Light Reflection and Refraction For Class 10 Physics Important Questions
Q 1 – Magnifying power of a concave lens is
a. always > 1
b. always < 1
c. always = 1
d. can have any value
Ans. b. always < 1
Q 2 – If the power of a lens is – 2 D, what is its focal length?
a. +50 cm
b. 100 cm
c. 50 cm
d. +100 cm
Ans. c. 50 cm
Q 3 – A spherical mirror and a spherical lens each have a focal length of 10 cm.
The mirror and the lens are likely to be
a. both concave
b. both convex
c. the mirror is concave and the lens is convex
d. the mirror is convex and the lens is concave
Ans. a. both concave
Q 4 – When the object is placed between f and 2f of a convex lens, the image formed is
a. at f
b. at 2f
c. beyond 2f
d. between O and f
Ans. c. beyond 2f
Q 5 – A point object is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a convex mirror of focal
length 20 cm. The image will form at:
a. at infinity
b. at focus
c. at the pole
d. behind the mirror
Ans. d. behind the mirror
Q 6 – A student does an experiment on tracing the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab for different angles of incidence. He can get a correct measure of the angle of incidence and the angle of emergence by following the labeling indicated in figure:
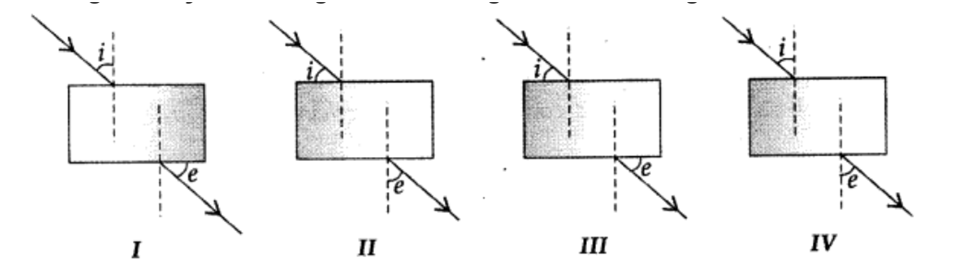
a. I
b. II
c. III
d. IV
Ans. d. IV
Q 7 – Fill in the Blanks:
1. Light shows the phenomena of reflection, refraction and ___________ based
on the _________ nature of light.
2. The speed of light in vacuum is________
3. A ________ lens will always give a virtual, erect and diminished image,
irrespective of the position of the object.
4. A positive sign in the value of magnification indicates that the image is
________
5. A ________ mirror is used as a head mirror by the doctors to concentrate
light on the body parts to be examined.
6. No matter how far you stand from a spherical mirror, your image appears
erect. The mirror may be _______ .
Ans. 1. Dispersion
2. 3 x 108 m/s
3. Concave
4. virtual
5. Concave
6. plane or convex mirror
Q 8 – Beams of light are incident through the holes A and B and emerge out of the box through the holes C and D respectively as shown in the figure. Which of the following could be inside the box?
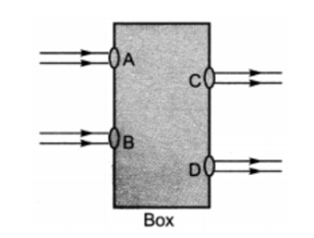
a. A rectangular glass slab
b. A convex lens
c. A concave lens
d. A prism
Ans. a. A rectangular glass slab
Since lateral displacement is taking place in the parallel rays, a rectangular glass slab could be inside the box. Lateral displacement is the distance by which the incident light has been displaced after bending through the glass slab.
Q 9 – A student obtains a sharp image of the distant window (W) of the school laboratory on the screen (S) using the given concave mirror (M) to determine its focal length. Which of the following distances should he measure to get the focal length of the mirror?
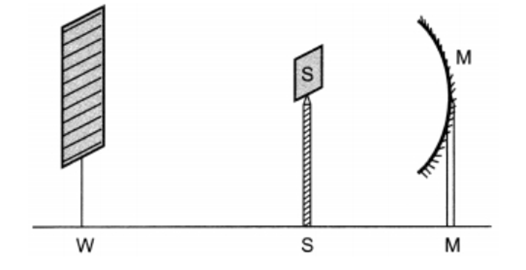
