Question 1.
Answer the following questions.
(i) Why are people considered a resource?
(ii) What are the causes for the uneven distribution of population in the world?
(iii) The world population has grown very rapidly. Why?
(iv) Discuss the role of any two factors influencing population change.
(v) What is meant by population composition?
(vi) What are population pyramids ? How do they help in understanding about the population of a country?
(i) People are a nation’s greatest resource. Nature’s bounty becomes significant only when people find it useful. It is people with their demands and abilities that turn them into ‘resources’. Human beings are the most important resource of a nation. In other words, human resource is the ultimate resource.
(ii) Population density depends on the number of factors as follows :-
Geographical Factors :-
- climatic conditions and topography of the place– Few people live in high latitude areas, tropical deserts, mountainous ‘terrains, and forest areas,whereas a large number of people reside in plains.
- Fertility of soils, availability of fresh water, minerals– are other major geographical factors behind the uneven distribution of population .
Social Factors:-
- Some social factors that boost the density of population in a region are better housing, education and health facilities.
- Places with cultural or historical significance are usually populated.
- Economic factors such as employment opportunities:– are another attraction for large chunks of population.
(iii) The world population has grown very rapidly because of the better food supplies, increase in medical facilities, reduced death rate, a birth rate almost remaining the same.
- The difference between birth rate and death rate is called natural growth rate. This natural growth is high due to better medical and food facilities leading to growth in population.
- Many people move from one country to another due to various reasons. This also leads to increase in population of the countries having the immigration.
(iv) Geographical factors: People prefer to live on plains more than mountains or plateaus and they live more in moderate climates than extreme hot or cold. From the agricultural point of view, fertile lands are preferred. Areas with mineral deposits are more populated.
Economic factors: People prefer industrial areas since they provide more and better employment opportunities. Due to this, industrial cities are thickly populated.
(v) Population composition refers to the structure of the population. People vary greatly in their age, sex, literacy level, health condition, occupation, and income level.
The composition of the population helps us to know how many are males or females, which age group they belong to, how educated they are and what type of occupations they are employed in, what their income levels and health conditions are. The study of all the above-mentioned parameters helps us to understand the quality of people’s lives better.
(vi) Population pyramid is also called age-sex pyramid. It shows:
- It shows division of population into various age groups like 5 to 9 years, 10 to 14 years etc.
- It gives the percentage of male female ratio, in each age group.
- It tells about number of dependents-young and old along with number of economically active peoples.
- It helps to understand the economic, health, social structure by indirectly referring to death, birth rate in terms of age and sex.
(vii) A population pyramid in which the base is broad and the top part is narrow means that although a large number of births take place, not all grow up to be adults and old; it means many die before reaching these ages. This indicates a large death rate and Kenya shows such a pyramid. This means a high population growth rate.
In countries like India, the death rate is decreasing, so the pyramid is broad in the younger age groups, and the size of the pyramid decreases steadily.
Question 2.
Tick the correct answer.
(i) Which does the term population distribution refer to?
(a) How population in a specified area changes over time.
(b) The number of people who die in relation to the number of people born in a specified area.
(c) The way in which people are spread across a given area.
(ii) Which are three main factors that cause population change?
(a) Births, deaths, and marriages.
(b) Births, deaths, and migration.
(c) Births, deaths, and life expectancy.
(iii) In 1999, the world population reached
(a) 1 billion
(b) 3 billion
(c) 6 billion
(iv) What is a population pyramid?
(a) A graphical presentation of the age, sex composition of a population.
(b) When the population density of an area is so high that people live in tall buildings.
(c) Pattern of population distribution in large urban areas.
(i) (c) The way in which people are spread across a given area.
(ii) (b) Births, deaths, and migration.
(iii) (c) 6 billion
(iv) (a) A graphical presentation of the age, sex composition of a population.
Question 3.
Complete the sentences below using some of the following words sparsely, favorable, fallow, artificial, fertile, natural, extreme, densely. When people are attracted to an area it becomes …………………….. populated.
