Important Questions For Class 9 based on Graphs.
Class 9 Science Extra Questions click here :-
CBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions With Answers
Q 1 – From the given v-t graph, it can be inferred that the object is (1 Marks)
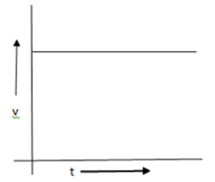
(a) At rest
(b) In uniform motion
(c) Moving with uniform acceleration
(d) In non-uniform motion
Ans – (b) In uniform motion
Q 2 – A particle is moving in a circular path of radius r . (1 Marks)
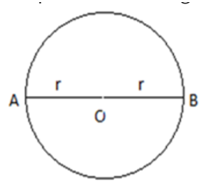
The displacement after half a circle would be:
(a) Zero
(b) πr
(c) 2r
(d) 2πr
Ans – (c) 2r
Q 3 – Which of the following statement is correct regarding the velocity and speed of a moving body? (1 Marks)
(a) Velocity of a moving body is always higher than its speed
(b) Speed of a moving body is always higher than its velocity
(c) Speed of a moving body is its velocity in a given direction
(d) Velocity of a moving body is its speed in a given direction
Ans – (d) Velocity of a moving body is its speed in a given direction
Q 4 – When a car driver travelling at a speed of 10 m/s applies brakes and brings the car to rest in 20 s, then the retardation will be: (1 Marks)
(a) + 2 m/s2
(b) – 2 m/s2
(c) – 0.5 m/s2
(d) + 0.5 m/s2
Ans – (d) + 0.5 m/s2
Q 5 – The speed–time graph of a car is given here. Using the data in the graph calculate the total distance covered by the car. (1 Marks)
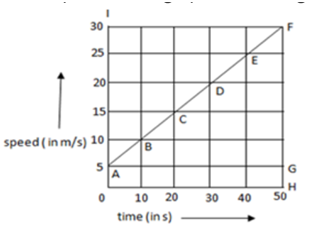
(a) 1250 m
(b) 875 m
(c) 1500 m
(d) 870 m
Ans – (b) 875 m
Important Questions For Class 9
Q 6 – In which of the following cases of motions, the distance moved and the magnitude of the displacement are equal? (1 Marks)
i. If the car is moving on a straight road
ii. If the car is moving in circular path
iii. The pendulum is moving to and fro
iv. The earth is moving around the sun
(a) only (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) only (i)
Ans – (d) only (i)
Q 7 – If the velocity of an object changes from an initial value u to the final value v in time t, the acceleration a will be: (1 Marks)
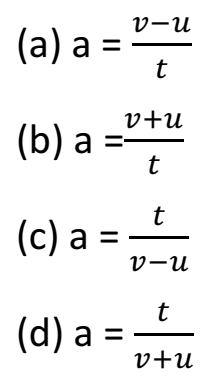
Ans :-
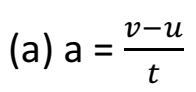
Q 8 – A body is thrown vertically upward with velocity u, the greatest height h to which it will rise is: (1 Marks)
(a) u/g
(b) u2 /2g
(c) u2 /g
(d) u/2g
Ans – (b) u2 /2g
Q 9 – Fill in the blanks. (1 Marks)
1) Newton’s ________ law is based on the concept of inertia.
2) _______ and ______ laid down the scientific foundation of concept of motion.
Ans-
a) First
b) Galileo, Newton
Important Questions For Class 9
Q 10 – State whether distance is a scalar or a vector quantity. (1 Marks)
Ans – Distance is a scalar quantity as it does not include any direction in its representation.
Q 11 – What name is given to the speed in a specified direction ? (1 Marks)
Ans – Velocity
Q 12 – Name the physical quantity obtained by dividing ‘Distance traveled’ by ‘Time taken’ to travel that distance. (1 Marks)
Ans – Speed
Q 13 – Under which condition can a body travel a certain distance and yet its resultant displacement be zero? (1 Marks)
Ans – If the body travels a certain distance and then returns back to its starting position its resultant displacement is zero.
