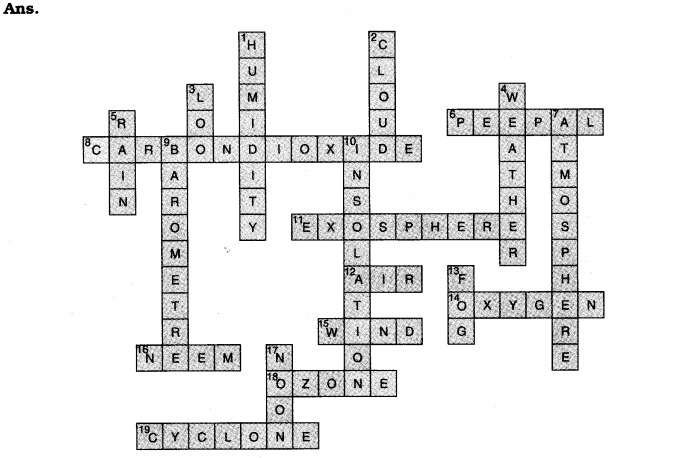
Question 1.
Answer the following questions briefly.
(i) What is the atmosphere?
(ii) Which two gases make the bulk of the atmosphere?
(iii) Which gas creates the greenhouse effect in the atmosphere?
(iv) What is the weather?
(v) Name three types of rainfall
(vi) What is air pressure?
(i) Atmosphere is a thin blanket of air that surrounds the earth. It protects us from the harmful rays of the sun. It consists of several gases in which nitrogen and oxygen occupy the major portion.
(ii) Nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%) make the bulk of the atmosphere.
(iii) Carbon dioxide creates a greenhouse effect in the atmosphere.
(iv) Weather is the hour-to-hour, day-to-day condition of the atmosphere.
(v)
- Convectional rainfall
- Orographic rainfall
- Cyclonic rainfall.
(vi) The pressure exerted by the weight of air on the earth’s surface is known as air pressure.
Question 2. Tick the correct answer:
(i) Which of the following gases protects us from harmful sun rays?
(a) Carbon dioxide (b) Nitrogen
(c) Ozone.
(ii) The most important layer of the atmosphere is
(a) Troposphere (b) Thermosphere
(c) Mesosphere.
(iii) Which of the following layers of the atmosphere is free from clouds?
(a) Trosphere (b) Stratosphere
(c) Mesosphere.
(iv) As we go up the layers of the atmosphere, the pressure
(a) Increases (b) Decreases
(c) Remains the same.
(v) When precipitation comes down to the earth in the liquid form, it is called
(a) Cloud (b) Rain
(c) Snow.
(i)—(c), (ii)—(a), (iii)—(b), (iv)—(b), (v)—(b).
Question 3.
Give reasons:
- Wet clothes take longer time to dry on a humid day.
- Amount of insolation decreases from equator torwards poles?
- As the air gets warmer its capacity to hold moisture, increases. Therefore it becomes more and more humid. On such days water from clothes or sweat from our body does not evaporate easily. Thus wet clothes take a longer time to dry.
- On the equator, insolation comes through vertical rays.
- It covers up less space. Hence heat is felt more.
- From the equator, it goes on coming through slanting rays. Slanting rays come on the earth passing longer distances through the atmosphere. They heat up more space. Hence there is less heat on a point of space.

(ii) Make a weather calendar for one week. Use pictures on symbols to show different types of weather. You can use more than one symbol in a day if the weather changes. For example, the sun comes out when the .rain stops. An example is given below:
Question 6 . How does carbon dioxide create green house effect?
Crbon dioxide creates greenhouse effect by trappeing the heat radiated from the earth.
Question 7. What is the significance of greenhouse gas?
Without the greenhouse gas the earth would have been too cold to the line in.
Question 8. What happens when air is heated?
When air is heated, it expands, becomes lighter and goes up.
Question 9. What is the nature of cold air?
It has a tendency to go down.
Question 10. Why do green plants use carbon dioxide?
Green plants use carbon dioxide to make their food and release oxygen.
Question 11. What is an important feature of Stratosphere?
Stratosphere contains a layer of ozone gas.
Question 12. How is ozone important for us?
It protects us from the harmful effect of the sunrays.
Question 13. What is temperature?
The degree of hotness and coldness of the air is known as temperature.
Question 14. What is insolation?
Insolation is the incoming solar energy intercepted by the earth.
Question 15. Why is there no air pressure on the moon?
There is no air on the moon and therefore no air pressure.
Question 16. Where is air pressure highest?
Air pressure is highest at the sea level.
Question 17. How does air move?
