Q 1. What are Amphoteric oxides? Give two examples of Amphoteric oxides.
Amphoteric oxides are the oxides, which react with both acids and bases to form salt and water.
E.g. ZnO and Al2O3 .
Q 2. Name two metals, which will displace hydrogen from dilute acids, and two metals which will not.
Very reactive metals like Zn and Mg displace hydrogen from dilute acids. On the other hand less reactive metals like Cu, Ag, etc. do not displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
Q 3. In the electrolytic refining of a metal M, what would you take as the anode, the cathode and the electrolyte?
Anode is impure, thick block of metal M. Cathode is a thin strip/wire of pure metal M. Electrolyte is a suitable salt solution of metal M.
Q 4. State two ways to prevent the rusting of iron.
By coating the surface of iron by rust proof paints.
By applying oil or grease to the surface of iron objects so that supply of air consisting of moisture is cut off form the surface.
Q 5. What types of oxides are formed when non-metals combine with oxygen?
When non-metals combine with oxygen it forms either neutral or acidic oxides. CO is a neutral oxide; N2O5 or N2O3 is an acidic oxide.
Q 6. Differentiate between metals and non-metals on the basis of their chemical properties.
| Metals | Non-Metals |
| 1. They have ionic bonds. | They have covalent bonds |
| 2. They are electropositive. | They are electronegative. |
| 3. They form basic oxides. | They form acidic oxides. |
| 4. They react with dilute acids to form salt and evolve hydrogen gas. | Since they cannot replace hydrogen thus they cannot react with dilute acids. |
Q 7. Explain why the surface of some metals acquires a dull appearance when exposed to air for a long time.
This is due to the surface oxidation of metals when exposed to moist air. For e.g. copper turns green on its surface due to the formation of basic copper carbonate Cu(OH)2 CuCO3 . Similarly silver becomes black due to the formation of black Ag2S and Aluminium forms a white coating of Al2O3 on its surface.
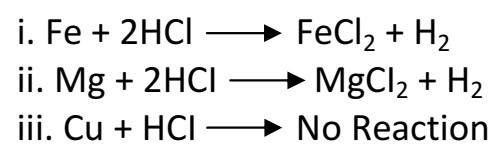
Q 8. State which of the following metals would give hydrogen when added to dilute hydrochloric acid.
i. Iron,
ii. Copper
iii. Magnesium
Copper does not react with dilute hydrochloric acid at all. This shows that copper is even less reactive than iron.
Q 9. Name a non-metallic element, which conducts electricity.
Carbon in the form of graphite conducts electricity, as there is a free electron in each carbon atom, which moves freely in between the hexagonal layers.
Q 10. Which metals do not corrode easily?
Gold and platinum and other noble metals do not corrode in air.
Q 11. What are alloys?
Alloys are homogeneous mixtures of two or more metals, or a metal and a non-metal. E.g. steel, brass, bronze, etc.
Q 12. Define the following terms.
(i) Minerals
(ii) Ores
(iii) Gangue
(i) Minerals
All compounds or elements, which occur naturally in the earth’s crust, are called minerals.
Example: Alums K2SO4 Al2(SO4)3 . 24H2O, Bauxite Al2O3 2H2O
(ii) Ores
Those minerals from which a metal can be profitably extracted are called ores.
Bauxite (Al2O3.2H2O) is the ore of Al, copper pyrite CuFeS2. All minerals are not ores but all ores are minerals.
When an ore is mined from the earth, it is always found to be contaminated with sand rocky materials. The impurity of sand and rock materials present in the ore is known as gangue.
Q 13. Name two metals that are found in nature in the free state.
Gold and platinum are found in the free state in nature.
Q 14. What is chemical process used for obtaining a metal from its oxide?
Q 15. Name two metals, which can form hydrides with metals.
Sodium and calcium form stable hydrides on reacting with hydrogen.
Q 16. Does every mineral have a definite and a fixed composition? Explain.
