Magnetic Effects of Electric Current For Class 10 Physics Important Questions
Q 1 – A current through a power line flows from south to North direction. The direction of magnetic field line 0.5m above it is
(a) North
(b) South
(c) West
(d) East
Ans. (c) West, Apply right-hand thumb rule.
Q 2 – When current is parallel to magnetic field, then force experience by the current carrying conductor placed in uniform magnetic field is
(a) Twice to that when angle is 60°
(b) Thrice to that when angle is 60°
(c) zero
(d) infinite
Ans. (c) Zero.
Q 3 – A magnet is moved towards a coil (i) quickly (ii) slowly. The induced potential difference
(a) more in (i) than in (ii) case
(b) more in (ii) than in (i) case
(c) same in both
(d) can’t say
Ans. (a) more in (i) than in (ii) case
Q 4 – Direction of rotation of a coil in electric motor is determined by
(a) fleming’s right hand rule
(b) fleming’s left hand rule
(c) faraday law of electromagnetic inductors
(d) None of above
Ans. (b) fleming’s left hand rule
Q 5 – If the key in the given arrangement is Closed (the circuit is made closed) and magnetic field lines are drawn over the horizontal plane ABCD, the lines are
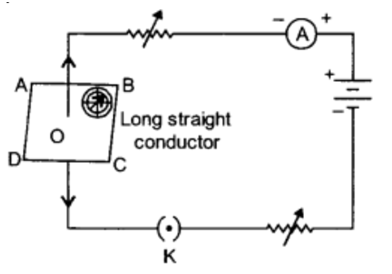
(a) concentric circles
(b) elliptical in shape
(c) straight lines parallel to each other
(d) concentric circles near the point O but of elliptical shapes as we go away from it
Ans. (b) fleming’s left hand rule
Q 6 – Who has stated the Right hand Thumb Rule?
(a) Orsted
(b) Fleming
(c) Einstein
(d) Maxwell
Ans. (d) Maxwell
Q 7 – In the following Questions, the Assertion and Reason have been put forward.
Read the statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following:
(a) Both the Assertion and the Reason are correct and the Reason is the correctexplanation of the Assertion.
(b) The Assertion and the Reason are correct but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but the Reason is false.
(d) The statement of the Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
- Assertion: Only a change in magnetic field lines linked with coil will induce current in the coil.
Reason: The presence of large magnetic flux through the coil maintains a current in a closed circuit coil. - Assertion: Fuse is a safety device which is installed to prevent electrical circuits and possible fires.
Reason: Fuse consist of tin-plated copper wire having low melting point, which melts and breaks the circuit if the current exceeds a safe value.
Ans. 1. (c) Assertion is true but the Reason is false.
2. (a) Both the Assertion and the Reason are correct and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
Q 8 – Identify the poles of the magnet in the given figure.
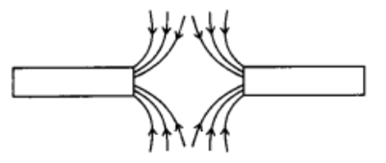
Ans. Both the poles facing each other represent south pole in nature as the magnetic field lines outside the magnet move from North to South Poles.
Q 9 – Fill in the Blanks:
- The magnetic field of a solenoid carrying a current is similar to that of a bar magnet.
- The direction of magnetic force acting on a charged particle moving in a magnetic field can be found by Fleming’s left hand rule
Q 10 – Relative strength of magnetic field at a point in the space surrounding the magnet is shown by the
(a) length of magnet
(b) thickness of magnet
(c) degree of closeness of the field.
(d) resistance offered by the surroundings
Ans. (c) degree of closeness of the field, The force acting on the pole of another magnet by the crowded magnetic field lines is greater.
Q 11 – What should be the core of an electromagnet?
a. soft iron
b. hard iron
c. rusted iron
d. none of above
Ans. a. soft iron
Q 12 – What is that instrument which can detect the presence of electric current in a circuit?
a. galvanometer
b. motor
c. generator
d. none of above
Ans. a. galvanometer
Q 13 – An alpha particle is diverted towards west is deflected towards north by a field. The field is magnetic. What will be the direction of field?
a. Towards south
b. towards east
c. downward
d. upward
Ans. a. galvanometer
Q 14 – Define Electromotive force.
Ans. The motion of a magnet, with respect to the coil, produces an induced potential ‘difference. This induced potential difference is called electromotive force which sets up an induced electric current in the circuit. The motion of a magnet, with respect to the coil, produces an induced potential difference.
Q 15 –The axis of earth’s magnetic field is inclined at an angle of about ______ with the geographical axis .
Ans. The axis of earth’s magnetic field is inclined at an angle of about 15 with the geographical axis .
Q 16 – What type of core should be put inside a current-carrying solenoid to make an electromagnet?
Ans. A soft iron core is placed inside a solenoid to make an electromagnet. When a soft iron core is placed inside a solenoid, then the strength of the magnetic field becomes very large because the iron core gets magnetized by induction. This combination of a solenoid and a soft iron core is called an electromagnet.
Q 17 – Explain why two magnetic lines of force do not intersect.
Ans. The magnetic lines of force do not intersect one another due to the fact that the resultant force on a north pole at any point can be only in one direction. But if the two magnetic lines of force intersect one another, then the resultant force on a north pole placed at the point of intersection will be along with directions, which is not possible.
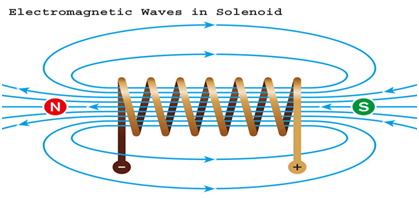
Q 18 – Distinguish between a solenoid and a bar magnet. Draw the magnetic lines for both.
