Manufacturing Industries For Class 10 Geography Important Questions
Q 1 – What was the aim of establishing industries in tribal and backward areas?
A. Bringing about modern goods
B. bringing down regional disparities
C. eradication of unemployment and poverty
D. Quality production
Ans – B. bringing down regional disparities
Q 2 – In what ratio are iron ore, coking coal and limestone required to make steel?
(a) 4 : 2 : 1
(b) 4 : 1 : 2
(c) 4 : 3 : 1
(d) 4 : 3 : 2
Ans – (a) 4 : 2 : 1
Q 3 – How have the agro-industries in India given a major boost to agriculture?
A. Manufactured irrigation pumps, fertilisers, insecticides, pesticides etc
B. Provided employment
C. Helped in trade
D. Financial help
Ans – A. Manufactured irrigation pumps, fertilisers, insecticides, pesticides etc
Q 4 – What is the Industry to market chain ?
A. Inputs, factory, transport, product, market, money
B. Input, transport, factory, transport, product, market, money
C. Input, Transport, factory, product, transport, market, money
D. Input, transport, factory, product, money
Ans – C. Input, Transport, factory, product, transport, market, money
Q 5 – Sixty percent of sugar mills are concentrated in which of the following states?
(a) Punjab and Haryana
(b) Maharashtra and Gujarat
(c) Uttar Pradesh and Bihar
(d) West Bengal and Orissa
Ans – (c) Uttar Pradesh and Bihar
Q 6 – What type of industries are TISCO, Bajaj Auto Ltd, Dabur Industries ?
A. Cooperative industry
B. Joint sector
C. Public sector
D. Private sector
Ans – D. Private sector
Q 7 – Which one of the following is not true regarding the National Jute Policy of 2005?
(a) Creating awareness about the use of biodegradable materials
(b) Ensuring good prices to the jute farmers
(c) Increasing productivity
(d) Improving quality of jute
Ans – (a) Creating awareness about the use of biodegradable materials
Q 8 – What is per capita consumption of steel per annum in India?
(a) 28 kg
(b) 30 kg
(c) 32 kg
(d) 34 kg
Ans – (c) 32 kg
Q 9 – Why is weaving highly decentralised?
A. To get more production
B. To attract more workers
C. To incorporate traditional skills and designs of weaving in cotton, silk, zari, embroidery
D. To get flavours from different places
Ans – C. To incorporate traditional skills and designs of weaving in cotton, silk, zari embroidery
Q 10 – Which are the two prime factors for the location of aluminium industry?
(a) Market and labour
(b) Transport network and water supply
(c) Cheap and regular supply of electricity and bauxite
(d) None of the above
Ans – (c) Cheap and regular supply of electricity and bauxite
Q 11 – The first cement plant was set up in India in 1904 in
(a) Jamshedpur
(b) Hyderabad
(c) Nagpur
(d) Chennai
Ans – (d) Chennai
Q 12 – To which of these countries does India export yarn to?
A. Japan
B. China
C. Italy
D. Sri Lanka
Ans – A. Japan
Q 13 – The first successful textile mill was established in:
(a) Delhi
(b) Vishakhapatnam
(c) Chennai
(d) Mumbai (Bombay)
Ans – (d) Mumbai (Bombay)
Q 14 – How are minerals formed in sedimentary rocks?
Ans – Minerals occur in beds or layers in sedimentary rocks. They are formed as a result of deposition, accumulation, and concentration in the horizontal strata. Minerals like gypsum, potash salt, and sodium salt are formed as a result of evaporation.
Q 15 – Why has the automobile industry of India witnessed fast growth? Give reasons.
Ans – Reasons for fast growth in automobile industry:
1. After liberalisation, the coming in of new and contemporary models stimulated the demand for vehicles in the market.
2. This led to the healthy growth of the industry including passenger cars, two and three-wheelers.
3. Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) brought in new technology and aligned the industry with global developments.
