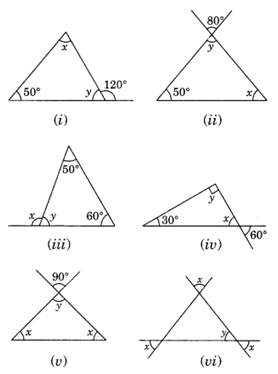
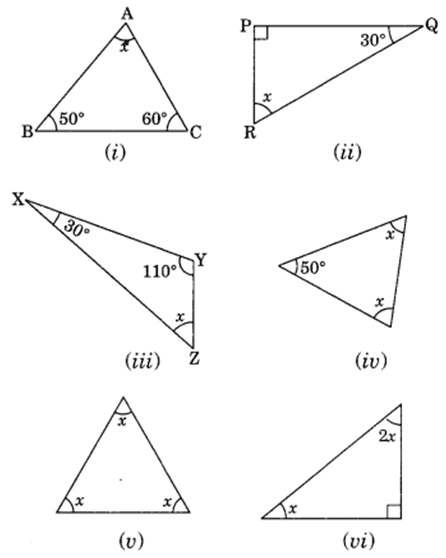
Q 1 – Find the value of the unknown x in the following diagrams:
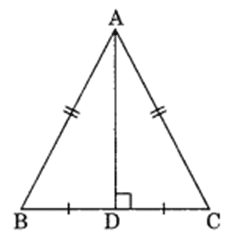
Q 3 – Verify by drawing a diagram if the median and altitude of an isosceles triangle can be same.
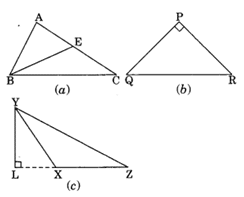
Q 4 – Draw rough sketches for the following:
(a) In ∆ABC, BE is a median.
(ib) In ∆PQR, PQ and PR are altitudes of the triangle.
(c) In ∆XYZ, YL is an altitude in the exterior of the triangle.
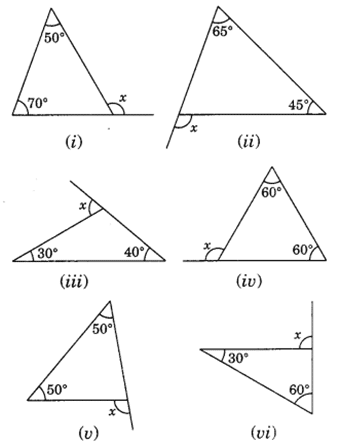
Q 5 – Find the value of the unknown exterior angle x in the following diagrams:
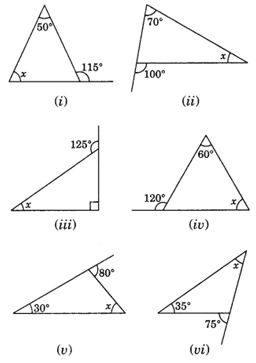
Q 6 – Find the value of the unknown interior angle x in the following figures:
Q 7 – Take any point O in the interior of a triangle PQR . Is
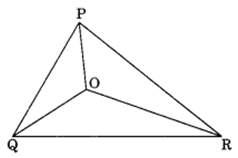
(i) OP + OQ > PQ?
(ii) OQ + OR > QR?
(iii) OR + OP > RP?
Q 8 – The length of two sides of a triangle are 12 cm and 15 cm. Between what two measures should the length of the third side fall?
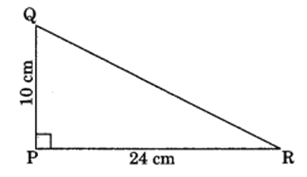
Q 9 – PQR is a triangle, right angled at P. If PQ = 10 cm and PR = 24 cm, find QR.
Q 10 – Which of the following can be the sides of a right triangle?
(i) 2.5 cm, 6.5 cm, 6 cm.
(ii) 2 cm, 2 cm, 5 cm.
(iii) 1.5 cm, 2 cm, 2.5 cm
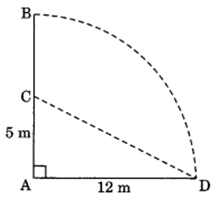
Q 11 – A tree is broken at a height of 5 m from the ground and its top touches the ground at a distance of 12 m from the base of the tree . Find the original height of the tree.
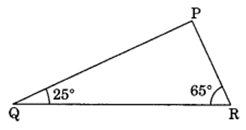
Q 12 – Angles Q and R of a APQR are 25° and 65°. Write which of the following is true.
(i) PQ2 + QR2 = RP2
(ii) PQ2 + RP2 = QR2
(iii) RP2 + QR2 = PQ2
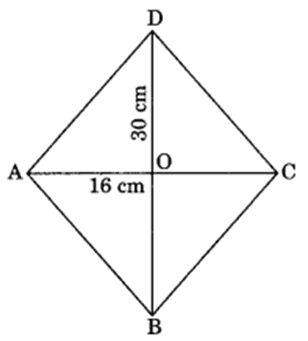
Q 13 – The diagonals of a rhombus measure 16 cm and 30 cm. Find its perimeter.