Air moves from high pressure areas to low pressure areas.
Question 18. Name three types of winds.
- Permanent winds
- Seasonal winds
- Local winds.
Question 19. What is the hot and dry wind of northern planes of India called?
It is called loo.
Q.20 What is called humidity?
Moisture in the air at any time is called humidity.
Q 21 Why do we feel uncomfortable on a humid day?
It is because sweat from our body does not evaporate easily.
Q.22 How is the flooding of low-lying areas caused?
When trees on hillsides are cut, rainwater flows down the bare mountains. This causes flooding of low-lying areas.
Q.21 Name various forms of precipitation.
- Rain
- Snow
- Sleet
- Hail
Q.22 How is a wind named?
A wind is named after the direction from which it blows.
Q.23 Give an account of the composition of the atmosphere. [
Our atmosphere is composed of mainly two gases—nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%). Other gases like carbon dioxide, helium, ozone, argon, and hydrogen are found in lesser quantities. Apart from these gases, tiny dust particles are also present in the air.
Q.24 How do Bacteria help plants use nitrogen?
Nitrogen is essential for the survival of the plant. But plants cannot take nitrogen directly from the air. Bacteria, that live in the soil and roots of some plants, take nitrogen from the air and change its form so that plants can use it.
Q.25 How does nature balance our life? What is the result if this balance is disturbed?
Green plants use carbon dioxide to make their food and release oxygen. Humans or animals release carbon dioxide. The amount of carbon dioxide released by humans or animals seems to be equal to the amount used by the plants which makes a perfect balance. But this balance is disturbed by the burning of fuels, which add billions of tons of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere. As a result, the increased volume of carbon dioxide is affecting the earth’s weather and climate.
Q.26 Why is temperature in cities much higher than that of villages ?
In cities, we find high rise buildings. The concrete and metals in these buildings and the asaphalt of roads get heated up during the day. This heat is released during the night.
Another reason is that the crowded high rise buildings of the cities trap the warm air and thus raise the temperature of the cities.
Q.27 Write a short note on the distribution of air pressure in the atmosphere
Air pressure is the pressure exerted by the weight of air on the earth’s surface. As we go up the layers of the atmosphere, the pressure falls rapidly. The air pressure is highest at sea level and decreases with height. Horizontally the distribution of air pressure is influenced by the temperature of the air at a given place. In areas where the temperature is high the air gets heated and rises. This creates a low-pressure area. In areas having lower temperatures, the air is cold, hence, it is heavy. Heavy air sinks and creates a high-pressure area.
Q.28 Why do astronauts wear special protective suits when they go to the moon?
Astronauts wear special protective space suits filled with air when they go to the moon. If they did not wear these space suits, the counter-pressure exerted by the body of the astronauts would make the blood vessels burst. The astronauts would bleed.
Q.29 How is rainfall important for us? What happens when there is excess rain?
Rainfall is very important for the survival of plants and animals. It brings fresh water to the earth’s surface. If rainfall is less, there is water scarcity which sometimes causes drought like situation. If there is excess rain, floods take place which makes the life of the affected people miserable.
Q.30 Give an account of the different layers of the atmosphere.
Our atmosphere has five different layers. They are:
- Troposphere: This is the most important layer of the atmosphere with an average height of 13 km from the earth. It is in this layer that we find the air that we breathe. Almost all the weather phenomena such as rainfall, fog, and hailstorm occur here.
- Stratosphere: This layer extends up to a height of 50 km. It presents the most ideal conditions for flying airplanes. It contains a layer of ozone gas that protects us from the harmful effect of sunrays.
- Mesosphere: This layer extends up to a height of 80 km. Meteorites bum up in this layer on entering from the space.
- Thermosphere: In this layer, the temperature rises very rapidly with increasing height. The ionosphere is a part of this layer. It extends between 80—400 km. This layer helps in radio transmission. Radio waves transmitted from the earth are reflected back to the earth by this layer.
- Exosphere: It is the uppermost layer where there is very thin air. Light gases such as helium and hydrogen float into space from here.
Q.31 What is wind? Mention its different types.
The wind is the movement of air from the high-pressure areas to low-pressure areas. It is divided into three types:
- Permanent winds
- Seasonal winds
- Local winds
1. Permanent winds. The trade winds, westerlies, and easterlies are the permanent winds. These blow constantly throughout the year in a particular direction.
2. Seasonal winds. These winds change their direction in different seasons. For example monsons in India.
3. Local winds. These winds blow only during a particular period of the day or year in a small area. For example land and sea breeze. Loo is a local wind which hot and dry and blows in the northern plains of India during summers.