4. Trucks, buses, cars, motorcycles, scooters, three-wheelers and multi-utility vehicles and commercial vehicles are manufactured in India at various centres such as Delhi, Gurgaon, Mumbai, Jamshedpur etc. This industry has experienced a quantum jump in less than 15 years.
Q 16 – What are ‘agglomeration economies’ in the industrial context?
Ans – Many industries tend to come together to make use of the advantages offered by the urban centres known as ‘agglomeration economies’. Gradually, a large industrial agglomeration or clustering takes place around an urban centre.
Q 17 – What are the problems faced by the cotton textile industry?
Ans – Problems faced by the cotton textile industry:
1. Power supply is erratic in our country.
2. Machinery needs to be upgraded, especially in weaving and processing sectors.
3. Low output of labour.
4. We still need to import cotton in spite of the fact that the production of cotton in the country has increased.
5. Stiff competition from the synthetic fibre industry.
Q 18 – Why are the sugar mills located close to the sugarcane fields?
Ans – Reasons for location of sugar mills close to the fields:
- The raw material used, (i.e.) sugarcane is bulky and perishable.
- It cannot be transported to long distances because its sucrose content dries up fast, so it should be processed within 24 hours of its harvest.
Q 19 – How conservation of environment can be done?
Ans – Overdrawing of ground water reserves by industry where there is a threat to ground water resources also needs to be regulated legally.
Particulate matter in the air can be reduced by fitting smoke stacks to factories with electrostatic precipitators, fabric filters, scrubbers and inertial separators.
Smoke can be reduced by using oil or gas instead of coal in factories.
Machinery and equipment can be used and generators should be fitted with silencers.
Almost all machinery can be redesigned to increase energy efficiency and reduce noise. Noise absorbing material may be used apart from personal use of earplugs and earphones.
Q 20 – India has reached great heights in information technology and electronics industry. Elucidate the statement.
Ans – The electronics industry covers a wide range of products from transistor sets to television, telephones, cellular telecom, pagers, telephone exchange, radars, computers and many other equipments required by the telecommunication industry.
Bengaluru has emerged as the electronic capital of India. Other important centres for electronic goods are Mumbai, Delhi, Hyderabad, Pune, Chennai, Kolkata, Lucknow and Coimbatore.
By 2010-11 (STPI) Software Technology Parks of India have come up across 46 locations at different centres of India. However, the major industry concentration is at Bengaluru, Noida, Mumbai, Chennai, Hyderabad and Pune.
A major impact of this industry has been on employment generation. It is encouraging to know that 30 per cent of the people employed in this sector are women. This industry has been a major foreign exchange earner in the last two or three years because of its fast growing Business Processes Outsourcing (BPO) sector. The continuing growth in the hardware and software is the key to the success of IT industry in India.
