearing livestock. Some areas where it is followed are Europe, eastern USA, Argentina, south-east Australia, New Zealand and South Africa. Plantations are a type of commercial farming where only a single crop (like tea, coffee, sugarcane, cashew, rubber, banana or cotton) is grown. Large amount of labour and capital are required. The produce is processed in the farm itself or nearby factories.
Q 52 – What are the important beverage crops. What are the climatic conditions required for their growth?
Ans. The important beverage crops are tea and coffee.
• Tea: It is grown on plantations. This requires cool climate and well-distributed high rainfall throughout the year for the growth of its tender leaves. It needs well-drained loamy soils and gentle slopes. It also needs labour in large number to pick up the leaves.
• Coffee: It is also grown on plantations. It requires warm and wet climate and well drained loamy soil. Hill slopes are more suitable for growth of this crop.
Q 53 – Look at the picture given below and answer the following questions:
Picture-I

(i) What is shown in the above figure?
(ii) Which method is used in the picture for the purpose of ploughing?
Ans. (i) Farmers ploughing a field is shown.
(ii) Traditional method is used.
Picture-II

(i) What type of plantation is shown in the above picture?
(ii) Who had discovered these plants?
Ans. (i) Coffee plantation.
(ii) Kaldi, an Arab goat – herder, had discovered the coffee plant.
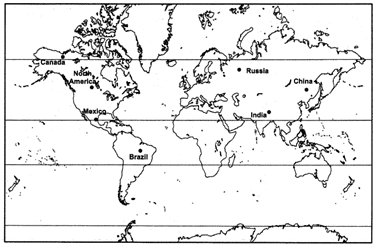
Q 54 – On an outline Map of World mark the following countries where Maize is grown:
(i) North America
(ii) Brazil
(iii) China
(iv) Russia
(v) Canada
(vi) India
(vii) Mexico
Ans.
Q 55 – Mark the countries where cotton is grown suitably on the outline Map of World.
(i) China
(ii) USA
(iii) India
(iv) Pakistan
(v) Brazil
(vi) Egypt
Ans.

Q 56 – Mark the countries on an outline Map of World showing major plantations found in the tropical regions of the world.
(i) Rubber in Malaysia
(ii) Coffee in Brazil
(iii) Tea in India
Ans.