Acids Bases and Salts For Class 10 Science Important Questions to cover all topics and get a good result.
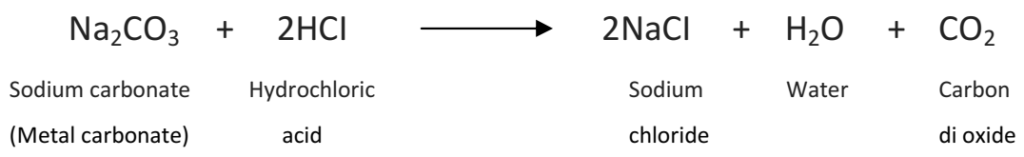
Q 1. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction between sodium carbonate and hydrochloric acid indicating the physical state of the reactants and products.
Na2CO3 (s) + 2HCl (ag) → 2NaCl (aq) + CO2 (g) + H2O (l)
Q 2. During the summer season, a milkman usually adds a small amount of baking soda to fresh milk. Give reason.
A milkman adds a very small amount of baking soda so as to prevent the spoilage of milk. It leads to a change in the pH which does not allow bacteria and enzymes to act and milk does not become sour due to fermentation.
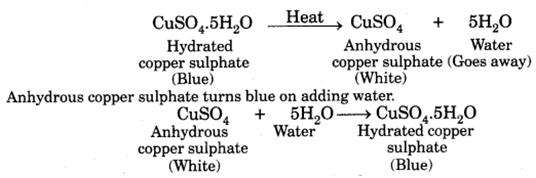
Q 3. What is meant by the water of crystallisation?
The water of crystallisation is the fixed number of water molecules chemically attached to each formula unit of salt in its crystalline form.
Q 4. Which one is a stronger acid, with pH = 5 or with pH = 2?
The acid with pH = 2 is a stronger acid.
Q 5. Name an example of olfactory indicators.
Vanilla.
Q 6. Fresh milk has a pH of 6. When it changes into curd (yogurt), will its pH value increases or decrease? Why?
Its pH will decrease because curd (yogurt) is sour in taste due to presence of acid in it.
Q 7. What is the difference between slaked lime and lime water?
A suspension of Ca(OH)2 in water is called slaked lime. Water containing traces of Ca(OH)2 is called lime water.
Q 8. Which acid is present in sour milk or curd?
Lactic acid.
Q 9. Name the chemical substance present in thick white and yellowish clouds present in the atmosphere of Venus.
Sulphuric acid.
Q 10. What are the pH values of distilled water and common salt solution?
Both are neutral and have pH close to 7.
Q 11. A dry pellet of a common base B, when kept in open absorbs moisture and turns sticky. The compound is also a by-product of chloralkali process. Identify B. What type of reaction occurs when B is treated with an acidic oxide? Write a balanced chemical equation for one such solution.
. Dry pellets of sodium hydroxide absorb moisture and turn sticky when kept in open which is also a by-product of chloralkali process. When sodium hydroxide is treated with an acidic oxide it produces salt and water.
![]()
Q 12. Name the chemist who had given the pH scale.
S.P.L. Sorensen (1909)
Q 13. Which bases are called alkalies? Give an example of an alkali.
Soluble bases. For example, sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
Q 14. Name the acid present in tomato.
Oxalic acid.
Q 15. A knife, which is used to cut a fruit, was immediately dipped into water containing drops of blue litmus solution. If the colour of the solution is changed to red, what inference can be drawn about the nature of the fruit and why?
Since the colour of the blue litmus has changed to red, this means that the fruit juice is acidic in nature.
Q 16. Acidic and basic solutions in water conduct electricity. Why?
Because they produce hydrogen and hydroxide ions respectively.
Q 17. How do H+ ions exist in water?
H+ ions in water combine with water (H2O) molecules and exist as H3O+ ion, called hydronium ion.
Q 18. The pH of a sample of vegetable soup was found to be 6.5. How is this soup likely to taste?
The taste will be slightly sour as it is weakly acidic.
Q 19. What should be done as remedy if stung by leaves of nettle plant in the wild?
The area should be rubbed with the leaf of dock plant.
Q 20. What would be the colour of litmus in a solution of sodium carbonate?
Red litmus will change to blue in sodium carbonate solution..
Q 21. What happens when nitric acid is added to egg shell?
Ans. Egg shell is made of calcium carbonate. When nitric acid is added to egg shell calcium nitrate, carbon dioxide and water are formed.
CaCO3 + 2HNO3 → Ca(NO3)2 + CO2 + H2O
Q 22. What is acid rain?
Rainwater having pH less than 5.6 is called acid rain.
Q 23. Which one of these has a higher concentration of H ions? 1 M HCl or 1 M CH3COOH.
1 M HCl has higher concentration of H+ ions.
Q 24. Name the hardest substance in the body.
Tooth enamel (Calcium phosphate).
Q 25. Name the chemical substance which is used in the manufacture of soap as well as used as a preservative in pickles.
Sodium chloride (NaCl)
Q 26. Name a chemical substance which can be used to detect the presence of moisture in a liquid.
Anhydrous copper sulphate.
Q 27. The pH of three solutions A, B and C are 4, 9 and 6 respectively. Arrange them in increasing order of acidic strength.
The increasing order of acidic strength is : B < C < A.
Q 28. There are two jars A and B containing food materials. Food in jar ‘A’ is pickled with acetic acid while ‘B’ is not. Food of which of jar will stale first? Explain. Name two synthetic indicators which are used to test acids and bases.
Food in jar ‘B’ will stale first because it will undergo oxidation and will also be attacked by microorganisms. Synthetic indicators: Phenolphthalein, methyl orange.
Q 29. What is the chemical formula of soda ash?
Na2CO3
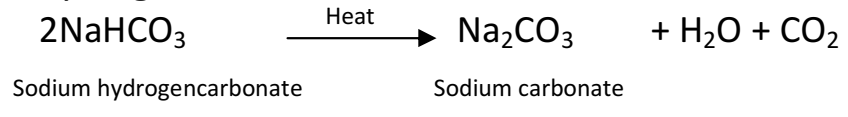
Q 30. How would you distinguish between baking powder and washing soda by heating?
Baking soda (NaHCO3) on heating produces carbon dioxide (CO2), which extinguishes a burning matchstick.
![]()
But washing soda (Na2CO3.10H2O) on heating does not produce any such gas, thus, it has no effect on burning matchstick.
![]()
Q 31. A sulphate salt of Group 2 element of the Periodic Table is a white, soft substance, which can be moulded into different shapes by making its dough. When this compound is left in the open for some time, it becomes a solid mass and cannot be used for moulding purposes. Identify the sulphate salt and why does it show such a behaviour? Give the reaction involved.
Calcium belongs to group 2. Calcium sulphate is a white soft substance. It is known as Plaster of Paris, which can be moulded into different shapes by making its dough.
When Plaster of Paris is left for some time in the open, it turns into a solid mass because of reaction with moisture present in the atmosphere. The solid mass so formed is known as gypsum and cannot be further used for moulding.