Q 14 – What is the acceleration of a body moving with uniform velocity ? (1 Marks)
Ans – If a body is moving with uniform velocity, acceleration is zero. The so–net force acting on it will be also zero. But the body has energy due to its constant motion.
Important Questions For Class 9
Q 15 – What type of motion is exhibited by a freely falling body ? (1 Marks)
Ans – Uniformly accelerated motion
Q 16 – A body goes around the sun with constant speed in a circular orbit. Is the motion uniform or accelerated? (1 Marks)
Ans – The motion is always accelerated as the direction keeps on changing. So the motion is accelerated. It is Uniform circular motion.
Q 17 – Give one example of a motion where an object does not change its speed but its direction of motion changes continuously. (1 Marks)
Ans – Uniform circular motion in which an object moves on the circular path with constant speed, but its direction keeps changing from its position to the center of the circular path.
Q 18 – What can you say about the motion of a body whose distance-time graph is a straight line parallel to the time axis ? (1 Marks)
Ans – As it is parallel to the time axis means it passes through only one point in the y-axis (or velocity axis). This means that velocity is constant over the time interval. And as the slope is zero (also velocity constant), so acceleration is zero.
Important Questions For Class 9
Q 19 – (a) What term is used to denote the change of velocity with time?
(b) Give one word which means the same as ‘moving with a negative acceleration’.
(c) The displacement of a moving object in a given interval of time is zero. Would the distance traveled by the object also be zero? Give reason for your answer. (2 Marks)
Ans – a) Acceleration is the term used to denote the change in velocity with time.
b) Retardation or Deceleration means the same as moving with a Negative Acceleration.
c) No, the Distance travelled by the moving body can never be 0. But the displacement can be 0.
Q 20 – A motorcyclist drives from place A to B with a uniform speed of 30 km h-1 and returns from place B to A with a uniform speed of 20 km h-1. Find his average speed. (2 Marks)
Ans – Let distance between A and B is D
Then, time taken by motorcyclist with uniform speed 30 km/h ,
T₁ = distance/speed = D/30 hrs
Again, they return with uniform speed 20 km , so time taken by motorcyclist,
T₂ = D/20 hrs
Now, average speed of motorcyclist = total distance/total time taken
= (D + D )/(D/30 + D/20) km/h
2 × 30 × 20/(30 + 20) km/h
= 24 km/h
Important Questions For Class 9
Q 21 – If a bus traveling at 20 m/s is subjected to a steady deceleration of 5 m/s2, how long will it take to come to rest? (2 Marks)
Ans – For the bus,
Initial Velocity, u = 20 m/s
Final Velocity, v = 0 m/s
Acceleration, a = – 5m/s² (minus sign because of deceleration)
Time, t = (?)
We know that,
a = (v – u) / t
t = (v – u) / a t = (0 – 20) / (–5)
t = (–20) / (–5)
∴ t = 4s
Thus, the bus will take 4 seconds to stop.
Q 22 – Write the formula to calculate the speed of a body moving along a circular path. Give the meaning of each symbol that occurs in it. (2 Marks)
Ans – In order to calculate the speed of the body along a circular path, one should divide the circumference of the circle by the time (t) taken to traverse the circle.
Therefore the total circumference of the circle =2 x π x r.
Here pi is the constant with a value of 22 / 7 while r is the radius of the circular path.
therefore, the final formula velocity v= (2 x π x r) / t
Important Questions For Class 9 updated 2021….
Q 23 – State an important characteristic of uniform circular motion. Name the force which brings about uniform circular motion. (2 Marks)
Ans – In a circular motion, the heading of the object changes at each point. Along these lines, the speed of the object likewise changes. Thus, the speed of an object moving at a uniform speed along the round way changes constantly.
Since the changing speed offers the ascend to increasing speed, the uniform circular motion is a case of a consistently quickened movement.
