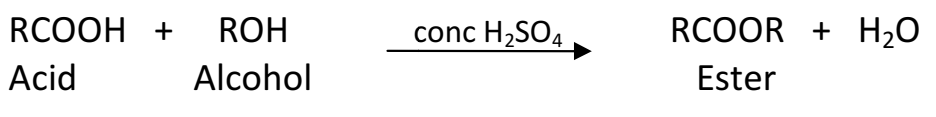Q 1. Buckminster fullerene is an allotropic form of
(a) phosphorus
(b) sulphur
(c) carbon
(d) tin
(c) Buckminster fullerene is an allotrope of carbon containing clusters of 60 carbon atoms joined together to form spherical molecules. Its formula is C (C-sixty). It is a dark solid at room temperature and as compared to another allotropic form of carbon (diamond and graphite), it is neither very hard nor soft.
Q 2. The hetero atoms present in CH3 – CH2 – O – CH2 – CH2Cl are
(i) oxygen
(ii) carbon
(iii) hydrogen
(iv) chlorine
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
(d) Atoms other than C and H, if present in organic compound, are called heteroatoms.
Q 3. In which of the following compounds -OH is the functional group?
(a) Butanone
(b) Butanol
(c) Butanoic
(d) Butanal
(b) Butanol, CH3 —CH2 —CH2 —CH2 —OH
The general formula of alcohols is CnH2n+1 — OH.
For butanol, n = 4. So, formula is
C4H9 —OH or CH3 —CH2 —CH2 —CH2 —OH
Q 4. The soap molecule has a
(a) hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail
(b) hydrophobic head and a hydrophilic tail
(c) hydrophobic head and a hydrophobic tail
(d) hydrophilic head and a hydrophilic tail
(a) A soap molecule is made up of two parts- a long hydrocarbon part and a short ionic part —COONa+ group. The long hydrocarbon chain is hydrophobic (water repelling) and ionic portion is hydrophilic (water attracting).
Q 5. Chlorine reacts with saturated hydrocarbons at room temperature in the
(a) absence of sunlight
(b) presence of sunlight
(c) presence of water
(d) presence of hydrochloric acid
(b) Chlorine reacts with saturated hydrocarbon at room temperature in the presence of sunlight.
Q 6. Butanone is a four carbon compound with functional group
(a) carboxylic acid
(b) aldehyde
(c) ketone
(d) alcohol
(c) In butanone, the functional group is Ketone .
Q 7. Ethane with molecular formula C2H6 has
(a) 6 covalent bonds
(b) 7 covalent bonds
(c) 8 covalent bonds
(d) 9 covalent bonds
There are 7 covalent bonds.
Q 8. Vinegar is a solution of
(a) 50% – 60% acetic acid in alcohol
(b) 5% – 8% acetic acid in alcohol
(c) 5% – 8% acetic acid in water
(d) 50% – 60% acetic acid in water
(c) A 5%-8% solution of acetic acid in water is called vinegar
Q 9. Which of the following does not belong to the same homologous series?
(a) CH4
(b) C2H6
(c) C3H8
(d) C4H8
(d) Because succesive members of a homologous series differ by —CH2 unit.
Thus, C4H10 is the next member of this series. So, homologous series of alkanes is:
methane (CH4), ethane (C2H6), propane (C3H8) and butane (C4H10).
So, C4H8 does not belong to the homologous series.
Q 10. How many structural isomers can you draw for pentane?
Q 10. How many structural isomers can you draw for pentane?
We can draw 3 structural isomers for pentane.
Q 11. What are the two properties of carbon that lead to the huge number of carbon compounds we see around us?
Due to its large valency, carbon atoms can form covalent bonds with a number of carbon atoms as well as with a large number of other atoms such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, chlorine and many more atoms. This leads to the formation of a large number of organic compounds.
LQ 12. A mixture of oxygen and ethyne is burnt for welding. Can you tell why a mixture of ethyne and air is not used?
When a mixture of oxygen and ethyne is burnt, it burns completely producing a blue flame. This blue flame is extremely hot which produced a very high temperature which is used for welding metals. But the mixture of ethyne and air is not used for welding purposes because the burning of ethyne in air produces a sooty flame, which is not enough to melt metals for welding.
Q 13. What are oxidizing agents?
Oxidizing agents are the substances that gain electrons in a redox reaction and whose oxidation number is reduced.
Q 14. Explain the nature of the covalent bond using the bond formation of CH3Cl.