Yes, every mineral has a definite and a fixed composition. Minerals are widely distributed in the earth’s crust in the form of oxides, carbonates, sulphides, sulphates, nitrates, etc. These minerals are formed as a result of chemical changes taking place during the formation of earth.
Q 17. Explain the meaning of malleable and ductile.
Malleable is being able to be beaten/hammered into thin sheets.
Ductile is being able to be drawn into thin wires.
Q 18. i. Write the electron dot structures for sodium, oxygen and magnesium.
ii. Show the formation of MgO and NaO by the transfer of electrons.
iii. What are the ions present in these compounds?

ii. Formation of Magnesium oxide
When magnesium reacts with oxygen, the magnesium atom transfers its two outermost electrons to an oxygen atom. By losing 2 elections, the magnesium atoms form a magnesium ion (Mg2+) and by gaining 2 electrons, the oxygen atom forms an oxide ion (O2).

Formation of Sodium oxide Two sodium atoms transfer their 2 outermost electrons to an oxygen atom. By losing two electrons, the two sodium atoms form two sodiumions (2Na+). And by gaining two electrons, the oxygen atom forms an oxide ion (O2-).
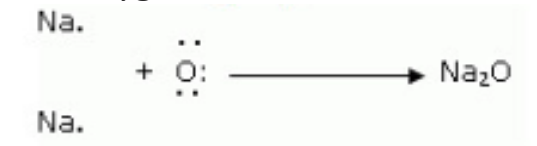
iii. The ions present in sodium oxide compound (Na2O) aie sodium ions (2Na+ and oxide ions (O2-). The ions present in Magnesium oxide compound (MgO) are magnesiumions Mg2+ and oxide ions (O2-).
Q 19. You must have seen tarnished copper vessels being cleaned with lemon or tamarind juice. Explain why these sour substances are effective in cleaning the vessels.
The sour substances such as lemon (or tamarind juice) contain acids. These acids dissolve the coating of copper oxide or basic copper carbonate present on the surface of tarnished copper vessels and make them shining red-brown again.
Q 20. Give an example of a metal which
i. is a liquid at room temperature.
ii. can be easily cut with a knife.
iii. is the best conductor of heat.
iv. is a poor conductor of heat.
i. Mercury is in liquid state at room temperature.
ii. Sodium and potassium are soft metals which can be easily cut with a knife.
iii. Silver is the best conductor of electricity.
iv. Mercury is a poor conductor of heat.
Q 21. Why sodium is kept immersed in kerosene?
Sodium metal is kept immersed in kerosene to prevent their reaction with oxygen, moisture and carbon dioxide of air.
Q 22. Why do ionic compounds have high melting points?
These compounds are made up of positive and negative ions. There is a strong force of attraction between the appositively charged ions, so a lot of heat energy is required to break this force of attraction and melt the ionic compounds. This is why ionic compounds have high melting points.
Q 23. A man went door to door posing as a goldsmith. He promised to bring back the glitter of old and dull gold ornaments. An unsuspecting lady gave a set of gold bangles to him which he dipped in a particular solution. The bangles sparkled like new but their weight was reduced drastically. The lady was upset but after a futile argument the man beat a hasty retreat. Can you play the detective to find out the nature of the solution he had used?
Aqua regia (By volume, this contains 3 parts of concentrated hydrochloric acid and 1 part of concentrated nitric acid) is the solution, which is used to sparkle the bangles like new, but their weight will be reduced drastically.
Q 24. Write equations for the reactions of
(i) iron with water
(ii) calcium and potassium with water
i). Iron reacts with steam to form magnetic oxide of Fe with the liberation of H2
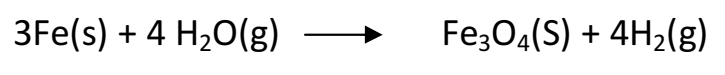
ii). Calcium reacts with water to form hydroxide and hydrogen
![]()
iii). Potassium reacts with cold water violently immediately with evolution of H2 which catches fire.