Factors that influence this include …………………… climate; good supplies of …………………….. resources and …………………….. land.
When people are attracted to an area it becomes densely populated.
Factors that influence this include a favorable climate; good supplies of natural resources and fertile land.
Question 4.
Activity:
Discuss the characteristics of society with “too many under 15s” and one with “too few under 15s”.
- A society with ‘too many under 15s’ needs more schools to be able to educate them.
- There should be efficient and laborious teachers.
- There should be provisions for items necessary for a child’s amusement, like toys.
- Children are prone to diseases. Facilities for hospitals should be improved in such a society.
- In a society with ‘too few under 15s’ will have more and more mature people.
- Pension schemes will work there fruitfully.
- There may be the need for wheelchairs.
- Labour supply will be easier. These people will also need hospitals.
Question 5.
Choose the correct option.
(i) The most populated continent is
(a) Asia
(b) Africa
(c) Europe
(d) South America
(ii) The least number of people live in this continent
(a) North America
(b) Europe
(c) Oceania
(d) Antarctica
(iii) According to population, what is India’s rank in the world?
(a) 7th
(b) 2nd
(c) 5th
(d) 1st
(iv) Which of these countries has a population below 100 million?
(a) Japan
(b) Peru
(c) USA
(d) India
(v) What is the average population density of the world? (in persons per sq km)
(a) 300
(b) 100
(c) 45
(d) 10
(vi) In which country is the city of Osaka located?
(a) the UK
(b) South Korea
(c) Japan
(d) None of these
(vii) Which of these countries is notable for the number of people who emigrate outside from there?
(a) Sudan
(b) Australia
(c) New Zealand
(d) None of these
(viii) Which of these characteristics of a population pyramid indicates the lowest levels of literacy and development?
(a) broad base, narrow top
(b) broad base, steady slope
(c) narrow base, narrow top
(d) broad base, broad top
(i) (a), (ii) (d), (iii) (b), (iv) (b), (v) (c), (vi) (c), (vii) (a), (viii) (a).
Question 6.
Fill in the blank spaces given to complete each sentence.
- ……….. is considered to be the ultimate resource.
- More than 90% of the world’s population resides on just …………… per cent of the total land surface.
- The top ten countries in population cover about …………. per cent of the total world population.
- ……….. is the most populated country in North America.
- The world’s population reached a billion in the year ………….
- Birth rate and death rate are usually expressed in terms of per ………… people.
- The difference between the ……… and the ………… is called natural growth rate of population.
- The age group 0-15 comes under the economically ………….. group.
- Human resource
- ten
- sixty
- USA
- 1820
- 1000
- birth rate, death rate
- dependent
Question 7.
State whether each of the following statements is true (T) or false (F).
- Many more people live to the south of the Equator than the north.
- Each of the top ten populated countries has a population of over 100 million.
- South-Central Asia has the highest density of population.
- The population of the world doubled between 1820 and 1999.
- In the United Kingdom, the birth rate as well as the death rate is low.
- Japan and Bangladesh are very densely populated. We can conclude that both are economically underdeveloped.
- False
- True
- True
- False
- True
- False
Question 8.
Match the items given in Column I correctly with those given in Column II.
(i) (f), (ii) (a), (iii) (d), (iv) (c), (v) (b), (vi) (e).
Question 9.
In what respects do different human beings differ?
Human beings differ from each other in age, sex, education, ethnicity, culture, physical and mental strength, etc.
Question 10.
With the help of figures, describe how the population varies across continents.
Around 61% of the world’s population lives in Asia, 12% in Europe, 13% in Africa, 8% in Central/South America, 5% in North America, and 1% in Oceania.
Question 11.
If 600 people live in your colony, and the area of your colony is 2 sq km, what is the population density of your colony?
If 600 people live in a 2 sq km area, on average, 300 people live in 1 sq km. So the density of the population is 300 persons per sq km.
Question 12.
Compare the population density of the world with that of India.
The population density of the world is around 45 persons per sq km, whereas that of India is over 320 persons per sq km.
Question 13.
How does climate affect the population distribution of an area?
