Prevention of soil pollution:
The persistent build-up of toxic compounds in the soil is defined as soil pollution. To prevent soil pollution, its causes must be controlled.
- Reduce the use of plastics: Plastics and polythene bags destroy the fertility of soil. Hence, these should be disposed off properly and if possible, their use should be avoided.
- Industrial pollutants: Some waste products from industries and homes pollute soil. These pollutants should be treated chemically to make them harmless before they are disposed off.
- Insecticides: Other pollutants of soil include pesticides and insecticides. Therefore, excessive use of these substances should be avoided.
Prevention of soil erosion:
Removal of the upper fertile layer of the soil (topsoil) by strong wind and flowing water is known as soil erosion. Following steps can be taken to reduce soil erosion:
- Mass awareness to reduce deforestation for industrial purposes.
- Helping local people to regenerate degrading forest.
- Planting trees.
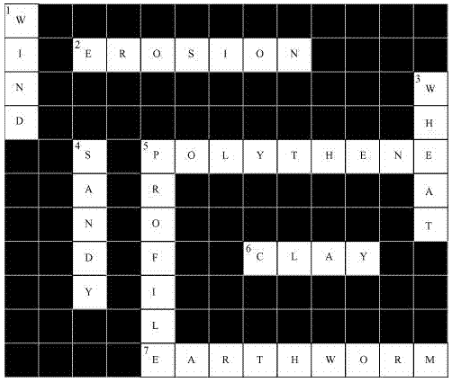
Across
2. Plantation prevents it. → Erosion
5. Use should be banned to avoid soil pollution. → Polythene
6. Type of soil used for making pottery. → Clay
7. Living organism in the soil. → Earthworm
Down
1. In desert soil erosion occurs. → Wind
3. Clay and loam are suitable for cereals. → Wheat
4. This type of soil can hold very little water. → Sandy
5. Collective name for layers of soil. → Profile