Q 1 – Magnetic field is produced by:
(a) electrostatic point charge
(b) only electric current
(c) only bar magnet
(d) bar magnet and electric current both
(d) bar magnet and electric current both
Q 2 – Choose the incorrect statements from the following regarding magnetic lines of field.
(a) the direction of magnetic field at a point is taken to be the direction in which the north pole of a magnetic compass needle points
(b) magnetic field lines are closed curves
(c) if magnetic field lines are parallel and equidistant, they represent zero-field strength
(d) relative strength of magnetic field is shown by the degree of closeness of the field lines.
(c) if magnetic field lines are parallel and equidistant, they represent zero field strength
Q 3 – Unit of intensity of magnetic ¦eld is:
(a) Tesla
(b) Ohm
(c) Ampere
(d) Volt-ampere
Q 4 – If the key in the arrangement figure given below is taken out (the circuit is made open) and magnetic . field lines are drawn over the horizontal plane ABCD, the lines are
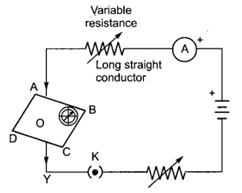
(a) concentric circles
(b) elliptical in shape
(c) straight lines parallel to each other (Due to earth’s magnetic field)
(d) concentric circles near the point O but of elliptical shapes as we go away from it.
(b) Concave
Q 5 – Unit of magnetic field intensity is:
(a) newton/(ampere-metre )
(b) newton/(ampere-metre)
(c) newton-ampere-metre
(d) newton2 /(ampere-metre)
(b) newton/(ampere-metre)
Q 6 – A circular loop placed in a plane perpendicular to the plane of paper carries a current when the keys are ON. The current as seen from points A and B (in the plane of the paper and on the axis of the coil) is anticlockwise and clockwise respectively. The magnetic field lines point from B to A. The N-pole of the resultant magnet is on the faces close to

(a) A
(b) B
(c) A if the current is small, and B if the current is large
(d) B if the current is small and A if the current is large.
(a) A
Q 7 – In following which is not unit of magnetic ¦eld:
(a) weber/m2
(b) tesla
(c) gauss
(d) newton/ampere2
(d) newton/ampere2
Q 8 – For a current in a long straight solenoid, N- and S-poles are created at the two ends. Among the following statements, the incorrect statement is
(a) the field lines inside the solenoid are in the form of straight lines which indicates that the magnetic field is the same at all points inside the solenoid
(b) the strong magnetic field produced inside the solenoid can be used to magnetize a piece of a magnetic material like soft iron when placed inside the coil
(c) the pattern of the magnetic field associated with the solenoid is different from the pattern of the magnetic field around a bar magnet
(d) the N- and S-poles exchange position when the direction of current through the solenoid is reversed.
(c) the pattern of the magnetic field associated with the solenoid is different from the pattern of the magnetic field around a bar magnet.
Q 9 – An electron is moving in a uniform magnetic ¦eld perpendicularly with velocity v. The force exerts on the electron will be:
(a) ev/B
(b) eve
(c) eB/v
(d) vB/e
(b) eve
Q 10 – In the arrangement shown in the figure there are two coils wound on a non-conducting cylindrical rod. Initially, the key is not inserted. Then the key is inserted and later removed.
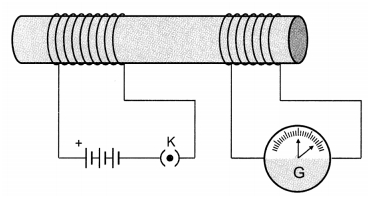
(a) the deflection in the galvanometer remains zero throughout.
(b) there is a momentary deflection in the galvanometer but it dies out shortly and there is no effect when the keys are removed.
(c) there are momentary galvanometer deflections that die out shortly; the deflections are in the same direction.
(d) there are momentary galvanometer deflections that die out shortly; the deflection is in opposite directions.
(d) there are momentary galvanometer deflections that die out shortly; the deflection is in opposite directions.
Q 11 – A current-carrying conductor is placed in between the poles of the stable magnetic ¦eld. The direction of force acting on the conductor
is given by the law:
(a) Maxwell’s Cark-screw rule
(b) Fleming’s Right-hand rule
(c) Fleming’s left-hand rule
(d) Ohm’s law.
(b) Fleming’s Right-hand rule
Q 12 – Choose the incorrect statement
(a) Fleming’s right-hand rule is a simple rule to know the direction of induced current.
(b) The right-hand thumb rule is used to find the direction of magnetic fields due to current-carrying conductors.
(c) The difference between the direct and alternating currents is that the current always flows in one direction, whereas the alternating current reverses its direction periodically.