The above said group 2 element is calcium sulpahte.
Q 32. Explain with suitable reason
(a) Ferric chloride is stored in air tight bottles.
(b) On exposure to atmosphere, Glaublar’s salt loses weight while quicklime gains weight.
(c) Common salt (containing traces of magnesium chloride) becomes sticky during the monsoons.
(a) Because ferric chloride is deliquescent in nature.
(b) Glaubar’s salt is efflorescent and loses water of crystallisation whereas quick lime is hygroscopic in nature and absorbs moisture from the air.
(c) This is because magnesium chloride is deliquescent and absorbs moisture from the atmospheric air and becomes moist.
Q 33. Name the acid present in ant sting and give its chemical formula. Also give the common method to get relief from the discomfort caused by the ant sting.
The acid present in ant sting: Methanoic acid
Chemical Formula of methanoic acid: HCOOH
Method to get relief from the discomfort caused by the ant sting: Rubbing baking soda over the area of ant sting.
Explanation: Rubbing baking soda (a base) over ant sting neutralises the methanoic acid present in the ant sting and gives relief from pain.
Q 34. List two differences between acids and bases on the basis of chemical properties.
(i) Dilute acids like HCl and H2SO4 evolve H2 gas on reacting with metals like Zn, Mg and Ca, etc. and dilute bases do not evolve hydrogen gas.
(ii) Acids react with oxides of metals while bases react with oxides of non-metals.
Q 35. List four main differences between acids and bases.
Ans.
| Properties | Acids | Bases |
| 1. Taste | Sour | Bitter |
| 2. Action on litmus paper | They turn blue litmus paper red. | They turn red litmus paper blue. |
| 3. Action with phenolphthalein | No action | They turn phenolphthalein pink. |
| 4. Action with carbonates and bicarbonates |
They decompose carbonates and bicarbonates to liberate carbon dioxide. | No action |
Q 36. Mention the terms defined by the following sentences:
(a) A soluble base
(b) The insoluble solid formed when two solution are mixed together.
(a) Alkali
(b) Precipitate.
Q 37. Explain why sodium hydroxide solution cannot be kept in aluminium containers? Write equation for the reaction that may take place for the same.
Sodium hydroxide solution reacts with aluminium to form sodium metaaluminate and hydrogen is evolved. Therefore, it cannot be kept in a container made of aluminium.
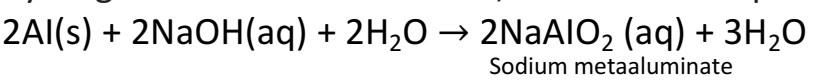
Q 38. How can you obtain the following gases by using dilute acid and one other substance?
(а) hydrogen
(b) carbon dioxide
(a) Fe + H2SO4 (dil.) → FeSO4 + H2 (g)
Mg + 2HCl(dil.) → MgCl2 + H2 (g)
(b) Na2CO3 + 2HCl(dil.) → 2NaCl + H2O + CO2(g)
NaHCO3 + HCl(dil.) → NaCl + H2O + CO2(g)
Q 39. A solution of HCl is taken in a beaker and an electric circuit with a bulb is set up with the solution in series. What happens to the bulb and why?
The bulb will start glowing. Glowing of the bulb indicates that there is a flow of electric current through the solution. Electric current is carried through the solution by ions.
Since the cation present in acids is H, this suggests that acids produce hydrogen ions, H (ag), in solution, which are responsible for carrying current through the solution.
Q 40. If 280 g of washing soda crystals are left in dry air for some time, a loss of weight of 162 g occurs. How can you account for this?
Washing soda (Na2CO3 . 10H2O) is an efflorescent substance (if exposed to air, it loses most of its water of crystallisation). 280 g of washing soda lose 162 g of its water of crystallisation.
Q 41. A sample of bleaching powder was kept in an air tight container. After a month, it lost some of its chlorine content. How will you account for it?
Bleaching powder if kept even in an air tight container, will slowly decompose on its own and form calcium chlorate and calcium chloride. The reaction is called auto oxidation. This will result in decrease in its chlorine contents.