People prefer to live in regions with a moderate climate, and not places of the extreme cold and hot climate. So moderate climate regions are densely populated.
Question 14.
What is life expectancy?
Life expectancy is the number of years an average person can expect to live, based on data.
Question 15.
What is the general trend of migrations from one country to another? Why is it so?
Generally, people migrate from less developed countries to more developed ones. This is done for better employment opportunities and other facilities.
Question 16.
What is an age-sex pyramid?
An age-sex pyramid is a graph showing the number of males and females under certain defined age groups.
Question 17.
Which of these countries is more densely populated: one with a small population in a large area or one with a large population in a large area?
A country with a large population in a small area is more densely populated out of the two.
Question 18.
Describe how various factors affect population distribution.
Topography, favorable climate, the fertility of soils, availability of fresh water, minerals are major geographical factors affecting the population density of a region.
People prefer to live on plains more than mountains or plateaus and they live more in moderate climates than extreme hot or cold. From the agricultural point of view, fertile lands are preferred. Areas with mineral deposits are more populated. Some social factors that boost the density of the population in a region are better housing, education, and health facilities. Places with cultural or historical significance are usually populated. Employment opportunities are another attraction for large chunks of the population.
Question 19.
Describe how the population of the world has grown in history. What has caused the population explosion?
The world population grew steadily initially. It reached a billion in the year 1820. But the next two billion were added in just a hundred and fifty years. By 1970 the population was 3 billion. In the next 29 years, i.e. by the year 1999, the population had
doubled to 6 billion. The population explosion has been mainly caused by the growth in medical facilities, which has decreased the death rate to a large extent.
Question 20.
What are the factors affecting the population change in a region?
Factors affecting the population change in a region are birth rate, death rate, and migrations. The birth rate is a statistic that measures the number of live births per 1000 people. The death rate is a statistic that measures the number of deaths per 1000 people. Along with the birth and death rates, another factor affecting population change is migration. Migration refers to the movement of people from one area to another. People leaving a country are called emigrants and the phenomenon is called emigration. People arriving in a country are called immigrants and the phenomenon is called immigration.
Question 21.
What is the population pyramid? What is its significance and what information can it give? Look at the population pyramid in the figure and answer these questions: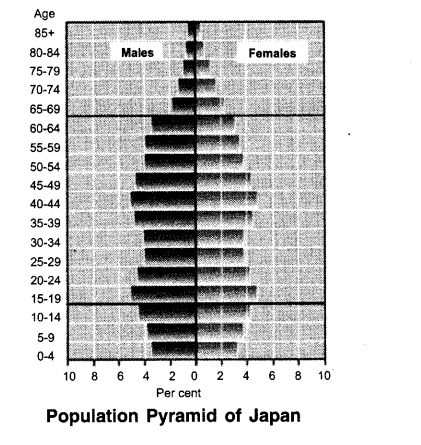
(a) What can you say about the birth rates of the country? Give evidence.
(b) What does the shape at the top of the pyramid indicate?
(c) Which country out of these is most likely to have such a pyramid? A developing country, a developed country, or an underdeveloped country?
pyramid gives information about the distribution of different age groups of people based on gender. The shape of the age-sex pyramid of a country is indicative of a lot of information about the country. The size towards the bottom may be used to estimate the birth rate, while the size towards the top estimates the death rate.
A population pyramid in which the base is broad and the top part is narrow means that although a large number of births take place, not all grow up to be adults and old; it means many die before reaching these ages. This indicates a large death rate and Kenya shows such a pyramid. This means a high population growth rate.
In countries like India, the death rate is decreasing, so the pyramid is broad in the younger age groups, and the size of the pyramid decreases steadily.
- The given population pyramid has a base narrower than some of its upperparts. This means that the birth rate of the country is not too much.
- As we go to the top, the shape indicates that more people reach old age. This shows a lower death rate as well.
- This is most likely to be the age-sex pyramid of a developed country. The population growth rate seems to be controlled. Moreover, the youth form a major part of the population, so the development levels must be high.