Q 1. Look at the diagram showing the positive feedback mechanism on page 13. (See NCERT Textbook). Can you list the inputs that went into tool making? What were the processes that were strengthened by tool-making?
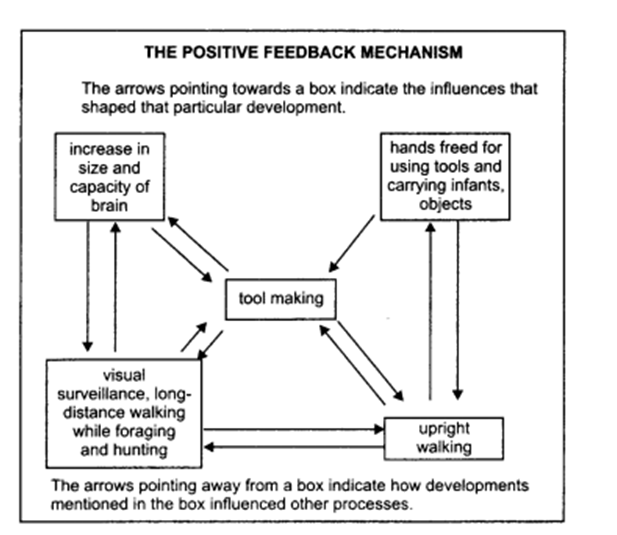
After going through the positive feedback mechanism following points can be inferred:
(a) Inputs that helped in tool making:
- Increased brain size and capacity of brain
- Upright walking
- Visual surveillance long distance
- Walking while foraging and hunting.
(b) The processes that were strengthened by tool making:
- Upright walking
- Increase in size and capacity of brain
- Visual surveillance, long distance walking while foraging and hunting.
Humans and mammals such as monkeys and apes have certain similarities in behaviour and anatomy. This indicates that humans have possibly evolved from the . apes. List these resemblances in two columns under the headings of
(a) behaviour and
(b) anatomy.
Q 2. Are there any differences that are noteworthy?
Similarities
(a) Behaviour
| Humans | Monkeys and Apes |
| 1. Humans can climb on trees. | Monkeys and apes can also climb on trees. |
| 2. Mothers give birth to their young ones. | Monkeys also give birth to their young ones. |
| 3. They can walk long distances. | They can also walk long distances. |
(b) Anatomy:
| Humans | Monkeys and Apes |
| 1. Humans are vertebrates. | 1. They are also vertebrates. |
| 2. Humans have two feet and two hands. | 2. Monkeys and apes are also quadrupeds. |
Q 3. Discuss the arguments advanced in favor of the regional continuity model of human origins. Do you think it provides a convincing explanation of the archaeological evidence? Give reasons for your answer
According to the Regional Continuity Model, the Homo sapiens evolved in different regions at different rates into modern humans. So there was a variation in the first appearance of modern humans in different parts of the world. It was based on the regional differences in the features of present day humans. The advocates of this view found that the dissimilarities are due to the differences between the Homo erectus and Homo heidelbergensis populations of the same regions.
The Regional Continuity Model does not give a convincing explanation of the archaeological evidence.
Q 4. Which of the following do you think is best documented in the archaeological record: (a) gathering, (b) tool making and (c) use of fire?
Tool making is documented in the archaeological record.
5. Discuss the extent to which: (a) hunting and (b) constructing shelters would have been facilitated by the use of language. What other modes of communication could have been used for these activities?
(a) Use of language helped hunting activities of human beings in numerous ways:
- Now people are in a position of organizing and managing hunting expeditions
- They are now free to exchange their ideas about different animals in different regions.
- They could now discuss the nature and behavior of animals.
- They could now discuss regarding the types of tools to be used.
(b) Language helped in constructing shelters for early humans in the following ways:
- Now people could discuss regarding secure and safe places for the construction of shelters.
- Now people could gather information about the materials used in the construction of shelter.
- Information regarding resources in and around their surroundings can be easily obtained.
- They were now in a position to discuss the means to protect their shelters in severe conditions.
Other modes: Signs, symbols, cave paintings, engraving on walls and on the ceilings of caves were the other modes of communication used for various activities
6. Choose any two developments each from Timelines 1 and 2 at the end of the chapter and indicate why these are significant.
