Q 1. Select the correct word from the following list and fill in the blanks.
float, water, crop, nutrients, preparation
(a) The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called _____
(b) The first step before growing crops is the _______ of the soil.
(c) Damaged seeds would ______ on top of the water.
(d) For growing a crop, sufficient sunlight and ______ and ______ from the soil are essential.
(a) crop
(b) preparation
(c) float
(d) water, nutrients
Question 2.
Match items in column A with those in column B.
| A | B |
| (i) Kharif crops | (a) Food for cattle |
| (ii) Rabi crops | (b) Urea and superphosphate |
| (iii) Chemical fertilisers | (c) Animal excreta, cow dung, urine and plant waste |
| (iv) Organic manure | (d) Wheat, gram, pea |
| (e) Paddy and maize |
(i) (e)
(ii) (d)
(iii) (b)
(iv) (c)
Question 3.
Give two examples of each.
(a) Kharif crop
(b) Rabi crop
(a) Kharif crop: Paddy and maize
(b) Rabi crop: Wheat and gram.
Question 4.
Write a paragraph in your own words on each of the following.
(a) Preparation of soil
(b) Sowing
(c) Weeding
(d) Threshing
(a) Preparation of soil: Soil preparation is necessary before growing a crop. It involves tilling and loosening the soil. This allows the roots to penetrate deep in the soil and to breath easily even when they are deep.
(b) Sowing: The process of putting seeds into the soil is called sowing. The tool used traditionally for sowing seeds is funnel-shaped. Nowadays a seed drill is used for sowing with the help of tractors. This tool sows the seed uniformly at a proper distance and depth.
(c) Weeding: Some undesirable plants grow along with crop and these unwanted plants are called weeds. The process of removing these unwanted plants is called weeding.
(d) Threshing: The process of separating the grain seeds from the chaff is called threshing.
Question 5.
Explain how fertilisers are different from manure.
| Fertilisers | Manures |
| (i) A fertiliser is an inorganic salt. | (i) Manure is a natural substance obtained by the decomposition of cattle dung, human waste and plant residues. |
| (ii) A fertiliser is prepared in factories. | (ii) Manure can be prepared in the fields. |
| (iii) A fertilizer does not provide any humus to the soil. | (iii) Manure provides a lot of humus to the soil. |
| (iv) Fertilisers are very rich in plant nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. | (iv) Manure is relatively less rich in plant nutrients. |
Question 6
What is irrigation? Describe two methods of irrigation that conserve water.
The artificial method of watering the plants for assisting in their growth is called irrigation. The main sources of irrigation are wells, tube-wells, ponds, lakes, rivers.
Two methods that help us to conserve water are:
(i) Sprinkler irrigation system: This irrigation system has an arrangement of vertical pipes with rotating nozzles on the top. It is more useful in uneven and sandy land where sufficient water is not available.
(ii) Drip irrigation system: This irrigation system has an arrangement of pipes or tubes with very small holes in them to water plants drop by drop just at the base of the root. It is very efficient as water is not wasted at all.
Question 7
If wheat is sown in the kharif season, what would happen? Discuss.
Wheat crop is sown from November/December to March/April. It is grown in winter and requires less water. If wheat is sown in Kharif season, its production will be decreased considerably.
Question 8.
Explain how soil gets affected by the continuous plantation of crops in a field.
Continuous plantation of crops makes the soil poorer in certain nutrients as the crops take up nutrients from the soil. The soil becomes infertile. It does not get enough time to replenish the nutrients.
Question 9.
What are the weeds? How can we control them?
The undesirable and unwanted plants which grow naturally along with the crop are called weeds. The growth of weeds can be controlled by adopting many ways. Tilling before sowing of crops helps in the uprooting and killing of weeds, which may then dry up and get mixed with the soil. Weeds are also controlled by using certain chemicals, called weedicides. Weedicides are sprayed in the fields to kill the weeds.
