Question 1.
Answer the following questions.
(i) What is agriculture?
(ii) Name the factors influencing agriculture.
(iii) What is shifting cultivation? What are its disadvantages?
(iv) What is plantation agriculture?
(v) Name the fibre crops and name the climatic conditions required for their growth.
(i) Agriculture is the primary activity that involves the cultivation of fruits, crops, vegetables, flowers, and the rearing of livestock.
(ii) The factors that influence agriculture are the topography of soil and climate.
(iii) Shifting cultivation is a type of cultivation practiced in the thickly forested areas of Tropical evergreen forests. In this type of farming people shift from one field to another when the fertility of the soil of the former one is exhausted. Shifting cultivation is also known as ‘Slash and Burn Agriculture‘.
Disadvantages:
- Deforestation
- Soil erosion
- Small patches for cultivation
- Not sufficient for feeding a large population.
(iv) Plantation agriculture is a type of commercial farming where only a single crop (like tea, coffee, sugarcane, cashew, rubber, banana, or cotton) is grown. A large amount of labor and capital are required. Near-by factories or farm factories can process the agricultural produce. Therefore, the road system is an essential requirement for Plantation Agriculture.
(v) Two major fibre crops are jute and cotton. Jute grows well on alluvial soil and requires high temperature, heavy rainfall, and a humid climate for its growth. Cotton needs high temperatures, light rainfall, and bright sunshine besides two hundred ten frost-free days for its growth.
Question 2.
Tick the correct Answer:
(i) Horticulture means
(a) growing of fruits and vegetables
(b) primitive farming
(c) growing of wheat
(ii) Golden fiber refers to
(a) tea
(b) cotton
(c) jute
(iii) Leading producers of coffee
(a) Brazil
(b) India
(c) Russia
Question 3.
Give reasons.
(i) In India agriculture is a primary activity.
(ii) Different crops are grown in different regions.
(i) Agriculture is an activity of growing crops, fruits, vegetables, flowers, and rearing of livestock. It is a primary activity since it directly involves natural resources. In India, a huge number of people (Two-thirds of India’s population ) earn their livelihood directly from Agriculture. People prefer agriculture since they acquire the required skills from their ancestors, and so feel comfortable with it.
(ii) Different crops are grown in different regions.
- Different topography.
- Different soils available in India.
- Different climatic conditions.
- Different lifestyles of the people in different regions.
Question 4.
Distinguish between the following.
(i) Primary activities and secondary activities.
(ii) Subsistence farming and intensive farming.
(i) Primary activities and secondary activities.
| Primary Activities | Secondary Activities |
| 1. Primary activities include all those connected with the extraction and production of natural resources. 2. Agriculture, fishing, and gathering are examples of primary Activities. |
1. Secondary activities are concerned with the processing of primary resources. 2. Manufacturing of steel, baking of bread are examples of Secondary Activities. |
(ii) Subsistence farming and intensive farming.
| Subsistence Farming | Intensive Farming |
| 1. In Subsistence farming, the agricultural out output is low . Traditional methods of farming and technology are adopted . Here less labour is used. 2. This method is prevalent in both populated as well as tribal areas of the tropical Areas as well as temperate regions of the World. |
1. In Intensive farming, the agricultural output is low. The farmer uses simple tools to cultivate small plot of land. Here more labour is used. The agricultural output is low. 2. This method is prevalent in the thickly populated areas of the monsoon regions of the south, southeast, and east Asia. |
Question 5.
Find out the difference between the lifestyle of farmers in the USA and India on the basis of pictures collected from magazines, books, newspapers, and the internet.
- The lifestyle of an Indian farmer is quite different from that of a farmer in the USA. An Indian farmer does not have much land about 1.5 heactares whereas the average size of a farm in the USA is about 250 hectares.
- An Indian farmer lives in his house but an American farmer lives in his farm.
- A farmer in India applies his own experience, and advice of other farmers and elders regarding farming practices. But a farmer in the USA gets his soil tested in laboratories to assess the nutrients of the soil.
- An Indian farmer does not know of any technical advancements whereas a farmer in the USA has a computer which is linked to the satellite. In comparison to an Indian farmer, an American farmer is much more advanced in every aspect
Question 6.
Choose the correct option
(i) Which of these is a tertiary activity?
(a) manufacturing wool
(b) selling grocery
(c) agriculture
(d) none of these
(ii) What is the breeding of fish known as?
(a) agriculture
(b) pisciculture
(c) sericulture
(d) viticulture
(iii) What is the main crop in intensive subsistence agriculture?