Q 42. A white powder is added while baking breads and cakes to make them soft and fluffy. Write the name of the powder. Name its main ingredients. Explain the function of each ingredient. Write the chemical reaction taking place when the powder is heated during baking.
The white powder is known as baking powder. The main ingredients are baking soda (NaHCO3) and tartaric acid (C4H6O
Q 43. Explain giving reasons:
(i) Tartaric acid is a component of baking powder used in making cakes.
(ii) Gypsum (CaSO4 . 2H2O) is used in the manufacture of cement.
(i) Role of tartaric acid in baking powder (mixture of tartaric acid and sodium hydrogencarbonate) is to neutralise sodium carbonate formed upon heating sodium hydrogencarbonate.
In case it is not done, cake will be better and sodium carbonate will also have injurious side effects.
(ii) The role of gypsum (CaSO4.2H2O) in the manufacture of cement is to slow down the process of setting of cement.
Q 44. What will be the action of the following substances on litmus paper?
Dry HCl gas, moistened NH3 gas, lemon juice, carbonated soft drink, curd, soap solution.
Dry HCl gas: No action
Moistened NH3 gas: Turns red litmus blue.
Lemon juice: Turns blue litmus red.
Carbonated soft drink: Turns blue litmus red.
Curd: Turns blue litmus red.
Soap solution: Turns red litmus blue.
Explanation:
- Dry HCl gas does not liberate hydrogen ion, hence no action takes place with litmus paper.
- NH3 gas forms ammonium hydroxide with water which turns red litmus paper blue.
- Lemon juice is citric acid, so it turns blue litmus paper red.
- Carbonate soft drink contains carbon dioxide dissolved in water. Carbon dioxide forms carbonic acid with water; which turns blue litmus paper red.
- Curd contains lactic acid and hence turns blue litmus paper red.
- Soap solution is basic in nature hence it turns red litmus paper blue.
Q 45. When zinc metal is treated with a dilute solution of a strong acid, a gas is evolved, which is utilised in the hydrogenation of oil. Name the gas evolved. Write the chemical equation of the reaction involved and also write a test to detect the gas formed.
Zinc metal gives hydrogen gas when it is treated with dilute sulphuric acid. Hydrogen gas is utilised in hydrogenation of oil. Therefore, the gas evolved is hydrogen.