Q 21 – Fill in the blank boxes for the Value addition in the textile industry:
Ans –
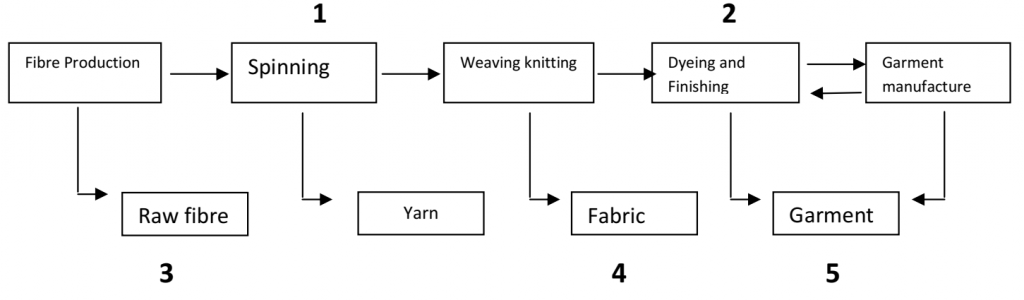
Q 22 – Fill in the blank boxes for the Ideal location of an Industry:
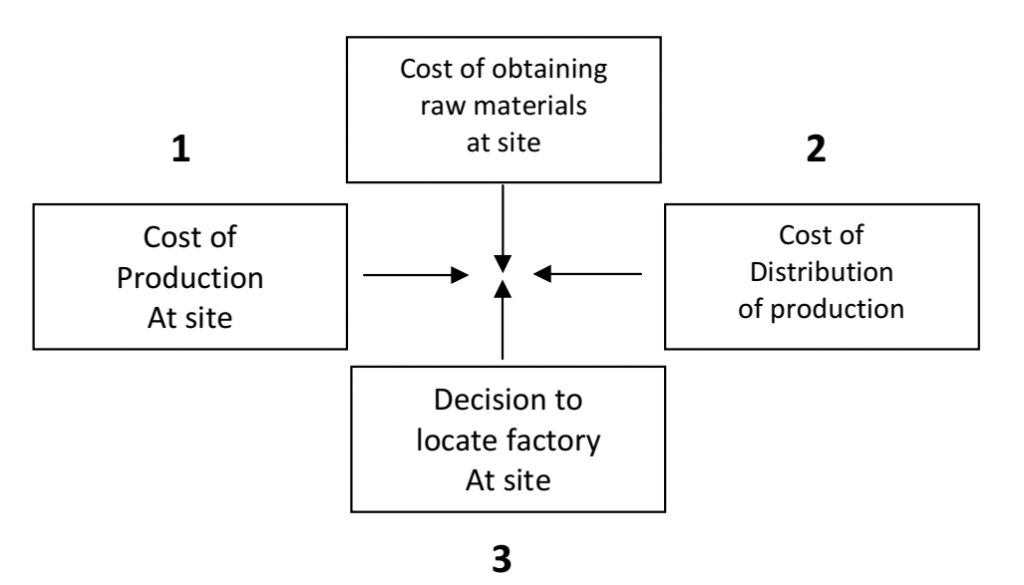
Q 23 – Why are most of the iron and steel industries concentrated in and around Chotanagpur Plateau Region? Give reasons.
Ans – Reasons:
1. Low cost of iron-ore which is mined here.
2. High grade raw materials in close proximity.
3. Availability of cheap labour.
4. Vast growth potential in the home market.
5. Efficient transport network for their distribution to the markets and consumers.
6. Availability of power because this region has many thermal and hydel power plants.
7. Liberalisation and FDI have also given boost to the industry with efforts of private entrepreneurs.
Q 24 – Write four characteristics and four major uses of aluminium.
Ans – Four characteristics of aluminium:
1. It is a light metal.
2. It is resistant to corrosion.
3. It is a good conductor of heat.
4. It is malleable and becomes strong when mixed with other metals.
Four uses (importance) of aluminium.
1. It is used for manufacturing aircrafts.
2. It is used for making utensils and packing material.
3. It is used for making wires.
4. It has gained popularity as a substitute of steel, copper, zinc and lead in a number of industries.
Q 25 – Why the manufacturing sector is considered is the backbone of development.
Ans – Manufacturing sector is considered the backbone of development in general and economic development in particular mainly because–
• Manufacturing industries not only help in modernising agriculture, which forms the backbone of our economy, they also reduce the heavy dependence of people on agricultural income by providing them jobs in secondary and tertiary sectors.
• Industrial development is a precondition for eradication of unemployment and poverty from our country. This was the main philosophy behind public sector industries and joint sector ventures in India. It was also aimed at bringing down regional disparities by establishing industries in tribal and backward areas.
• Export of manufactured goods expandstrade and commerce, and brings in much
needed foreign exchange.
• Countries that transform their raw materials into a wide variety of finished goods of higher value are prosperous.
India’s prosperity lies in increasing and diversifying its manufacturing industries as quickly as possible.