Q 1 – Political parties are allotted symbols by
(a) The government of India
(b) The constitution of India
(c) The party leaders
(d) The Election Commission
Ans- (d) The Election Commission
Q 2 – The number of political parties registered with the Election Commission of India is
(a) 750 parties
(b) more than 750 parties
(c) Less than 750 parties
(d) 705 parties
Ans- (b) more than 750 parties
Q 3 – Fill in the Blanks
1. In some countries, such as _______, members and supporters of a party choose its candidates.
2. A political party is a group of people who come together with a view to promote _______.
3. A government is expected to base its policies on the line taken by the _________.
4. Formally, laws are debated and passed in the ________ .
5. The parties that lose in the elections play the role of ______ to the party in power by criticising its failures.
Ans- 1. The USA
2. collective good
3. ruling party
4. legislature
5. opposition
Q 4 – Match the following:
| Column-A | Column-B |
| 1. Indian National Congress founded in | (а) 1980 |
| 2. Bharatiya Janta Party founded in | (b) 1925 |
| 3. Bahujan Samaj Party formed in | (c) 1999 |
| 4. Communist Party of India founded in | (d) 1984 |
| 5. Nationalist Congress Party formed in | (e) 1885 |
Ans –
| Column-A | Column-B |
| 1. Indian National Congress founded in | (e) 1885 |
| 2. Bharatiya Janta Party founded in | (а) 1980 |
| 3. Bahujan Samaj Party formed in | (d) 1984 |
| 4. Communist Party of India founded in | (b) 1925 |
| 5. Nationalist Congress Party formed in | (c) 1999 |
Q 5 – In USA:
(a) Members and supporters of a party choose its candidates
(b) Top party leaders choose candidates for contesting elections
(c) Supporters of a party choose its candidates
(d) All of the above
Ans- (a) Members and supporters of a party choose its candidates
Q 6 – In 2020, the number of recognised parties in the country were:
(a) Three
(b) Four
(c) Five
(d) Six
Ans- (d) Six
Q 7 – MPs and MLAs have to accept whatever the:
(a) Party leaders decide
(b) Party decides
(c) Government decides
(d) Election Commission decides
Ans- (a) Party leaders decide
Q 8 – The term ‘partisan’ means:
(a) A group of people who come together to promote common beliefs.
(b) Aware of the state or the science of governance.
(c) A person who is strongly committed to a party.
(d) The ruling party which runs the government.
Ans- (c) A person who is strongly committed to a party.
Q 9 – Name any one State/ Regional Party of Telangana.
Ans- Telangana Rashtra Samithi and Telugu Desam Party
Q 10 – Name any one political party that has national level political organization but not recognized as the national party.
Ans- Samajwadi Party, Samta Party and Rashtriya Janata Dal are the examples of the parties that have national level political organizations but are not recognised as national political parties.
Q 11 – Why is one party political system not considered a good democratic system ?
Ans- One-party system is not considered a good option in democratic system because voters are not offered any choice at the time of voting.
Q 12 – Name any two State/ Regional parties of Jammu and Kashmir.
Ans- Main political parties include the Jammu & Kashmir National Conference (NC), the Indian National Congress (Congress), Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) and the Jammu and Kashmir Peoples Democratic Party (PDP).
Q 13 – When was the Communist Party of India (Marxist) founded ?
Ans- 7 November 1964

Q 14 – Define Partisan.
Ans- A person who is strongly committed to a party, group or faction. Partisanship is marked by a tendency to take a side and inability to take a balanced view on an issue.
Q 15 – What is meant by offering the meaningful choice to the voters by political parties?
Ans- Policies are political party are nearly same they have only minor difference this does not give choice to voters. So, political parties should go for different policies as to provide a meaningful choice to voters.
Q 16 – Explain the meaning of defection.
Ans- Changing party allegiance from the party on which a person got elected (to a legislative body) to a different.
Q 17 – What are the facilities offered by the Election Commission to a recognized political party?
Ans- The recognized parties are given a unique symbol — only the official candidates of that party can use that election symbol.
Q 18 – What is meant by state funding of elections?
Ans- The government should give parties money to support their election expenses. This support could be given in kind: petrol, paper, telephone etc. and cash to some extent.
Q 19 – How do state or regional political parties contribute in strengthening federalism and democracy in India? Explain with examples.
Ans- State and regional political parties contribute in strengthening federalism and democracy in India in the following ways.
- They provide a variety of choice to people as each of them has different agendas and focus on different issues.
- They provide a platform for different pressure and social groups, and communities to put forward their demands.
- They help in power sharing by sharing power of government with the help of coalition government.
Q 20 – Differentiate between party system of USA and India.