![]()
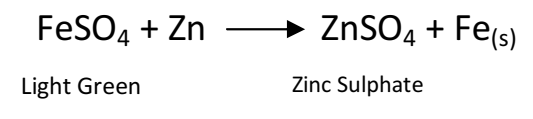
Q 25. What would you observe when zinc is added to a sodium of iron(II) sulphate? Write the chemical reaction that takes place?
Zinc is more reactive (more electro positive) than iron. Therefore it displaces iron from its salt solution. The colour of ferrous sulphate is pale green which becomes colourless.
Q 26. Pratyush took sulphur powder on a spatula and heated it. He collected the gas evolved by inverting a test tube over the burning sulphur. What will be the action of this gas on: Dry litmus paper and Moist litmus paper? Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction taking place.
a) When sulphur is brunt in air then sulphur dioxide gas is formed.
(i) Sulphur dioxide gas has no action on dry litmus paper.
(ii) Sulphur dioxide gas turns moist blue litmus paper to red.
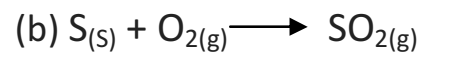
Q 27. Why is that iron does not occur as a metal in the crust of the earth? What are the common compound forms in which iron occurs? Which of these is more often used for extracting iron? Why are carbon and limestone mixed with iron ore before feeding it into the blast furnace? Write the chemical equations for the reduction step and the slag formation step.
Iron is quite reactive and so it does not occur as a metal in the crust of the earth. The common compounds formed are its oxide, a carbonate and a sulphide. The oxide ore of iron called haematite is more often used for extracting iron. The carbon and limestone which is mixed with iron ore is called the charge. This charge is responsible for the formation of iron metal. Coke acts the reducing agent and addition of limestone helps to remove the earthy impurities like sand from the blast furnace by forming fusible slag. Reduction of Iron(III)oxide or haematite to Iron: carbon monoxide reduces iron(III) oxide to iron metal.
Q 28. i) What is the composition of molten slag, formed in the extraction of iron in the blast furnace?
ii) What is the use of slag?
i) Molten slag in the extraction of iron is calcium silicate(CaSiO3).
ii) Slag is used for constructions of roads.
Q 29. What property of hydrogen is observed in the following experiments?
i) Balloon, filled with hydrogen, floats.
ii) Pop sound is heard when a burning splint is introduced at the mouth of hydrogen filled jar.
iii) When black cupric oxide is heated in a stream of hydrogen, reddish colour is obtained.
i) Hydrogen is light. So hydrogen filled balloons float.
ii) Pop sound is due to the combustible property of hydrogen. Hydrogen burns with oxygen at the mouth of the hydrogen filled jar.
iii) Hydrogen has reducing property. Hence it reduces black cupric oxide to red copper metal.
Q 30. What are the uses of ammonia?
i) Ammonia is used in the manufacture of fertilizers like ammonium sulphate and ammonium nitrate.
ii) To manufacture nitric acid by Ostwald’s process.
iii) To prepare dyes, explosives, cellulose acetate etc.
Q 31. Why do some metals like, Na, K, Ca, Mg not occur in nature as free elements?
Metals like Na, K, etc (alkali metals) and Ca, Mg etc (alkaline earth metals) are very reactive and hence they react with atmospheric oxygen and carbon dioxide and also with other non-metals like sulphur present in the earth’s crust to form compounds like oxides, carbonates, sulphides, sulphates and chlorides. So they do not occur in free state, but are found in the form of the above compounds.
Q 32. State briefly how you will extract iron from its ore. Draw a neat and labelled diagram. Write all the chemical reactions involved in it.
Iron is usually extracted from its chief ore, Haemitite.
The various steps involved in the production of iron metal from haematite are as follows:
1. Concentration of ore
The concentration of haematite or is done by the method of hydraulic washing. The ore is spilt into small pieces and then washed in a stream of water to remove sand, clay. In this way, a fairly concentrated ore is obtained and usually there is no need of any further concentration.
2. Calcination
The washed iron ore is then strongly heated in the absence of air to expel water sticking to it.
