Q 1 – The distance travelled by the vehicles is recorded by
(a) monometer
(b) odometer
(c) speedometer
(d) motometer
Ans. (b) odometer
Q 2 – A bus travels 54 km in 90 minutes. The speed of the bus is
(a) 0.6 m/s
(b) 10 m/s
(c) 5.4 m/s
(d) 3.6 m/s
Ans. (b) 10 m/s
Q 3 – The clocks and watches which are used for measuring time are based on
(a) rectilinear motion
(b) circular motion
(c) periodic motion
(d) rotational motion
Ans. (c) periodic motion
Q 4 – The device which is used for measuring time intervals in sports activities is called
(a) wrist watch
(b) stop watch
(c) stop clock
(d) quartz watch
Ans. (b) stop watch
Q 5 – If the speed of an object along a straight line keeps changing, its motion is said to be
(a) uniform motion
(b) non-uniform motion
(c) linear motion
(d) none of these
Ans. (b) non-uniform motion
Q 6 – The most well known periodic motion is that of
(a) sundial
(b) stop watch
(c) simple pendulum
(d) sand clock
Ans. (c) simple pendulum
Q 7 – Which of the following is based on the study of the shadow cast by the sun?
(a) Simple pendulum
(b) Atomic clock
(c) Sun dial
(d) Quartz clock
Ans. (c) Sun dial
Q 8 – The most appropriate unit for expressing the speed of a space rocket is
(a) m/s
(b) km/s
(c) km/h
(d) km/min
Ans. (b) km/s
Q 9 – Swami walks to his school which is at a distance of 4 km from his home in 30 minutes. On reaching he finds that the school is closed and comes back in his friend’s vehicle to home in 10 minutes. His average speed in km/h is
(a) 8 km/h
(b) 24 km/h
(c) 16 km/h
(d) 20 km/h
Ans. (c) 16 km/h
Q 10 – When an object changes position with time, it is said to be in
(a) rest
(b) stationary
(c) circle
(d) motion
Ans. (d) motion
Q 11 – A motion in a straight line in a fixed direction represents a
(a) circular motion
(b) uniform motion
(c) non-uniform motion
(d) periodic motion
Ans. (b) uniform motion
Q 12 – A simple pendulum executes a
(a) periodic motion
(b) oscillatory motion
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these
Ans. (c) both (a) and (b)
Q 13 – The distance-time graph of an object under uniform motion is a
(a) curved line
(b) straight line
(c) circle
(d) parabola
Ans. (b) straight line
Q 14 – The S.I unit of speed is
(a) m/s
(b) km/h
(c) m/h
(d) km/s
Ans. (a) m/s
Q 15 – Which of the following measures the most accurate time?
(a) Sand clock
(b) Water clock
(c) Quartz clock
(d) Sundial
Ans. (c) Quartz clock
Q 16 – All oscillatory motions are
(a) rotatory motions
(b) rectilinear motions
(c) circular motions
(d) periodic motions
Ans. (d) periodic motions
Q 17 – The motion of the moon around the earth represents a
(a) periodic motion
(b) oscillatory motion
(c) curvilinear motion
(d) none of these
Ans. (a) periodic motion
Q 18 – Which of the following is the S.I unit of distance?
(a) km
(b) m
(c) cm
(d) mm
Ans. (b) m
Q 19 – The motion of the spikes in the wheels of a moving cycle is
(a) rectilinear motion
(b) circular motion
(c) oscillatory motion
(d) none of these
Ans. (b) circular motion
Q 20 – Observe the figure given below:
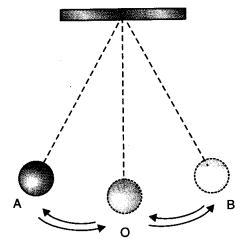
The time period of a simple pendulum is the time taken by it to travel from
(a) A to B and back to A
(b) O to A, A to B and B to A
(c) B to A, A to B and B to O
(d) A to B
Ans. (a) A to B and back to A
Q 21 – If a pendulum is vibrating at 10 Cycles-1, its time period is
(a) 1 sec
(b) 0.1 sec
(c) 0.5 sec
(d) 0.01 sec
Ans. (b) 0.1 sec
Q 22 – The rate of change in position of a body is called
(a) Speed
(b) Acceleration
(c) Rest
(d) Motion
Ans. (a) Speed
Q 23 – The speed of the vehicle is recorded by
(a) Ammeter
(b) Odometer
(c) Speedometer
(d) Voltmeter
Ans. (c) Speedometer
Q 24 – The basic unit of speed is:
(a) km/min
(b) m/min
(c) km/h
(d) m/s
Ans. (d) m/s
Q 25 – The meter that is used to measure the distance moved by the vehicle is known as _____
(a) Speedometer
(b) Odometer
(c) Chronometer
(d) Ammeter
Ans. (b) Odometer
Q 26 – A velocity-time graph gives (i) the distance (ii) the displacement (iii) the acceleration (iv) the speed
(a) (i) and (ii) only
(b) (ii) and (iii) only
(c) (i) and (iii) only
(d) (i), (ii) and (iii)
Ans. (b) (ii) and (iii) only
Q 27 – Time interval of 1000 years is called
(a) A millennium
(b) Trillion
(c) Century
(d) Decade
Ans. (a) A millennium
Q 28 – To and fro movement of body is termed as
(a) Vibratory motion
(b) Oscillatory motion
(c) Circular and periodic motion.
(d) Periodic motion
Ans. (b) Oscillatory motion
Q 29 – Watch used to measure short interval of time is
(a) Stop watch
(b) Pendulum watch
(c) Atom watch
(d) Quartz watch
Ans. (a) Stop watch
Q 30 – When a body covers equal distance in equal interval of time. The speed of the body is called as
(a) Average speed
(b) Non-uniform speed
(c) Uniform speed
(d) Linear speed
Ans. (c) Uniform speed
Q 31 – When the motion of the object is not along a f ixed path with changing direction
(a) Random motion
(b) Oscillatory motion
(c) Periodic motion
(d) Circular motion
Ans. (a) Random motion
Q 32 – It is a part of wall clock and perf orms oscillatory motion. Its time period is f ixed. It is
(a) a pendulum
(b) bob of a pendulum
(c) pendulum clock
(d) None of these
Ans. (a) a pendulum
Q 33 – One kilometer is equal to
(a) 100 m
(b) 10 m
(c) 10000 m
(d) 1000 m
Ans. (d) 1000 m
Q 34 – Pendulum of a given length always takes
(a) Equal times in some oscillation
(b) Unequal times in one oscillation
(c) Equal times in one oscillation
(d) Unequal times in some oscillation
Ans. (c) Equal times in one oscillation
Q 35 – Total distance covered by a body in unit interval of time in particular direction is called
(a) Speed
(b) Momentum
(c) Velocity
(d) Motion
Ans. (c) Velocity
Q 36 – Speed is scalar quantity but velocity is a
(a) Either scalar or vector
(b) Vector quantity
(c) Neither vector nor scalar
(d) Also scalar quantity
Ans. (b) Vector quantity
Q 37 – A car is moving with 72 km/hrs. The speed of the car in m/s is
(a) 30 m/s
(b) 20 m/s
(c) 40 m/s
(d) 25 m/s
Ans. (b) 20 m/s