Ans-
| India | USA |
| There are currently 2 major national parties – the INC and the BJP Although there are hundreds of regional parties in the political arena. | There are two major political parties here. They are the Republican Party and the Democratic Party. |
| Elected head of Government is the Prime Minister. He is the executive head where as the President is the constitutional head of state. Citizens cast their vote directly to elect their representatives to the Lok Sabha. The majority party gets invited by the President to form the government. The leader of that party becomes the Prime Minister. Elections to the Lok Sabha are held every five years generally. | Head of State is the President. Citizens cast their ballot in every state to elect members of the electoral college (popular vote) who in turn cast electoral votes to determine the President. The President holds office for a four-year term. |
| The government can lose the mandate if its majority cannot be proved in the event of a no-confidence motion in the Lok Sabha. This would lead to mid-term elections. Parliamentary form of government. | The President is not dependent on the strength of his party in Congress (legislative body). He remains in power for the four years of his term unless he is impeached or incapacitated. Presidential form of government. |
| The Prime Minister appoints members of his cabinet from his party or from those supporting his coalition (if it’s a coalition government). | President nominates cabinet members and sends them to the Senate for confirmation. The cabinet members need not be Congress members, they could just be industry experts. |
| The Parliament is the supreme legislative body. It is a bicameral legislature comprising of the President, the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha. Lok Sabha (House of the People) members are elected directly by the people. There are 545 members. Rajya Sabha (Council of States) members are elected by the State legislative assemblies. Its total membership is 245. | Congress is the legislature of the USA. The Senate and the House of Representatives are the two chambers of the Congress The House of Representatives (commonly referred to as the House) is the Lower House while the Senate is the Upper House. |
| There is no strict separation of powers. The executive is part of the elected legislature and remains in power while the House is in motion. The Prime Minister cannot override the legislature to make laws. A bill becomes a law only when both Houses pass it and it is signed by the President. The president can send any bill back to the parliament for consideration if he deems fit. But if it’s passed again, he should sign it. Supreme Court can strike down any law that it considers unconstitutional. | Here, there is a clear separation of powers between the executive, the legislature and the judiciary. A law passed by the Congress can be vetoed by the President. He can send it back for consideration, or he can also bypass the Congress and issue an executive order (which has the force of law). However, Congress can override the veto by obtaining a 2/3rd majority in both Houses. |
| India can be said to be a case of cooperative federalism. There is only one constitution for the whole country. India is neither purely federal nor purely unitary. It is a federal structure with a strong unitary bias. | It has a federal system with each state having its own constitution. Here, power is shared between the federal government and state governments. |
Q 21 – The party was founded in 1999 following a split in the congress Party. Identify the party. what is the ideology of this party?
Ans- Nationalist Congress Party (NCP):
- Formed in 1999 following a split in the Congress party.
- Espouses democracy, Gandhian secularism, equity, social justice and federalism.
Wants that high offices in government be confined to natural born citizens of the country.
Q 22 – Which four challenges do you feel are being faced by political parties in India? Give your opinion.
Ans- The three challenges which are being faced by the political parties in India are :
1. Defection and horse-trading : The elected members of a party sometimes try to support other party on account of money or other things and play their role in downfall of government.
2. Lack of Internal Democracy : There is no internal democracy among the political parties in India. The positions in parties and ministries are given on the basis of favor rather than talent and work.
3. Dynastic Succession : The members of a political party from the top to the bottom are succeeded by their young ones. So those who don’t know anything about politics later become our leaders.
Q 23 – Distinguish between a regional and a national party based on the area of their functionality and the criterion of their recognition as state and national party.
Ans-
| National parties | Regional parties |
| National parties are powerful in the nation, it deals with national issues | Regional parties’ power is limited to a specific region or state, only the issues and demands of a specific region are discussed by regional parties. |
| National parties’ actions offer preference to national issues over regional problems | Regional parties’ operations are confined to the country or the state in which they work, concentrating mostly on local issues. |
| A party must gain at least 6 % of the total votes in lok sabha or assembly elections in four states in order to be a national party and win at least four seats in lok sabha. | A party has to receive at least 6 % of the total votes in the legislative election to become a regional party and win at least two seats. |
| Instances of national parties are the BJP, Congress and BSP. | The instances of regional parties are Anta Dal, Manipur People Party, Assam United Decomcractic Front etc |
Q 24 – Suggest any five political reforms to strengthen democracy.
Ans-
Some of the reforms to strengthen the working of political parties are as follows:
(i) Anti-defection law – under which a member would be disqualified if he/she goes against the directions of the party.
(ii) Reduction in the influence of money– Cash votes have been banned by the election commission and anybody involved in the process is likely to be punished.
(iii) It is important for a candidate to file an affidavit giving details of his property and eliminate cases pending against him/her.
(iv) The election commission has made it necessary for political parties to hold their organizational elections and file their income tax returns.
(v) A law is strictly advisable to make or regulate the internal affairs of political parties. It should be made mandatory for political parties to give a minimum number of tickets, about one-third, to women candidates.
Q 25 – Now categorise these photographs by the functions of political parties they illustrate. Find one photograph or news clipping from your own area for each of the functions listed below.
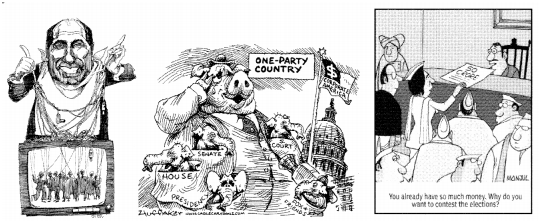
Can you identify which of the challenges described in this section are being highlighted in these cartoons? What are the ways to curb the misuse of money and muscle power in politics?
Ans-
- In democracy all over the world we find disparities between the rich and the poor. The reason is that the gains of economic growth is not evenly distributed among the people.
- A smaller number of ultra-rich enjoy a highly disproportionate share of wealth and incomes. But those at the bottom of the society have very little to depend upon. Their incomes have been declining.
- Sometimes they find it difficult to meet their basic needs of life, such as food, clothing, house, education and health. To get a voice for a better share in a nation the poor need to come together and draw government’s attention towards their problems.
- If needed, they should start protest movements to get coverage in media. The poor countries should get united and raise their voice collectively to draw the attention of the rich and powerful countries towards the problems they are suffering from.
- They should point out how rich countries are accountable to some of their problems and how they exploit natural resources so carelessly. The poor countries should hold meetings and discussions to pressurise the rich countries to stop doing injustices.