| Timeline 1 (mya) | |
| 36-24 mya | Primates; Monkeys in Asia and Africa |
| 24 mya | (Superfamily) Hominoids; Gibbons, Asian orang-utan and African apes (gorilla, chimpanzee and bonobo or ‘pygmy’ chimpanzee) |
| 6.4 mya | Branching out of hominoids and hominids |
| 5.6 mya | Australopithecus |
| 2.6-2.5 mya | Earliest stone tools |
| 2.5-2.0 mya | Cooling and drying of Africa, resulting in decrease in woodlands and increase in grassland |
| 2.5-2.0 mya | Homo |
| 2.2 mya | Homo habilis |
| 1.8 mya | Homo erectus |
| 1.3 mya | Extinction of Australopithecus |
| 0.8 mya | ‘Archaic’ sapiens, Homo heidelbergensis |
| 0.19-0.16 mya | Homo sapiens (Modern humans) |
| Timeline 2 (years ago) | |
| Earliest evidence of burials | 300,000 |
| Extinction of Homo erectus | 200,000 |
| Development of voice box | 200,000 |
| Archaic Homo sapiens skull in the Narmada valley, India | 200,000 130,000 |
| Emergence of modern humans | 195,000 160,000 |
| Emergence of Neanderthals | 130,000 |
| Earliest evidence of hearths | 125,000 |
| Extinction of Neanderthals | 35,000 |
| Earliest evidence of figurines made of fired clay | 27,000 |
| Invention of sewing needles |
Developments from Timeline-1
- The evidence of the first Hominids was found about 5.6 mya. The Hominids evolved from Hominoids. They had some common features. Hominids had larger brain than Hominoids. Hominids had an upright posture and bipedal locomotion. There was a marked difference in regard to hand. It helped them in use of tools.
- Around 2.5 mya, large parts of the earth were covered with snow. There were major changes in the environment. It led to expansion of grassland.
Developments from Timeline-2
- Around 200,000 years ago, the evolution of the voice box took place. After the evolution of voice box, now the man was about to speak and express his views.
- About 27,000 years ago, the earliest evidence of figurines made of fired clay was also found. The invention of sewing machines made the life of people more comfortable.
7. Which sources enable us to understand the history of early humans?
The sources which enable us understand the history of early humans are stone tools, fossils, etc.
8. What do you know about Carl Fuhlrott?
Carl Fuhlrott was a teacher and natural historian in Germany, Dusseldorf. He was handed over a skull and some skeletal fragments of early humans by workmen who were engaged in quarrying for limestone in the Neander valley region in August 1856.
9. Name the book published by Charles Darwin. When was it published and what did he argue in it?
The book published by Charles Darwin was ‘ On the Origin of Species’. It was published on 24 November, 1859. In it, he argued about the evolution of mankind.
10. Define ‘Fossils’.
The word ‘Fossils’ is used to describe the remains of very old plants, human beings or animals which have left their marks on the rock. These remains are preserved for many years.
11. What are the two differences between Hominids and Hominoids?
The differences between Hominids and Hominoids are as follows:
- Hominoids have a smaller brain as compared to Hominids.
- Hominids have an upright posture and bipedal locomotion while Hominoids are quadrupeds.
12. Write any two evidences that Hominoids have African origin.
Evidences which suggest that Hominoids have African origin are:
- A group of African apes is closely related to Hominoids.
- Early Hominoids have been found in East Africa dated back to 5.6 mya
13. To which family does Hominids belong to?
Hominids belong to Hominidae family. This family belongs to all forms of human beings existing on the earth.
14. Describe in brief the distinctive features of Hominids.
The distinctive features of Hominids are as follows:
- They have large brain size.
- They have bipedal locomotions and upright posture.
15. How will you differentiate Hominoids from monkeys?
Hominoids are different from monkeys in following ways:
- Hominoids have a larger body.
- They do not have tails like monkeys.
- There is a longer period of development and dependency amongst Hominoids.
16. What are ‘Genus’? Name two important genus of Hominids
Hominids are divided into different branches. They are known as genus. Two different genus of Hominids are Australopithecus and Homo.
17. Define ‘Species’. How human species are differentiated from each other?
The term ‘Species’ is used to describe the group of organisms that can produce fertile offsprings. Human species are differentiated from each other on the basis of the structure of their bones.
18. When did glaciation phase come into being? What were its impact?
The glaciation phase is literally known as Ice Age. It came into being around 2.5 mya.
Impact:
- Temperature started decreasing.
- Grassland began to expand at the cost of forests.
19. How have the fossils of human species been classified?
The fossils of human species have been classified by the scientists into three categories. These are:
- Homo habilis
- Homo erectus
- Homo sapiens.
20. Name two places where the fossils of Homo habilis have been discovered.
The places where the fossils of Homo habilis have been discovered are:
- Omo (Ethiopia)
- Olduvai Gorge (Tanzania)
21. Where were the fossils of earlier Homo erectus found?
They were found at following sites:
- Kenya
- Modjokerto
- Sangiran
- Java
22. Give two examples where the names of the fossils are derived from.
- Homo heidelbergensis: The species of Homo heidelbergensis have been discovered from German city Heidelberg.
- Homo neanderthalensis: Its species have been found in Neander valley, Dusseldorf, a German city.
23. The fossils of which Homo heidelbergensis have been widely distributed and where they are found?
The fossils of Homo heidelbergensis have been widely distributed. They are found in different parts of Africa, Asia and Europe.