(d) In India, the AC changes direction after every 1/50 second.
(d) In India, the AC changes direction after every 1/50 second.
Q 13 – Intensity of magnetic ¦eld due to current carrying solenoid depends on:
(a) nature of the material of the core
(b) the magnitude of electric current
(c) number of turns in the coil
(d) all the above
(d) all the above
Q 14 – A constant current flows in a horizontal wire in the plane of the paper from east to west as shown in the figure. The direction of the magnetic field at a point will be North to South
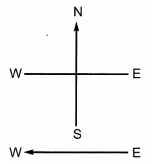
(a) directly above the wire
(b) directly below the wire
(c) at a point located in the plane of the paper, on the north side of the wire
(d) at a point located in the plane of the paper, on the south side of wire.
(b) directly below the wire
Q 15 – Electric motor converts:
(a) chemical energy into electric energy
(b) electric energy into mechanical energy
(c) mechanical energy into electric energy
(d) electric energy into chemical energy.
(d) electric energy into chemical energy.
Q 16 – The strength of magnetic field inside a long current carrying straight solenoid is
(a) more at the ends than at the center
(b) minimum in the middle
(c) same at all points
(d) found to increase from one end to the other
(c) same at all points
Q 17 – Unit of magnetic flux is:
(a) Weber / metre2
(b) Weber
(c) Weber/metre
(d) Weber-metre2
(b) Weber
Q 18 – The most important safety method used for protecting home appliances from short-circuiting or overloading is by
(a) earthing
(b) use of fuse
(c) use of stabilizers
(d) use of the electric meter.
(b) use of fuse
Q 19 – 1 Tesla is equal to:
(a) 1 Weber/m2
(b) 1 Gauss
(c) 10-4 Weber/m2
(d) 10-4 Gauss
(a) 1 Weber/m2
Q 20 – Select the incorrect statement
(а) Magnetic field lines are closed curves
(b) No two field lines can cross each other
(c) Field lines can cross each other
(d) The relative strength of the magnetic field is shown by degree of closeness of the field lines.
(c) Field lines can cross each other
Q 21 – If Ø = magnetic §ux, B = magnetic ¦eld intensity, A = area, then the correct relationship between them is:
(a) B = Ø/A
(b) Ø = B/A
(c) A = BØ
(d) B = ØA
(a) B = Ø/A
Q 22 – Magnetic field lines around a straight conductor forms a pattern of
(a) concentric circles
(b) concentric ellipse
(c) straight line
(d) square shape.
(a) concentric circles
Q 23 – Unit of magnetic flux is:
(a) newton-ampere-metre
(b) newton-metre/ampere
(c) newton/ampere-metre
(d) newton-ampere/metre
(b) newton-metre/ampere
Q 24 – Electric motor is a device that converts
(a) mechanical energy to electrical energy
(b) electrical energy to mechanical energy
(c) chemical energy to mechanical energy
(d) mechanical energy to light energy.
(b) electrical energy to mechanical energy
Q 25 – The magnitude of induced e.m.f. is:
(a) proportional to the rate of change of field lines
(b) proportional to earth’s magnetic field
(c) depend on the material of the coil
(d) inversely proportional to the rate of change of speed of magnet.
(a) proportional to the rate of change of field lines
Q 26 – The direction of the induced current is given by
(a) Fleming’s right-hand rule
(b) Fleming’s left-hand rule
(c) Right-hand thumb rule
(d) Left-hand thumb rule.
(a) Fleming’s right-hand rule
Q 27 – Lenz’s law is based on which conservation law:
(a) charge
(b) mass
(c) momentum
(d) energy
(d) energy
Q 28 – The instrument which converts mechanical energy into electric energy, is:
(a) motor
(b) dynamo
(c) galvanometer
(d) transformer
(b) dynamo
Q 29 – The insulation color of an earth wire is
(a) blue
(b) red
(c) green
(d) white.
(c) green
Q 30 – Dynamo converts:
(a) chemical energy into electric energy
(b) sound energy into magnetic energy
(c) mechanical energy into electric energy
(d) mechanical energy into light energy.
(c) mechanical energy into electric energy.
Q 31 – In India the potential difference between a live wire and the neutral wire is
(a) 240 V
(b) 250 V
(c) 280 V
(d) 220 V.
(d) 220 V
Q 32 – The magnetic field is the strongest at
(a) the middle of the magnet.
(b) north pole.
(c) south pole.
(d) both poles.
(d) both poles.