CH3Cl (methyl chloride) is made up of one carbon atom, three hydrogen atoms and one chlorine atom. Carbon atom has 4 valence electrons, each hydrogen atom has one valence electron, and a chlorine atom has 7 valence electrons. Carbon atom shares its four valence electrons with three hydrogen atoms and 1 chlorine atom to form methyl chloride as follows:
From the above reaction, in the dot structure of methyl chloride (CH3Cl) there are four pairs of shared electrons between carbon and other atoms. Each pair of shared electrons constitutes one single covalent bond. So, methyl chloride has four single covalent bonds.
Q 15. What is a homologous series? Explain with an example.
Homologous series is a series of compounds with a similar general formula, possessing similar chemical properties due to the presence of the same functional group, and shows a gradation in physical properties as a result of increase in molecular size and mass. For example, methane has a lower boiling point than ethane since it has more intermolecular forces with neighbouring molecules. This is because of the increase in the number of atoms making up the molecule.
Q 16. How Ethanol and Ethanoic acid are differentiated on the basis of their physical and chemical properties?
(i) Ethanol has a pleasant smell whereas ethanoic acid has the smell of vinegar.
(ii) Ethanol has a burning taste whereas ethanoic acid has a sour taste.
(iii) Ethanol has no action on litmus paper whereas ethanoic acid turns blue litmus paper red.
(iv) Ethanol has no reaction with sodium hydrogencarbonate but Ethanoic acid gives brisk effervescence with sodium hydrogencarbonate.
Q 17. Explain the formation of scum when hard water is treated with soap.
The precipitate form of scum is formed when soap is used for washing clothes. With hard water, a large amount of soap is wasted in reacting with the calcium and magnesium ions of hard water to form an insoluble precipitate. The precipitate form formed by the action of hard water on soap, sticks to the clothes being washed and interferes with the cleaning ability of the additional soap. This makes the cleaning of clothes difficult.
Q 18. What is hydrogenation? What is its industrial application?
It is a class of chemical reactions in which the net result is addition of hydrogen (H2) to unsaturated organic compounds such as alkenes, alkynes, etc. Hydrogenation is widely applied to the processing of vegetable oils and fats. Complete hydrogenation converts unsaturated fatty acids to saturated ones.
Q 19. Which of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition reactions : C2H5, C3H8, C3H6, C2H2 and CH4
Alkenes and alkynes (unsaturated hydrocarbons) undergo addition reactions. From the above hydrocarbons C2H2 is an alkyne, whereas C3H6 is an alkene. So, C2H2 and C3H6 will undergo addition reactions.
Q 20. Give a test that can be used to differentiate chemically between butter and cooking oil.
Bromine water test can be used to differentiate chemically between butter and cooking oil. Add bromine water to a little of cooking oil and butter taken in separate test tubes.
a. Decolorizing of bromine water by cooking oil (unsaturated compound)
b. Butter (saturated compound) does not decolorize bromine water.
Q 21. Would you be able to check if water is hard by using a detergent?
We would not be able to check whether a sample of water is hard by using a detergent, this is because a detergent forms lather easily even with hard water.
Q 22. A piece of black electrode used in dry cell on strong heating in air gave a colourless gas which turned lime – water milky. What was the material of the electrode?
We know that graphite is used for making the electrodes. So, the piece of black electrode used in the dry cell is made of graphite (which is an allotrope of carbon element). This is confirmed by the fact that the piece of electrode, on strong heating in air, gave a colourless gas carbon dioxide which turned lime- water milky. Thus, the material of the electrode is graphite.
Q 23. Why graphite conducts electricity, but not diamond?
In case of diamond, each carbon atom of a single crystal is surrounded by four other carbon atoms by covalent bonds such that they form four corners of a regular tetrahedron because of four covalent bonds with each carbon atoms there are no free electrons available. Due to the non-availability of free electrons within crystalline structure, diamond acts as a bad conductor of electricity.
In case of graphite, every carbon atom in a single crystal is covalently bonded to three carbon atoms. As each carbon atoms has four valence electrons one valence electron is left free for each carbon atom. These free electrons can be easily made to flow within the crystalline structure of graphite by applying electric potential. Thus, graphite is a good conductor of electricity.
Q 24. Write three important uses of ethanol.
Ethanol is used as a solvent to dissolve varnishes, medicines and other organic compounds
It is used as beverage (for drinking as an intoxicant) in different forms viz; Brandy, Whisky etc.