24. Write any two differences between Australopithecus and Homo.
Australopithecus and Homo are different from each other on account of the following reasons:
- Australopithecus has a smaller brain as compared to Homo.
- Australopithecus has heavier jaws and larger teeth as compared to Homo who have smaller jaws and teeth.
25. Who were Primates? When did they come into existence?
Primates were a sub-group of a large group of mammals, i.e. monkeys, apes and humans. The Primates came into existence in about 36 mya.
26. Write any two evidences to show that Hominids originated in Africa.
The following evidences suggest that Hominids originated in Africa:
- African monkeys are closely related to Hominids.
- Their earlier removing has been traced from Eastern Africa.
27. What is meant by Australopithecus? Why are the earliest human called so?
The word Australopithecus is derived from Latin word ‘austral’ means southern and a Greek word ‘pithekos’ which means ‘apes’. Hence, the word means southern apes (Southern Monkey). The earliest human is called so because he resembles them.
28. When and where were the traces of earliest Australopithecus found?
The traces of earliest Australopithecus were found from Olduvai Gorge by Mary and Louis Leaky on 17th July, 1959.
29. How did early man obtain his food?
Early man obtained his food by gathering, hunting and fishing.
30. When did hunting begin? From where do we get its earliest evidence?
Hunting began about 500,000 years ago. We get the earliest evidence of hunting from Boxgrove in Southern England.
31. Where is Dolni Vestonice? Why is it famous for?
Dolni Vestonice is in Czech Republic. It is famous for hunting sites.
32. What are artefacts?
Artefacts are man-made objects, which include several kinds of articles such as tools, paintings, sculptures, etc.
33. When were the caves and open-air sites began to be used? From where do we get its evidence?
The caves and open-air sites began to be used around between 400,000 and 125,000 years ago. We get evidence of such sites from Lazaret cave in Southern France.
34. What are the advantages of living in caves?
Advantages of living in caves are given below:
- It helped in protecting men from severe cold.
- It also protected them from the predators.
- It also protected them from the danger of wild animals.
35. From where do we find the pieces of baked clay and burnt bone along with stone tools?
We find the pieces of baked clay and burnt bones from Chesowanja, Kenya and Swartkrans. These tools are dated between 1.4 and 1 mya.
36. How did the discovery of fire help early man?
The discovery of fire helped early man in the following ways:
- It helped him cook his food.
- It helped him protect from the danger of wild animals.
37. From where do we get the earliest evidence for making and use of stone tools? Who were earliest tool makers?
We get the earliest evidence for making and use of stone tools from two sites:
- Ethiopia
- Kenya
The Australopithecus were the first or earliest stone tool makers.
38. How do we notice the improvement in the technique for making tools for hunting wild animals? When did such changes occur?
With the use of stone tools like spear throwers, bow and the arrow, we notice the improvement in technique for making tools. Such changes occurred around 35,000 years ago.
39. When did spoken language emerge?
Spoken language emerged as early as 2 mya. Its emergence has been seen closely connected with art.
40. Where is Altamira cave site? Who brought these caves into notice and when?
Altamira cave site is in Spain. The Altamira caves were brought into notice by Marcelino sanz de Sautuola and his daughter, Maria. The site came into notice in November 1879.
41. Name a few places where cave painting depicting the pictures of animals have been found.
The cave painting depicting the pictures of animals such as bison, horses, deer, ma mmoths, lions, panthers, bear, owls, etc. have been found in Lascaux and Chauvet (Both in France) and in Altamira (in Spain).
42. Define the concept of‘Anthropology’.
It is a branch of science which deals with human culture and evolutionary aspects of human biology.
43. Who was Jame Woodbum?
Jame Woodbum was a famous anthropologist. He gave a new insight to Hadza group in 1960.
44. Where did Hadza group live? Write any two features.
The Hadza group lived around Lake Eyasi.
Features
- They were mainly hunters.
- They never claimed over land as its resources.
45. What is Ethnography?
The study of contemporary ethnic groups is called Ethnography. It deals with examination of their modes of livelihood, rituals, customs and traditions.
46. When did people of different corners of the world begin to learn domestication of plants and animals?
People of different corners of the world began to learn domestication of animals and plants around between 10,000 and 4,500 years ago.
47. When did last Ice age come to an end? What was its result?
About 13,000 years ago, last Ice age came to an end. As a result of this favourable conditions for growing crops prevailed.
48. Give reasons to prove why the people living in Hadza did not face food scarcity.
People living in Hadza did not face any food scarcity due to abundance of food items such as tuber, berries, fruits, etc.
49. What were the dietary habits of Hadza group?
The dietary habits of Hadza group included wild tubes, meat and honey.
50. List the wild animals hunted and consumed as meat by Hadza groups.
Hadza groups consumed the meat of zebra, giraffe, buffalo, shinoceor and waterduck, baboon, lion, leopard, hare and many more.