Test for hydrogen gas: When a burning candle is brought near hydrogen gas, it bums with a pop sound which confirms the presence of hydrogen gas.
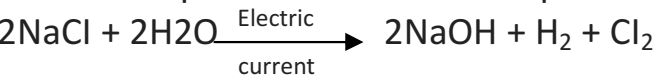
Q 46. (i) Identify the compound of calcium which is a yellowish powder and is used for disinfecting drinking water. Write its chemical name and formulae.
(ii) Write the balanced chemical equation of chlor-alkali process.
(i) The yellowish white solid is known as bleaching powder. Chemically, it is calcium oxychloride or calcium hypochlorite. Its chemical formula is CaOCl2
(ii) Chemical equation for chlor-alkali process is
Q 47. Write any three chemical properties of acids.
(i) They react with metals to give out hydrogen gas, for example, 
(ii) They react with bases to form salt and water, for example,

(iii) They react with metal carbonates to liberate carbon dioxide gas.
Q 48. What is tooth enamel chemically? State the conditions when it starts corroding. What happens when food particles left in the mouth after eating degrade? Why do doctors suggest use of powder/tooth paste to prevent tooth decay?
(i) The tooth enamel is chemically calcium phosphate with the formula Ca3(PO4)2 . It is quite hard.
(ii) The enamel starts corroding when the pH inside our mouth falls below 5.5 because the saliva present in the mouth becomes acidic.
(iii) The bacteria present in the mouth breakdown the food particles into acids which damage our teeth by corroding them.
(iv) The contents of the tooth paste are of basic nature. They neutralise the excess acid present. As a result, the corrosion of enamel and decay of teeth are checked.
Q 49. A compound which is prepared from gypsum has the property of hardening when mixed with proper quantity of water.
(i) Identify the compound.
(ii) Write the chemical equation for its preparation.
(iii) Mention one important use of this compound
(i) Plaster of Paris
![]()
(iii) It is used for plastering fractured bones.
Q 50. (a) A solution has a pH of 7. Explain how you would
(i) increases its pH
(ii) decrease its pH
(b) If a solution changes the colour of litmus from red to blue, what can you say about its pH?
(c) What can you say about the pH of a solution that liberates CO2 from sodium carbonate?
(a) (i) By adding some alkali like NaOH
(ii) By adding some acid like HCl
(b) Since the solution changes the colour of litmus from red to blue it is alkaline and hence it has pH > 7.
(c) Since the solution liberates CO2 from sodium carbonate, it should be acidic and has pH < 7
Q 51 – A sulphate salt of Group 2 element of the Periodic Table is a white, soft substance, which can be moulded into different shapes by making its dough. When this compound is left in the open for some time, it becomes a solid mass and cannot be used for moulding purposes. Identify the sulphate salt and why does it show such a behavior? Give the reaction involved.
Calcium belongs to group 2. Calcium sulphate is a white soft substance. It is known as Plaster of Paris, which can be moulded into different shapes by making its dough.
Q 52 – When Plaster of Paris is left for some time in the open, it turns into a solid mass because of reaction with moisture present in the atmosphere. The solid mass so formed is known as gypsum and cannot be further used for moulding.

The above said group 2 elements is calcium sulpahte.
Q 53 – List four main differences between acids and bases.
| Properties | Acids | Bases |
| 1. Taste | Sour | Bitter |
| 2. Action on litmus paper | They turn blue litmus paper red | They turn red litmus paper blue. |
| 3. Action with phenolphthalein | No action | They turn phenolphthalein pink. |
| 4. Action with carbonates and bicarbonates | They decompose carbonates and bicarbonates to liberate carbon dioxide. | No action |
Q 54 – What will be the action of the following substances on litmus paper?
Dry HCl gas, moistened NH3 gas, lemon juice, carbonated soft drink, curd, soap solution.
Dry HCl gas: No action
Moistened NH3 gas: Turns red litmus blue.
Lemon juice: Turns blue litmus red.
Carbonated soft drink: Turns blue litmus red.
Curd: Turns blue litmus red.
Soap solution: Turns red litmus blue.
Explanation:
- Dry HCl gas does not liberate hydrogen ion, hence no action takes place with litmus paper.
- NH3 gas forms ammonium hydroxide with water which turns red litmus paper blue.
- Lemon juice is citric acid, so it turns blue litmus paper red.
- Carbonate soft drink contains carbon dioxide dissolved in water. Carbon dioxide forms carbonic acid with water; which turns blue litmus paper red.
- Curd contains lactic acid and hence turns blue litmus paper red.
- Soap solution is basic in nature hence it turns red litmus paper blue.
Q 55 – Write any three chemical properties of acids.
(i) They react with metals to give out hydrogen gas, for example,
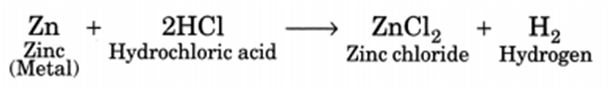
(ii) They react with bases to form salt and water, for example,

(iii) They react with metal carbonates to liberate carbon dioxide gas.