Q 14 – How many elements are there in a triangle?
(a) 3
(b) 6
(c) 4
(d) None of these.
Q 15 – How many vertices does a triangle have?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Q 16 – How many angles are there in a triangle?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Q 17 – If two sides of a triangle are not equal, the triangle is called
(a) scalene
(b) isosceles
(c) equilateral
(d) right-angled
Q 18 – If two sides of a triangle are equal, the triangle is called
(a) isosceles
(b) equilateral
(c) scalene
(d) right-angled
Q 19 – If all the three sides of a triangle are equal, the triangle is called
(a) equilateral
(b) right-angled
(c) isosceles
(d) scalene
Q 20 – If all the angles of a triangle are acute, the triangle is called
(a) obtuse-angled
(b) acute-angled
(c) right-angled
(d) none of these
Q 21 – If one angle of a triangle measures 90°, the triangle is called
(a) acute-angled
(b) obtuse-angled
(c) right-angled
(d) none of these
Q 22 – If one angle of a triangle is obtuse, the triangle is called
(a) acute-angled
(b) obtuse-angled
(c) right-angled
(d) none of these
Q 23 – How many medians can a triangle have?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Q 24 – How many altitudes can a triangle have?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Q 25 – The total measure of the three angles of a triangle is
(a) 360°
(b) 90°
(c) 180°
(d) none of these
Q 26 – The measure of each angle of an equilateral triangle is
(a) 30°
(b) 45°
(c) 90°
(d) 60°
Q 27 – Which of the following statements is true?
(a) A triangle can have two right angles
(b) A triangle can have two obtuse angles
(c) A triangle can have two acute angles
(d) A triangle can have all the three angles less than 60°
Q 28 – Which of the following statements is true?
(a) A triangle can have all the three angles equal to 60°.
(b) A triangle can have all the three angles greater than 60°.
(c) The sum of any two angles of a triangle is always greater than the third angle.
(d) The difference between the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the length of the third side
Q 29 – Which of the following statement is false?
(a) The sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is less than the third side.
(b) In a right-angled triangle, the square on the hypotenuse = sum of the squares on the legs.
(c) If the Pythagorean property holds, the triangle must be right-angled.
(d) The diagonal of a rectangle produce ‘by itself the same area as produced by its length and breadth
Q 30 – Two angles of a triangle measure 90° and 30°. The measure of the third angle is
(a) 90°
(b) 30°
(c) 60°
(d) 120°
Q 31 – The ratio of the measures of the three angles of a triangle is 2 : 3 : 4. The measure of the largest angle is
(a) 80°
(b) 60°
(c) 40°
(d) 180°
Q 32 – In the following figure, the side BC of ∆ ABC is extended up to the point D. If ∠A = 55° and ∠B = 60°, then the measure of ∠ACD is
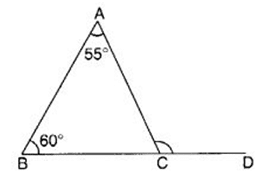
(a) 120°
(b) 110°
(c) 115°
(d) 125°
Q 33 – In the following figure, the measure of ∠A is
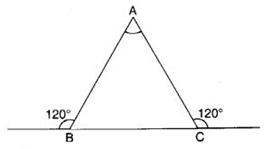
(a) 30°
(b) 45°
(c) 90°
(d) 30°
Q 34 – In the following figure, the measure of ∠A is
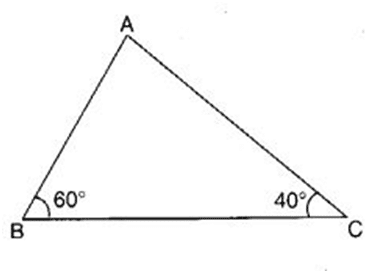
(a) 70°
(b) 90°
(c) 80°
(d) 100°
Q 35 – In the following figure, m || QR. Then, the measure of ∠QPR is
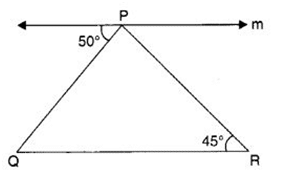
(a) 80°
(b) 85°
(c) 75°
(d) 70°
Q 36 – In the following figure, find ∠ x and ∠ y, if ∠x – ∠y – 10°
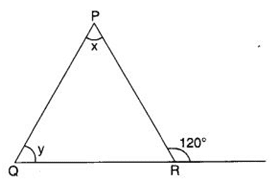
(a) 65°, 55°
(b) 55°, 45°
(c) 45°, 35°
(d) 60°, 60°
Q 37 – In the following figure, find ∠ B.
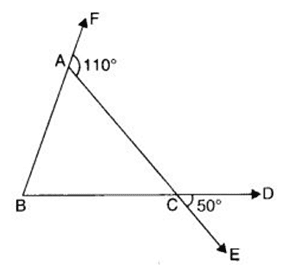
(a) 30°
(b) 45°
(c) 40°
(d) 60°
Q 38 – In the following figure, ∆ ABC is an equilateral triangle. Find ∠x.