Ans. Solenoid :
1. A Solenoid is a long coil containing a large number of close turns of insulated copper wire.
2. Solenoid needs electricity for creating magnetic field around it.
Bar magnet :
1. It is a long, rectangular bar of uniform cross-section which attracts the pieces of iron, nickel, and cobalt.
2. Bar magnet does not need electricity for creating magnetic Field around it.
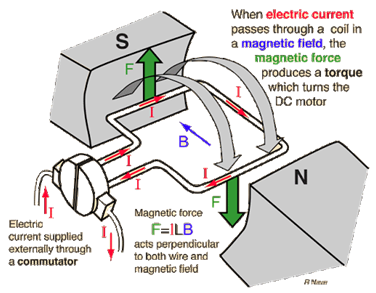
Q 19 – Explain the principle, construction and working of a DC Motor.
Ans. An electric motor is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
Electric motors and their functions:
- A power supply – In general, a simple motor has a DC power source. It provides power for the armature of the motor or field coils.
- Field Magnet (can be a permanent magnet or an electromagnet) – The magnetic field by virtue of Fleming’s left-hand law, helps to produce a torque on the rotating armature coil.
- An Armature or rotor – Maintains the position of the armature coil and provides mechanical support.
- Commutator – It is the Armature Coil revolving interface with a stationary circuit.
- Armature Coil – Supporting the engine to run.
- Brushes – It is a system that conducts current between stationary wires and moving parts, mostly rotating shafts.
- Axle
Working principle of electric motors
The working of an electric motor is based on the assumption that a conductive current generates a magnetic field around it. Consider the following situation,Take two bar magnets, and leave a small space between the poles facing each other. Now, take a small conductive wire length and make a loop. Keep this connection between the magnets, so that it is still inside the magnet’s area of influence. Now for the final part. Attach loop ends to battery terminals.
As electricity flows through your simple circuit, you will find that your loop “moves.” The magnet’s magnetic field interferes with that generated by the conductor’s electrical current flow. Because the loop has become a magnet, it will draw one side of it to the magnet’s north pole, and the other to the south pole. That causes the loop to rotate continuously. This is the idea of an electric motor working.
The space surrounding a magnet in which magnetic force is exerted, is called a magnetic field. Magnetic field lines are the lines that are drawn at every point indicating the direction in which a north pole would move if placed at that point.
Q 20 – What are magnetic field lines? How is the direction of a magnetic field at a point determined? Mention two important properties of the magnetic field lines.
Ans. The space surrounding a magnet in which magnetic force is exerted, is called a magnetic field. Magnetic field lines are the lines that are drawn at every point indicating the direction in which a north pole would move if placed at that point.
Some important properties of magnetic field lines are;
(i) The tangent drawn at any point on the field line indicates the direction in which a north pole would move if placed at that point.
(ii) The relative strength of the field is proportional to the degree of closeness of the lines. The more clustered they are, the stronger the field in that region.
(iii) The magnetic field lines never intersect. This is because a pole can move only in zone direction and if the lines intersect they would have to move in two direction simultaneously which is impossible.
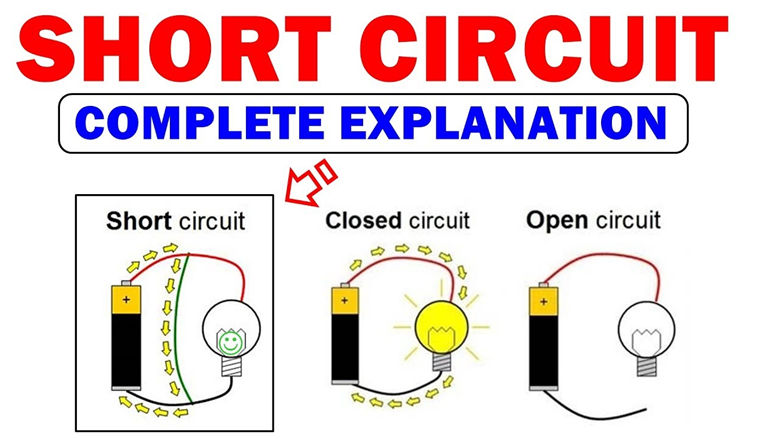
Q 21 – Explain what is short-circuiting and overloading in an electric supply.
Ans. Short circuiting
- If the plastic insulation of the live wire and neutral wire gets torn, then the two wires touch each other.
- This touching of the live wire and neutral wire directly is known as short-circuiting.
- The current passing through the circuit formed by these wires is very large and consequently a high heating effect is created which may lead to fire.
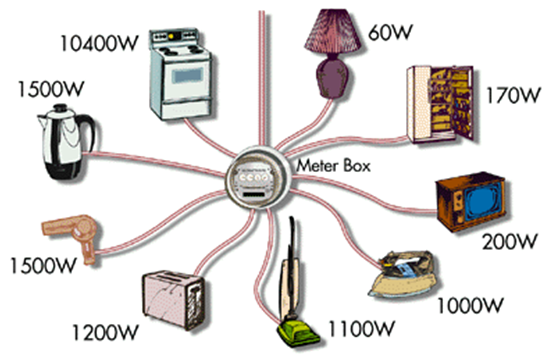
Overloading
- The current flowing in domestic wiring at a particular time depends on the power ratings of the appliances being used.
- If too many electrical appliances of high power rating are switched on at the same time, they draw an extremely large current from the circuit. This is known as overloading.
- Due to this large current flowing through them, the copper wires of household wiring get heated to a very high temperature and may lead to fire.
Q 22 – Which of the following circuits will be dangerous even if the fuse blows off and electric iron stops working during a short circuit ?
Ans. Circuit A is not dangerous after fuse blows because fuse is in live wire; Circuit B is dangerous even if fuse blows because the fuse is in neutral wire.