3. Reduction
The washed and dried ore is mixed with weighed quantities of coke and limestone and put into a blast furnace from the top .A blast of hot air is blown into the furnace from near its bottom.
This air is to supply for the burning of coke. The two reactions which take place in the blast furnace leading to the formation of iron metal are: formation of carbon monoxide and reduction of haematite.
Q 33. The copper vessels used in homes are found to be coated with green colour. Answer the following.
a) What is the chemical composition of the green coating?
b) Why do copper vessels form such a green coating?
c) What is the name of the phenomenon, responsible for the green coating?
d) Copper vessels are best cleaned with tamarind or lemon juice, but not with soap. Why?
a) Green coloured coating on copper is due to the formation of basic copper carbonate, CuCO3 Cu(OH)2.
b) Copper forms green coating of basic copper carbonate as it reacts with water, atmospheric oxygen and carbon dioxide.
c) Corrosion phenomenon is responsible for the formation of basic copper carbonate (green).
d) Since basic copper carbonate is basic in nature, it can be removed by tartaric acid present in tamarind or citric acid, present in lemon. Soap is basic in nature. So copper vessels are best cleaned with tamarind or lemon. Attracting foreign investment in agriculture and also free trade in grains will not only increase agricultural production, but will also create massive employment and reduce poverty in rural areas.
Q 34. Give reasons for the following
i. Silicon counts among metalloids
ii. Carbon is not used for making aluminium from aluminium oxide.
iii. For making hydrogen by reaction with hydrochloric acid, granulated zinc is preferred to a block of zinc.
i. Silicon shows properties of both metals and non-metals and hence silicon counts among metalloids.
ii. Carbon has less affnity for oxygen than Aluminium and hence it cannot eliminate oxygen from Aluminium oxide.
iii. Zinc granules are preferred to a block of zinc because it offers a large surface area for the reaction with the acid.
Q 35. How is chloride of lime chemically different from calcium chloride? Why does chloride of lime gradually lose its chlorine when kept exposed to air?
Chemically, chloride of lime is calcium oxy chloride, CaOCl2 also called bleaching powder. When exposed to air it gradually lose its chlorine because it reacts with carbon dioxide present in air to produce calcium carbonate and chlorine gas.
Chemically, chloride of lime is calcium oxy chloride, CaOCl2 also called bleaching powder. When exposed to air it gradually lose its chlorine because it reacts with carbon dioxide present in air to produce calcium carbonate and chlorine gas.
Q 36. Write short notes on the bleaching action of sulphur dioxide.
a) Sulphur dioxide bleaches the vegetable colours in the presence of moisture.
b) It bleaches the vegetable colours by reduction. It removes oxygen from coloured material.
c) Its bleaching action is temporary, because atmospheric oxygen again oxidises the bleached article back to its original colour.
d) SO2 is used to bleach delicate fabrics like wool, silk etc.
Q 37. a) State why hydrogen is said to be a clean fuel?
b) What property of hydrogen is involved in being a good fuel?
c) What is hydrogenation of oils? Write one application.
a) Hydrogen is a clean fuel because its reaction with oxygen produces only water. It does not form gases like CO2, NO2 etc, which pollute air.
b) Hydrogen, on combustion with oxygen, produces water and a lot of heat. This is an exothermic reaction.
c) Oils are unsaturated molecules, containing double bond. So hydrogen atoms are added at the double bonds of the molecules of oil. The reaction of hydrogen with oils is known as hydrogenation. The hydrogenation reaction takes place at 473 K and in the presence of nickel catalyst. Vanaspati or dalda ghee is prepared by hydrogenation of vegetable oils.
Q 38. Which of the following pairs will give displacement reactions ?
(a) NaCl solution and copper metal.
(b) MgCl2 solution and aluminium metal.
(c) FeSO4 solution and silver metal.
(d) AgNO3 solution and copper metal
(d) AgNO3 solution and copper metal
Q 39. An element reacts with oxygen to give a compound with a high melting point. This compound is also soluble in water. The element is likely to be
(a) calcium
(b) carbon
(c) silicon
(d) iron
(a) calcium
Q 40. Food cans are coated with tin and not with zinc because
(a) zinc is costlier than tin
(b) zinc has a higher melting point than tin
(c) zinc is less reactive than tin
(d) zinc is more reactive than tin.