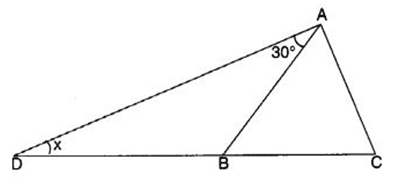
(a) 30°
(b) 45°
(c) 60°
(d) 90°
Q 39 – In the following figure, one angle of triangle ABC is 40°. If the difference of the other two angles is 30°, find the larger of the other two angles.
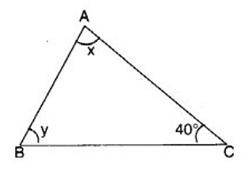
(a) 85°
(b) 80°
(c) 75°
(d) 70°
Q 40 – In the following figure, find
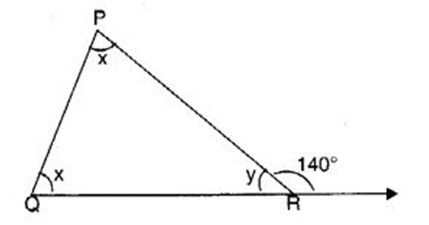
(a) 60°
(b) 70°
(c) 80°
(d) 75°
Q 41 – In the following figure, find x if BA || CE.
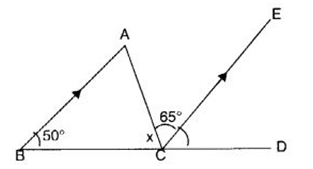
(a) 60°
(b) 40°
(c) 45°
(d) 65°
Q 42 – Find the value of the unknown interior angle x in the following figure:
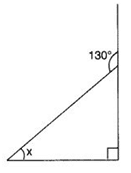
(a) 30°
(b) 35°
(c) 40°
(d) 45°
Q 43 – Find the value of unknown x in the following figure:
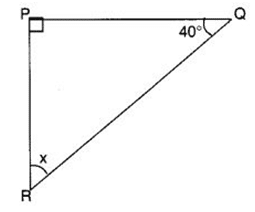
(a) 40°
(b) 50°
(c) 45°
(d) 55°
Q 44 – Find the value of unknown x in the following figure:
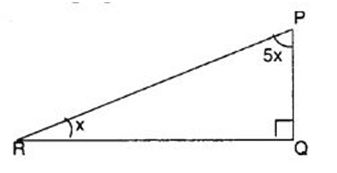
(a) 10°
(b) 15°
(c) 20°
(d) 25°
Q 45 – Find angle x in the following figure:
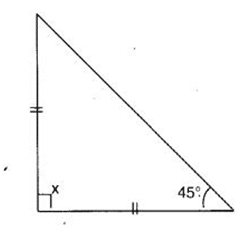
(a) 90°
(b) 80°
(c) 95°
(d) 100°
Q 46 – Find angle x in the following figure:
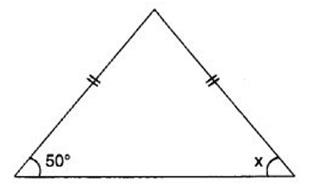
(a) 40°
(b) 50°
(c) 45°
(d) 60°
Q 47 – Find angle x in the following figure:
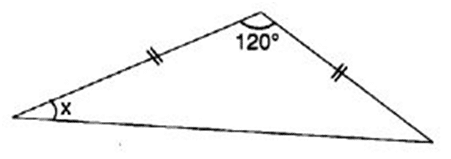
(a) 40°
(b) 30°
(c) 25°
(d) 35°
Q 48 – Find angle x in the following figure:
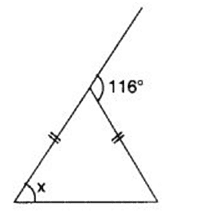
(a) 40°
(b) 45°
(c) 35°
(d) 50°
Q 49 – Find angle x in the following figure:
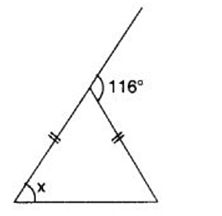
(a) 58°
(b) 59°
(c) 57°
(d) 56°
Q 50 – Find angle x in the following figure:
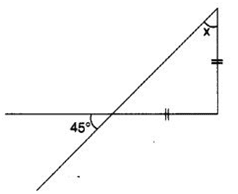
(a) 45°
(b) 40°
(c) 35°
(d) 50°
Q 51 – In which case of the following lengths of sides of a triangle, is it possible to draw a triangle?
(а) 3 cm, 4 cm, 7 cm
(b) 2 cm, 3 cm, 7 cm
(c) 3 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm
(d) 3 cm, 3 cm, 7 cm
Q 52 – Which of the following cannot be the sides of a right triangle?
(а) 2 cm, 2 cm, 4 cm
(b) 5 cm, 12 cm, 13 cm
(c) 6 cm, 8 cm, 10 cm
(d) 3 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm
Q 53 – How many sides are there in a triangle?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4