a. MW
b. MS
c. SW
d. MW- WS
Ans. b. MS
The concave mirror forms the image of the distant object at its focus. MW is the object distance while MS is the image distance which is equal to the focal length of the mirror. To determine the focal length of the mirror, the student needs to measure MS.
Q 10 – Which of the following statements is true?
a. A convex lens has 4 dioptre power having a focal length 0.25 m
b. A convex lens has -4 dioptre power having a focal length 0.25 m
c. A concave lens has 4 dioptre power having a focal length 0.25 m
d. A concave lens has -4 dioptre power having a focal length 0.25 m.
Ans. a. A convex lens has 4 dioptre power having a focal length 0.25 m
Q 11 – Rays from Sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed so that size of its image is equal to the size of the object?
a. 15 cm in front of the mirror
b. 30 cm in front of the mirror
c. between 15 cm and 30 cm in front of the mirror
d. more than 30 cm in front of the mirror
Ans. b. 30 cm in front of the mirror
The ray diagram illustrates that, in the case of a concave mirror, the image size becomes equal to the object size when the object distance equals the radius of curvature, i.e, twice the focal length. So, the object has to be placed at a distance of (15 2) = 30 cm in front of the concave mirror.
Q 12 – In torches, search lights and headlights of vehicles the bulb is placed
a. between the pole and the focus of the reflector
b. very near to the focus of the reflector
c. between the focus and centre of curvature of the reflector
d. at the centre of curvature of the reflector
Ans. b. very near to the focus of the reflector
Q 13 – You are given water, mustard oil, glycerine and kerosene. In which of these media a ray of light incident obliquely at same angle would bend the most?
a. Kerosene
b. Water
c. Mustard oil
d. Glycerine
Ans. d. Glycerine
Glycerine
Refractive index for water, mustard oil, glycerine and kerosene are:
μw =1.33 , μm=1.47, μg =1.473, μk =1.44
Since refractive index of glycerine is highest, ray bends the most in case of glycerine.
Q 14 – Which of the following ray diagrams is correct for the ray of light incident on a concave mirror as shown in figure?
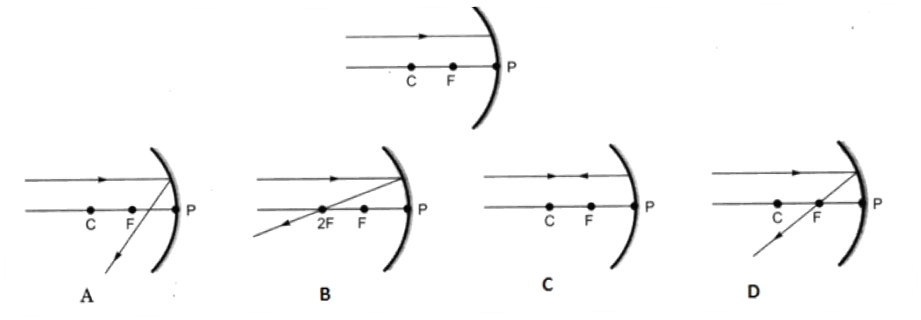
a. Fig. A
b. Fig. B
c. Fig. C
d. Fig. D
Ans. d. Fig. D
Q 15 – A child is standing in front of a magic mirror. She finds the image of her head bigger, the middle portion of her body of the same size and that of the legs smaller. The following is the order of combinations for the magic mirror from the top.
a. Plane, convex and concave
b. Convex, concave and plane
c. Concave, plane and convex
d. Convex, plane and concave
Ans. c. Concave, plane and convex
Q 16 – How far should an object be placed from a convex lens of focal length 20 cm to obtain its image at a distance of 30 cm from the lens? What will be the height of the image if the object is 6 cm tall?
Ans.