(a) rice
(b) maize
(c) wheat
(d) oilseeds
(iv) Which form of farming is also called “slash and bum” agriculture?
(a) subsistence farming
(b) shifting cultivation
(c) plantation
(d) mixed farming
(v) Which of these is not a plantation product?
(a) rubber
(b) coffee
(c) rice
(d) tea
(vi) In what season is wheat grown in India?
(a) summer
(b) winter
(c) monsoon
(d) autumn
(vii) Name the staple diet of tropical and sub-tropical regions.
(a) wheat
(b) rice
(c)jute
(d) coffee
(i) (b), (ii) (b), (iii) (a), (iv) (b),
(v) (c), (vi) (b), (vii) (b).
Question 7.
Fill in the blank spaces given to complete each sentence.
- In the world, ………. percent of the population is engaged in agriculture.
- …………. is the commercial rearing of silkworms.
- ………. and …………… are two fundamental types of farming.
- In the thickly populated areas of monsoon regions of Asia, the major class of farming done is ……………..
- …………, ………….., ………….. and …………. are animals usually reared by nomadic herders.
- In ………., the land is used for growing food and fodder crops and rearing livestock.
- ………….. and ……….. are fibre crops.
- Tea is a major…………… crop in India.
- Wheat thrives best in ……………. soil.
- The three major millets in India are ………….. and ………..
- 50
- Sericulture
- Subsistence farming and commercial farming
- intensive subsistence farming
- Yak, sheep, goat, camel
- mixed farming
- Cotton, jute
- plantation
- loamy
- jowar, bajra, ragi
Question 8.
State whether each of the following statements is true (T) or false (F).
- Favourable topography of soil and climate is vital for agriculture.
- Household labour is involved in subsistence farming.
- A transport network is significant for plantation agriculture.
- Major plantations are found in tundra regions.
- In the USA, the farmer usually resides on the farm.
- True
- True
- True
- False
- True
Question 9.
Match the items given in Column I correctly with those given in Column II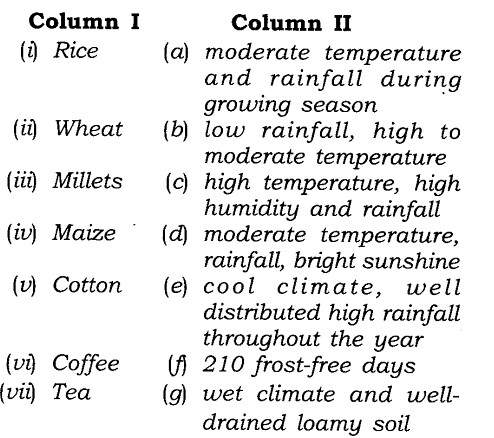
Question 20.
What is the basic function of the three basic types of economic activities?
The three types of economic activities are involved in the transformation from a plant to a finished product.
Question 21.
What are the tertiary activities?
Tertiary activities are those which provide support to primary and secondary activities.
Question 22.
In what sorts of areas are agricultural activities concentrated?
Agricultural activities are concentrated in those areas of the world which have suitable conditions of growing crops.
Question 23.
What is arable land?
The land on which crops are grown is called arable land.
Question 24.
How is subsistence farming classified?
Subsistence farming is classified into intensive and primitive subsistence agriculture.
Question 25.
In what sort of areas is nomadic herding practised?
Nomadic herding is practised in semi-arid and arid regions of Sahara, Central Asia, and some parts of India.
Question 26.
Why is mixed farming called so?
In mixed farming, the land is used for growing crops as well as rearing livestock.
Question 27.
What is the main feature of plantation agriculture?
In plantation agriculture, only a single crop is grown.
Question 28.
What weather conditions are required in the growing and harvesting seasons of wheat?
In the growing season, wheat requires moderate temperature and rainfall and in the harvesting season, it needs bright sunshine.
Question 29.
Which two countries lead in the production of jute?
India and Bangladesh are the leading producers of jute.
Question 30.
Write a short note on the types of economic activities. Give examples.
The three types of economic activities are primary, secondary, and tertiary. Primary Activities. Activities which involve direct extraction and production of natural resources are called primary activities. Examples: agriculture, fishing, mining. Secondary Activities. Activities which are concerned with the processing of natural resources are called secondary activities. Examples: manufacturing of finished products. Tertiary Activities. Activities which fall neither in the primary category nor the second category are called tertiary activities. They form support to primary and secondary activities. Examples: selling goods, advertising, and banking.