It is used for industrial uses in the name of denatured spirit.
Q 25. State what you will observe when sugar crystals is heated strongly. State what you will observe when sugar crystals is treated with conc. Sulphuric acid ?
The sugar crystal will initially melt. Gradually, they turn brown and start swelling up. They give off large amount of steam. Finally black porous residue of carbon is left behind.
The sugar crystals will initially turn brown. Lot of frothing takes place with the evolution of large amount of heat and steam is given off. Finally a black porous residue of carbon is left behind.
Q 26. How are the molecules of aldehyde and Ketone structurally different?
In aldehyde, the carbon atom of the carbonyl group is attached to one alkyl group (R) and one hydrogen atom but in ketone, the carbonyl group is attached to two alkyl groups.
Q 27. What change has been made in the composition of detergents to make them biodegradable?
Detergents made from long chain hydrocarbons having the minimum branching in their molecules are degraded more easily.
Q 28. A hydrocarbon molecule contains 4 hydrogen atoms. Give its molecular formula, if it is an:
(i) alkane, (ii) alkene (iii) alkyne.
i) An alkane containing 4 hydrogen atoms in its molecule is methane, CH4 .
(ii) An alkene containing 4 hydrogen atoms in its molecule is ethane, C2H4
(iii) An alkyne containing 4 hydrogen atoms in its molecule is propane, C3H4
Q 29. Why common salt is added in soap making?
Common salt is added to the mixture to make the soap come out of solution. Though most of the soap separates out on its own but some of it remains in solution. Common salt is added to precipitate out all the soap from the aqueous solution. Actually, when we add common salt to the solution, then the solubility of soap present in it decreases, due to which all the soap separates out from the solution in the form of a solid.
Q 30. What is meant by denatured alcohol? What is the need to denature alcohol?
The alcohol which is rendered unit by mixing it with some poisonous substances, such as methanol, pyridine, copper sulphate, etc is known as denatured alcohol. Ethanol is an important industrial chemical. Therefore, it subjected to very small excise duty. To prevent its misuse for drinking purpose, there is a need to denature alcohol.
Q 31. What is meant by the term “functional group”?
A functional group in an organic compound is an atom or a group of atoms binded together in a unique fashion, which is usually the site of chemical reactivity in an organic molecule.
Q 32. Give a chemical test to distinguish between Ethane and Ethene.
Ethene decolorizes the yellow colour of bromine water while ethane does not.
Q 33. Which organic compound is added to make ethanol unfit for drinking purposes? What is the name of the mixture formed?
Methanol which is highly poisonous is added to make ethanol unfit for drinking purpose. The mixture is called methylated spirit or denatured alcohol.
Q 34. What are the properties of carbon which lead to huge number of carbon compounds we see around us?
(i) Self linking property called catenation
(ii) Carbon is tetravalent and can readily unite with atoms like hydrogen, oxygen etc by electron sharing.
Q 35. Why conversion of ethanol into ethanoic acid is an oxidation reaction?
Ethanoic acid has one O2, atom more and two hydrogen atoms less then ethanol. And loss of hydrogen is known as oxidation and gain of oxygen is known as oxidation. Therefore it is an oxidation reaction.
Q 36. A mixture of ethyne and oxygen is used for welding. Can you justify why a mixture of ethyne and air is not-used?
When ethyne is burnt in oxygen, large quantity of heat and light is produced. The heat evolved can be used for gas welding which is used for welding broken pieces of articles. As air contains a mixture of nitrogen and oxygen and nitrogen which is more in amount does not support combustion. Therefore it is always better to use oxygen for the combustion of ethyne.
Q 37. Why CHO group cannot be present in the middle of the carbon atom chain?
The CHO group is a terminal functional group since three valencies of the C-atom are already satisfied, so this group cannot be present in the middle of the chain.
Q 38. What would be the electron dot structure of carbon dioxide which has the formula of CO2?
Q 39. What would be the electron dot structure of a molecule of sulphur which is made up of eight atoms of sulphur?
Q 40. What is the role of concentrated H2SO4 in the esterification reaction?
In an esterification reaction a carboxylic acid reacts with alcohol to form ester and water in the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid. This reaction is reversible and this reverse reaction is called ester hydrolysis.
Concentrated sulphuric acid being a strong dehydrating agent removes water from the reaction mixture. As a result, the reaction proceeds only is the forward direction to form ester.