Q 17– A 4 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 24 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 16 cm. Find the position, size and nature of the image formed, using the lens formula.
Ans.

Q 18 – In an experiment with a rectangular glass slab, a student observed that a ray of light incident at an angle of 55° with the normal on one face of the slab, after refraction strikes the opposite face of the slab before emerging out into air making an angle of 40° with the normal. Draw a labeled diagram to show the path of this ray. What value would you assign to the angle of refraction and angle of emergence?
Ans.
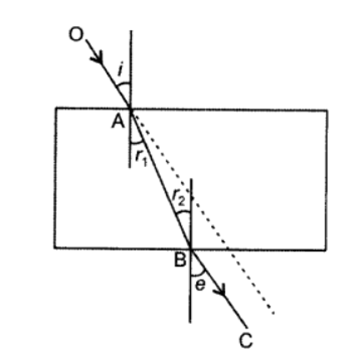

Q 19 – State the law of refraction of light that defines the refractive index of a medium with respect to the other. Express it mathematically. How is refractive index of any medium ‘A’ with respect to a medium ‘B’ related to the speed of propagation of light in two media A and B? State the name of this constant when one medium is vacuum or air. The refractive indices of glass and water with respect to vacuum are 3/2 and 4/3 respectively. If the speed of light in glass is 2 x 108 m/s, find the speed of light in (i) vacuum, (ii) water.
Ans. Snell’s law: The ratio of sine of angle of incidence (i.e. sin i) to the sine of angle of refraction (i.e. sin r) is always constant for the light of given colour and for the given pair of media.

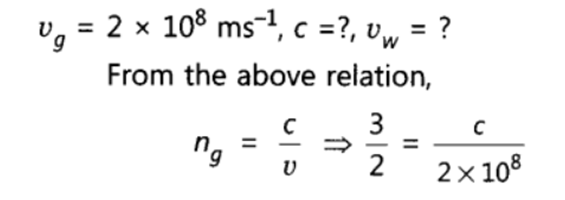
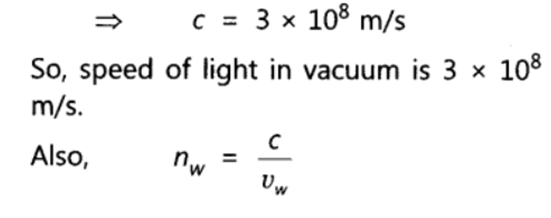
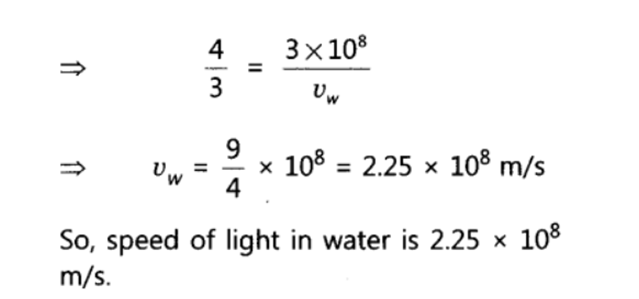
Q 20 – What is the principle of reversibility of light? Show that the incident ray of light is parallel to the emergent ray of light when light falls obliquely on a side of a rectangular glass slab.
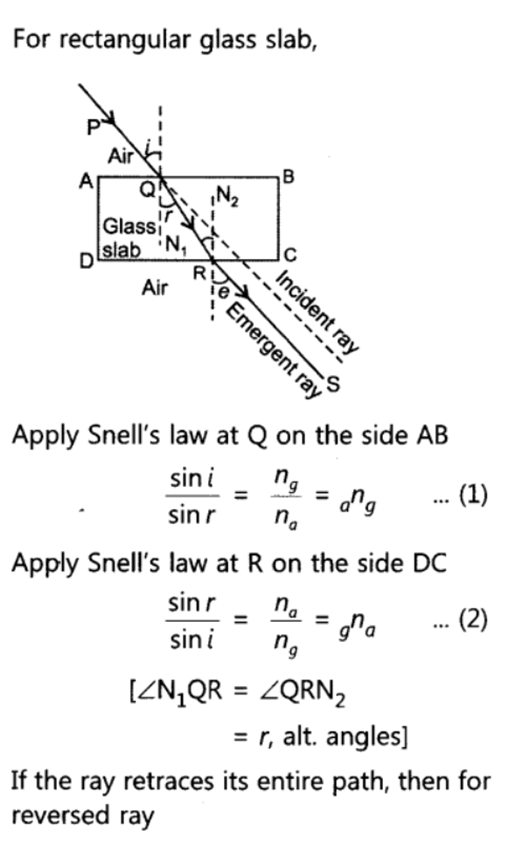

Hence incident ray PQ is parallel to the emergent ray RS when light falls obliquely on a side of a rectangular glass slab.