Q 33 – The material of the core of a strong magnet is
(a) aluminum
(b) soft iron
(c) copper
(d) steel
(b) soft iron
Q 34 – Match the following:
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Right-hand thumb rule | (а) converts electrical energy into mechanical energy |
| 2. Fleming’s left-hand rule | (b) gives the direction of the magnetic field around a conductor |
| 3. Fleming’s right-hand rule | (c) converts mechanical energy into electrical energy |
| 4. Alternating current | (d) gives the direction of the force on current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field |
| 5. Direct current | (e) the direction of current changes periodically |
| 6. Electric motor | (f) gives the direction of induced current |
| 7. Generator | (g) current always flows in one direction. |
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Right-hand thumb rule | (b) gives the direction of the magnetic field around a conductor |
| 2. Fleming’s left-hand rule | (d) gives the direction of the force on current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field |
| 3. Fleming’s right-hand rule | (f) gives the direction of induced current |
| 4. Alternating current | (e) the direction of current changes periodically |
| 5. Direct current | (g) current always flows in one direction. |
| 6. Electric motor | (а) converts electrical energy into mechanical energy |
| 7. Generator | (c) converts mechanical energy into electrical energy |
Q 35 – An electric generator actually acts as
(a) a source of electric charge.
(b) a source of neat energy.
(c) an electromagnet.
(d) a converter of energy.
(d) a converter of energy.
Q 36 – Switches are connected to
(a) live wire.
(b) neutral wire.
(c) earth wire.
(d) any one.
(a) live wire.
Q 37 – Which of the following statement is not correct about the magnetic field?
(a) Magnetic field lines form a continuous closed curve.
(b) Magnetic field lines do not interest each other.
(c) Direction of the tangent at any point on the magnetic field line curve gives the direction of the magnetic field at that point.
(d) Outside the magnet, magnetic field lines go from the South to the North pole of the magnet.
(d) Outside the magnet, magnetic field lines go from South to the North pole of the magnet.
Q 38 – The most important safety method used for protecting home appliances from short-circuiting or Overloading is
(a) earthing
(b) use of stabilizers
(c) use of fuse
(d) use of electric meter
(c) use of a fuse
Q 39 – The nature of magnetic field line passing through the center of current carrying circular loop is
(a) circular
(b) ellipse
(c) parabolic
(d) straight line
(d) straight line
Q 40 – The best material to make permanent magnets is
(a) aluminum
(b) soft iron
(c) copper
(d) alnico
(d) alnico
Q 41 – The strength of each magnet reduces to half when it is cut along its length into the equal parts magnetic field strength of a solenoid. The polarity of the solenoid can be determined by
(a) use of compass needle
(b) Right-hand thumb rule
(c) fleming left-hand rule
(d) either (a) or (b)
(d) either (a) or (b)
Q 42 – When current is parallel to a magnetic field, then force experience by the current-carrying conductor placed in a uniform magnetic field is
(a) Twice to that when the angle is 60°
(b) Thrice to that when the angle is 60°
(c) zero
(d) infinite
(a) Twice to that when the angle is 60°
Q 43 – In an electric motor, to make the coil rotating continuously in the same direction, the current is reversed in the coil after every half rotation by a device called
(a) carbon brush
(b) commutator
(c) slip ring
(d) armature
(b) commutator
Q 44 – The condition for the praenomen of electromagnetic induction is that there must be a relative motion between
(a) the galvanometer and magnet
(b) the coil of wire and galvanometer
(c) the coil of wire and magnet
(d) the magnet and galvanometer
(c) the coil of wire and magnet
Q 45 – A magnet is moved towards a coil (i) quickly (ii) slowly. The induced potential difference
(a) more in (i) than in (ii) case
(b) more in (ii) than in (i) case
(c) same in both
(d) can’t say
(a) more in (i) than in (ii) case
Q 46 – A D.C generator works on the principle of
(a) this law
(b) Joule’s law of heating
(c) faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction.
(d) none of the above
(c) faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction.
Q 47 – Earth wire carries
(a) current
(b) voltage
(c) no current
(d) heat
(c) no current
Q 48 – The main advantage of A.C power transmission over D.C power transmission over long distances is
(a) AC transmit without much loss of energy
(b) less insulation problem
(c) less problem of instability
(d) easy transformation.
(a) AC transmit without much loss of energy
Q 49 – Overloading is due to
(a) Insulation of wire is damaged
(b) fault in the appliances
(c) accidental hike in supply voltage
(d) All of the above
(d) All of the above
Q 50 – Commercial electric motors do not use
(a) an electromagnet to rotate the armature
(b) an effectively large number of turns of conducting wire in the current-carrying coil
(c) a permanent magnet to rotate the armature
(d) a soft iron core on which the coil is wound
(c) a permanent magnet to rotate the armature