In a uniform circular motion, an object is quickened by altering just its course and not its size. Centripetal force is in charge of an object move along a circular way.
Q 24 – Describe the motion of a body that is accelerating at a constant rate of 10ms–2. If the body starts from rest how much distance will it cover in 2 s ? (2 Marks)
Ans – As the body is moving in constant acceleration, the motion of the body is linear.
If the body starts from rest means its initial velocity is zero which is represented mathematically as u = 0.
The acceleration is constant i.e. a = 10 m/s 2 and the time covered will be t = 2s.
So provided the data’s such as initial velocity, acceleration and time covered given, the distance covered in 2s can be calculated using the Newton’s third equation of motion, i.e
x = ut + 1/2 at2 …. (1)
By substituting the known values in (1), we get
x = (0 x 2) + (1/2 x 10 x 22 )
∴ x = 20 m
Thus, the distance covered by the body in 2s is 20 meters.
Important Questions For Class 9
Q 25 – A train starting from rest moves with a uniform acceleration of 0.2 m/s2 for 5 minutes. Calculate the speed acquired and the distance traveled in this time. (2 Marks)
Ans –Initial speed, u = 0
time taken = 5 min = 300 s
let final speed = v
then, use kinematics equation ,
v = u + at
= 0 + 0.2 × 300 = 60 m/s
and let the distance travelled = S
using formula,
S = ut + 1/2at2
0 x 300 + 1/2 × 0.2 × (300)2
0.1 × 90000
= 9000 m
= 9 km
Q 26 – The distance between Delhi and Agra is 200 km. A train travels the first 100 km at a speed of 50 km/h. How fast must the train travel the next 100 km, so as to average 70 km/h for the whole journey? (3 Marks)
Ans – Given,
The total distance = 200 km
Let, total time be ‘t’ hours
speed of train for the first 100 km is 50km/h
time taken for the first 100km (t1) = distance / speed = [100km / (50km/h)] = 2 hours
Average speed = total distance/total time taken
= total distance (s1 + s2) / total time (t1 + t2)
where, s2 = next 100 km traveled by train.
t2 = time taken to travel next 100 km
∴70 km/hr = 200 km / (2 + t2) hours
70 = 200 / (2 + t2)
140 + 70 t2 = 200
70t2 = 60
t2 = 60 / 70
t2 = 6 / 7 hours.
∴ speed required by train to travel next 100 km so as to attain 70km / h average speed is:
speed (v2) = distance / time
100km / (60 / 70)
= 700/6
= 116.67 km/hr
Important Questions For Class 9
Q 27 – (a) Derive the formula : ν = u + ɑt, where the symbols have usual meanings.
(b) A bus was moving at a speed of 54 km/h. On applying brakes it stopped in 8 seconds. Calculate the acceleration. (3 Marks)
Ans – a) Let u be the initial velocity
v = Final velocity
In the velocity-time graph , the particles increase their speed from u in t = 0 to in t = t
So, we can write an expression for acceleration as
a = (v – u) / (t – 0)
a = ( v – u ) / t
at = v – u
v = u + at
b) Initial speed ( u ) = 54 km/hr = 54 x 1000 m/ 3600 s = 54 x 5/18 = 15 m/s
( 1 km = 1000 m and 1 hr = 60 min = 60 x 60 sec = 3600 sec )
Time = 8 sec .
Final velocity ( V ) = 0
We know that ,
v = u + at
0 = 15 + a x 8
0 = 15 + 8a
a = –15/8 m/s²
Therefore , acceleration is –15/8 m/s² also ,
S = ut + 1/2at2
S = 15 x 82 + 1/2 x ( –15/8) x 8²
15 x 64 – 15 x 4
= 15( 64 – 4 )
= 15(60)
S = 900 m
Hence stopping distance traveled before stopping is 900 m .
Important Questions For Class 9
Download PDF Important Questions For Class 9 Science Motion Chapter 8