(d) zinc is more reactive than tin
Q 41. Why does Calcium floats in water?
Calcium floats in water due to hydrogen gas, evolved hydrogen gas got stricken to the calcium Surface, hydrogen being lighter gas than water, make calcium float.
Q 42. What is the name of alloys of mercury?
Amalgam
Q 43. What is thermite reaction? What is its application?
Iron is displaced from its oxide using Alumunium. The reaction is highly exothermic.
Fe2O3 (s)+ 2Al(s) →Fe(s) + Al2O3 (s) + Heat
The heat obtained is so high that iron is obtained in molten form.
This reaction is used to join railway tracks or cracked machine parts.
Q 44. Why ionic compounds are having higher melting and boiling point?
Ionic compounds are having higher melting and boiling point because they are bonded together by strong electrostatic force of attraction. Their particles are strongly bonded together. It is difficult to break their strong force of attraction. So, it requires a very high energy and hence temperature to increase the inter molecular space.
Q 45. An element A reacts with water to form a compound B which is used in white washing. The compound B which is used white washing. The compound B on heating forms an oxide C which on treatment with water gives back B. Identify A,B and C and give reaction involved.
Element A is Calcium (ca, when it reacts with water, it form Calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2, which is used in white washing.
Ca+2H2O→Ca(OH)2+H2 (g)
Compound B on heating gives CaO Therefore, C is Calcium Oxide (CaO).
Ca(OH)2→CaO+H2O
CaO+H2O→Ca(OH)2
Q 46. Explain the formation of MgO by transfer of Electrons.
Formation of MgO
Magnesium losses two electrons, and forms Magnesium ions, to complete its octet.
Mg→Mg2++2e– Oxygen gains that two electrons to become O2-
Mg2+ + O2- →MgO
Q 47. (a) When calcium metal is added to water, the gas evolved does not catch fire but the same gas evolved on adding potassium metal to water catches fire. Explain why ?
(b) Name a metal for each case :
(i) It displaces hydrogen gas from nitric acid.
(ii) It does not react with any physical state of water.
(iii) It does not react with cold as well as hot water but reacts with steam.
(a) In both cases, the gas evolved is H2. When calcium reacts with water the heat evolved is not sufficient for hydrogen to catch fire. On the other hand, potassium reacts with water violently and lot of heat is evolved which is sufficient for hydrogen to catch fire.
(b) (i) Zinc
(ii) Copper
(iii) Aluminium
Q 48. Explain any 3 methods used for preventing Corrosion of metals?
Alloying: Mixing of the metal with another metal or non-metal can help in preventing Corrosion of metals. Example:- Alloying Iron with Carbon to form steel .
Electroplating: Platting a layer of Chromium over the surface of metal can help in preventing metals from getting corroded.
Galvanization: Iron metal is dipped in molten zinc, which forms a layer of zinc over Iron.
Q 49. Two Ores on Heating, A gives CO2, whereas ore B gives SO2 .Explain the processes with help of balanced chemical equation, which is used to convert ores A and B into their oxide ores with an example.
Ore A is Carbonate Ore.
The process involved in converting ores
Calcination: The Carbonate ore is heated strongly in absence of air.
ZnCO3→ZnO+CO2
Roasting: The sulphide ore is heated strongly in presence of excess of air, this is known as roasting.
ZnSO3→ZnO+SO2
Q 50. A metal X left in moist air for a longer time, loses its shiny brown surface and gains a green coat. Why has this happened ? Name and give the chemical formula of this given coloured compound and identify the metal. List two ways to prevent this process.
The metal has corroded because of being exposed to moist air. Green compound is basic copper carbonate [CuCO3.Cu(OH)2] . The metal is copper. Two ways to prevent this process : Painting, Greasing, Oiling, Galvanizing.