Question 10
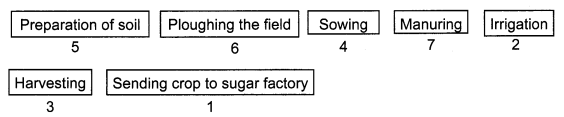
Arrange the following boxes in the proper order to make a flow chart of sugarcane crop production.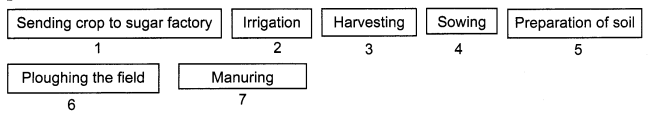
Question 11.
Complete the following word puzzle with the help of clues given below.
Down
1. Providing water to the crops.
2. Keeping crop grains for a long time under proper conditions.
5. Certain plants of the same kind grown on a large scale.
Across
3. A machine used for cutting the matured crop.
4. A rabi crop that is also one of the pulses.
6. A process of separating the grain from the chaff.
Answer: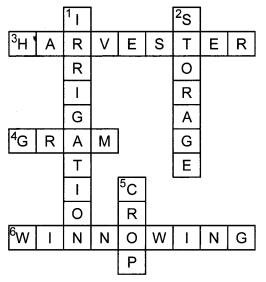
Take a beaker and fill half of it with water. Put a handful of wheat seeds and stir well. Wait for some time.
Solution:
We observe that most of the seeds sink while some float on water. Damaged seeds become hollow and lighter so they float. In this way, we can separate damaged seeds from healthier ones.
Jake moong or gram seeds and germinate them. Select three equal-sized seedlings out of these. Now take three empty glasses or similar vessels. Mark them A, B and C.To glass A add a little amount of soil mixed with a little cow dung manure. In the glass, B put the same amount of soil mixed with a little urea. Take the same amount of soil in glass C without adding anything [Fig. 1.2(a)]. Now pour the same amount of water into each glass and plant the seedlings in them. Keep them in a safe place and water them daily. After 7 to 10 days observe their growth [Fig. 1.2(b)].

Solution:
After 7-10 days we observed that the growth was fastest in glass B followed by glass A. Glass C showed mini-mum growth.
Question 11
Select the correct word from the following list and fill in the blanks :
float, water, crop, nutrients, preparation
(a) The same kind of plants grown on a large scale at a place is called …………..
(b) The first step before growing crops is …………. of the soil.
(c) Damaged seeds would …………. on top of water.
(d) For growing a crop sufficient sunlight, …………….. and …….. the soil are essential.
(a) crop
(b) preparation
(c) float
(d) nutrients, water
Question 12.
Match items in column ‘A’ with those in column ‘B’
| (A) | (B) |
| 1. Kharif crops 2. Rabi crops 3.Chemicalfertilisers 4. Organic manure |
(a) Food for cattle (b) Urea and super phosphate (c) Animal excreta,cowdung, urine and plant waste. (d) Wheat, gram, pea. (e) Paddy and maize |
| (A) | (B) |
| 1. Kharif crops 2. Rabi crops 3. Chemical fertilisers 4. Organic manure |
(e) Paddy and maize (d) Wheat, gram, pea (b) Urea and super phosphate (c) Animal excreta, cow dung, urine and plant waste. |
Question 13
What are crops?
Crops are plants of the same kind grown in large quantities for food.
Question 14.
What is the basis of classification of crops in our country?
In our country, crops are classified on the basis of the season in which they grow.
Question 15.
What are Kharif crops?
The crops which are sown in the rainy season and harvested in September/October are called Kharif crops.
Question 16.
What are summer crops?
The crops which are grown in the summer season and harvested before rainy season are called summer crops or zayed crops.
Question 17.
Name two summer season crops.
Moong and muskmelon are summer season crops.
Question 18.
What are rabi crops?