Q 56 – Choosing only substances from the list given in the box below, write equations for the reactions which you would use in the laboratory to obtain:
(a) Sodium sulphate
(b) Iron (II) sulphate
(c) Zinc carbonate.
Dilute sulphuric acid, copper, iron, copper carbonate, sodium, zinc, sodium carbonate
(a) Sodium sulphate
Na2CO3 + H2SO4 (dil.) → Na2SO4 + H2O + CO2 (g)
(b) Iron (II) sulphate
Pe + H2SO4 (dil.) → FeSO4 + H2 (g)
(c) Zinc carbonate
Zn + CuCO3 → ZnCO3 + Cu
Q 57 – Write balanced equations to satisfy each statement:
(a) Acid + Chloride → Salt + Hydrochloric acid gas
(b) Acid + Carbonate → Salt + Water + Carbon dioxide
(c) Acid + Sulphite → Salt + Water + Sulphur dioxide
(a) H2SO4 + NaCl → NaHSO4 + HCl (g)
(b) 2HCl + Na2CO3 → 2NaCl + H2O + CO2 (g)
(c) 2HCl + CaSO3 → CaCl2 + H2O + SO2 (g)
Q 58 – In the following schematic diagram for the preparation of hydrogen gas as shown in Figure. What would happen if following changes are made?
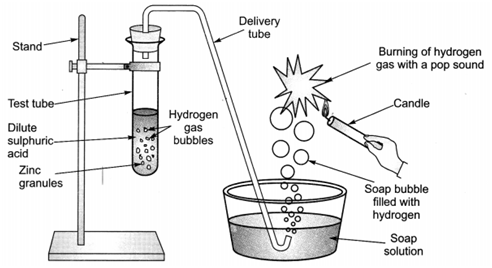
(a) When zinc dust is taken instead of zinc granules to react with sulphuric acid, hydrogen gas is formed. But the rate of reaction increases in the case of zinc dust compared to zinc granules, because of increased surface area of zinc dust which increases the rate of reaction.
Thus, when zinc dust is used in the place of zinc granules, hydrogen gas is produced at a faster rate.
(b) Zinc granules give hydrogen gas; along with zinc chloride; when they react with hydrochloric acid.
Thus, when hydrochloric acid is used in place of sulphuric acid, zinc chloride is formed instead of zinc sulphate; along with hydrogen gas and the reaction takes place at the same rate.
c) Copper does not react with dilute acids under normal conditions because copper lies at lower position in the reactivity series and does not displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
Thus, if copper turnings are taken in place of zinc granules, no reaction will take place.
(d) If sodium hydroxide is taken in place of dilute sulphuric acid and the tube is heated, sodium zincates is formed along with hydrogen gas. Heating the test tube will increase the rate of formation of hydrogen gas as heating the reaction mixture increases the rate of reaction.

Q 59 – (i) Name the products formed when sodium hydrogen carbonate is heated.
(ii) Write the chemical equation for the reaction involved in it.
(i) On heating sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3), it decomposes to form sodium carbonate (Na2.CO3), water (H2O) and carbon dioxide (CO2).

Q 60 –A salt X when dissolved in distilled water gives a clear solution which turns red litmus blue. Explain this phenomenon.
Ans. Basic solutions turn red litmus paper blue. The salt of a weak acid and a strong base gives a basic solution. SO, the given salt X is the salt of a weak acid and a strong base. . Example: When sodium carbonate is dissolved in water, it gets hydrolysed to some extent and forms sodium hydroxide and carbonic acid.

Being a strong base, sodium hydroxide is fully ionized and gives a large amount of hydroxide ions (OH–). Carbonic acid is a weak acid which is only slightly ionized and hence, gives a small amount of hydrogen ions (H+). The H+ ions produced by carbonic acid neutralizes only a small amount of OH-ions produced by sodium hydroxide and the rest amount of OH–ions are present in the solution. Hence, the Na2 CO3 solution is basic in nature. It turns red litmus blue.
Q 61 –What is meant by water of crystallization ? Explain that the crystalline salts contains water of crystallization.
Water of crystallization is a fixed number of water molecules present in one formula unit of a salt. One formula unit of copper sulphate contains five water molecules (5H2O). The water molecules which form part of the structure of a crystal are called water of crystallisation. When hydrated salts are heated strongly, they lose their water of crystallisation.
On strong heating, blue copper sulphate crystals turn white (due to the loss of water of crystallization).