The crops which are grown in the winter season and harvested in March/April are called rabi crops.
Question 19.
Why paddy cannot be grown in the summer season?
Paddy requires a lot of water, so it can only be grown during the rainy season.
Question 20.
What is meant by agricultural practices?
The activities undertaken by farmers over a period of time for cultivation of crops are known as agricultural practices.
Question 21.
Write a paragraph in your own words on preparation of soil.
Soil is prepared by tilling i.e., loosening and turning of soil.
Question 22.
Name the tool used for tilling of soil.
A plough is used for tilling of soil.
Question 23.
What are crumbs?
A ploughed field may have big pieces of soil called crumbs.
Question 24.
How are crumbs broken?
The crumbs are broken with the help of a plank.
Question 25.
Why should loose soil be levelled?
Loose soil be levelled for sowing and irrigation.
Question 26.
How is levelling of soil done?
Levelling of soil is done with the help of a leveller.
Question 27.
How is ploughing done these days?
Now a days ploughing is done by tractor having a multipronged plough.
Question 28.
What is meant by sowing?
Sowing is the process of putting seeds in the soil.
Question 29.
What is meant by good quality seeds?
Good quality seeds mean clean and healthy seeds of a good variety free from diseases.
Question 30.
What is the advantage of sowing seeds with a seed drill?
The advantage of sowing seeds with a seed drill is that the seeds are sown at a proper depth under the soil and the distance between them is uniform.
Question 31.
What are manure and fertilizers?
The substances which are added to the soil in the form of nutrients for the healthy growth of plants are called manure and fertilizers.
Question 32.
What is organic manure?
Manure obtained from animal or plant waste such as cattle dung, droppings are called organic manure.
Question 33.
What is meant by crop rotation?
Growing crops alternatively to prevent depletion of any one nutrient from the soil is called crop rotation.
Question 34.
What is meant by irrigation?
The supply of water to crops in the fields at different intervals is called irrigation.
Question 35.
What is the drip system of irrigation?
Falling of water drop by drop at the roots of the plant is called drip irrigation.
Question 36.
Why should weeds be removed?
Weeds compete with the crop plants for water, nutrients, space and light and thus affect the growth of the crop. So, they should be removed.
Question 37.
Name the process of removal of weeds.
Weeding is the process of removal of weeds.
Question 38.
How is harvesting done in our country?
Harvesting in our country is done either manually by sickle or by a machine called harvester.
Question 39.
Name the farm machine used for harvesting and threshing both.
Combine.
Question 40.
What is meant by winnowing?
After threshing, the grain is separated from the chaff, with the help of wind. This is known as winnowing.
Question 41.
How are food grains stored?
Food grains are dried in the sun to remove the excess moisture and then stored.
Question 42.
Why should grains be dried before storage?
Grains should be dried before storage to remove the excess moisture in them, so that microbes are not able to attack the grains.
Question 43.
What is meant by animal husbandry?.
The study of the care of animals is known as animal husbandry.
Question 44.
Name some animals from whom milk can be obtained.
Milk can be obtained from cow, buffalo, she goat and she camel.
Question 45.
How is fish useful for us?
Fish is highly nutritious and easily digestible food. Cod liver oil from fish is also a rich source of vitamin D.
Question 46.
Name some animals which are reared for their meat.
Sheep, goat, pigs, chicken and fish are reared for their meat.
Question 47.
Why is honey so useful?
Honey is an antiseptic and its enzymes help in digestion. It is also used for making several ayurvedic medicines.
Question 48.
If wheat is sown in the kharif season, what would happen? Discuss.
The farmer will not get a good crop because wheat should be sown in winter season.
Question 49.
Explain how soil gets affected by the continuous plantation of crops in a field.
Question 50.
What are weeds? How can we control them?
Weeds are unwanted plants in the fields. It can be controlled by
- During tilling they are removed.
- By removing them manually.
- By using weedicides.