Question 1.
What kinds of cloth had a large market in Europe?
Chintz (derived from the Hindi word chhint), Cossaes (or Khassa) and Bandanna (referred to a variety of brightly coloured cloth, produced through a method of tying and dying) . All these printed cotton textiles cloth had a large market in Europe.
Question 2.
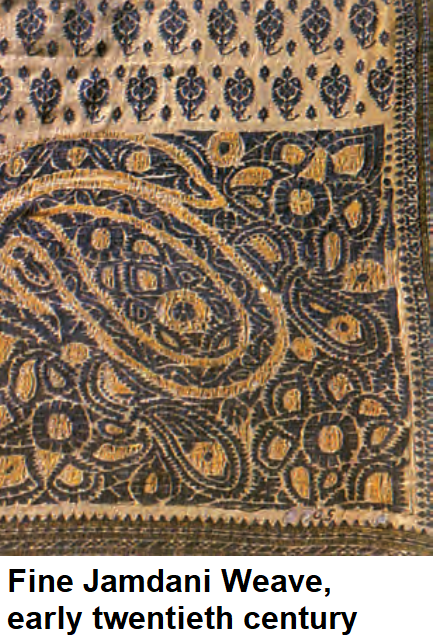
What is jamdani?
Jamdani is a fine muslin on which decorative motifs are woven on the loom, typically in grey and white. Often a mixture of cotton and gold thread was used, as in the cloth in the picture below.

Question 3.
What is bandanna?
Bandanna is a brightly coloured and printed scarf for neck and head. This word was derived from the word Bandhan. It referred to a variety of brightly coloured cloth, produced through a method of tying and dying.
Question 4.
Who are the Agarias?
Groups of men and women carrying basket-loads of iron are known as the Agarias.
Question 5.
Fill in the blanks:
- The word chintz comes from the word ________
- Tipu’s sword was made of _____ steel.
- India’s textile exports declined in the _____ century.
- Chhint
- Wootz
- 19th .
Question 6.
How do the names of different textiles tell us about their history?
- European traders first saw fine cotton cloth from India in Mosul in present-day Iraq. They referred to all finely woven textiles as “muslin”.
- Portuguese first came to India in search of spices and landed in Calicut on the Kerala coast in south-west India. They took back cotton textiles to Europe, along with the spices. They named it “Calico”. Subsequently Calico became the general name for all cotton textiles.
- Many other words point to the popularity of Indian textiles in Western markets.
- The pieces included printed cotton cloths called Chintz, Cossaes (or Khassa) and Bandanna is a brightly coloured and printed scarf for the neck or head. This term was derived from the word “Bandanna” (Hindi for tying).
- Other clothes were known by their place of origin: Kasimbazar, Patna, Calcutta, Orissa and Charpoore.
- The widespread use of such words shows how popular Indian textiles had become in different parts of the world.
Question 7.
Why did the wool and silk producers in England protest against the import of Indian textiles in the early eighteenth century?
Textile industry had just begun to develop in England in the early 18th century. The wool and silk producers in England found themselves unable to compete with Indian textiles. They wanted to secure the market within the country by preventing the entry of Indian textiles. Therefore, they protested against its import.
Question 8.
How did the development of cotton industries in Britain affect textile producers in India?
Cotton industries in Britain developed and adversely affected textile producers in India in several ways:
1. Indian textiles faced competition from British textiles in the European and American markets.
2. Export of textiles to England became more and more difficult because the British Govt, imposed very high duties on Indian textiles.
3. In the beginning of the 19th century, cotton textiles made in Britain successfully ousted Indian goods from their traditional markets in Africa, America and Europe.
4. Thousands of weavers in India were now thrown out of employment.
- Bengal weavers were the worst hit.
- English and European companies stopped to buy Indian goods. Their agents (Gomasthas) no longer gave out advances to weavers to secure supplies.
- Distressed weavers wrote petitions to the government to help them.
5. By the 1830s British cotton cloth flooded Indian markets. Actually by the 1880s, 67% of all the cotton clothes worn by Indians were made of cloth produced in Britain. This affected not only specialist weavers but also spinners.
6. Thousands of rural spinner women were rendered jobless.
Question 9.
Why did the Indian iron smelting industry declined in the nineteenth century?
There were several reasons:
- The new forest laws of the colonial government prevented people from entering the reserved forests. Now it became difficult for the iron smelters to find wood for charcoal. Getting iron ore was also a big problem. Hence, many gave up their craft and looked for other jobs.
- In some areas the government did grant access to the forest. But the iron smelters had to pay a very high tax to the forest department for every furnace they used. This reduced their income.
- By the late 19th century iron and steel were being imported from Britain. Ironsmiths in India began using the imported iron to manufacture utensils and implements. This inevitably lowered the demand for iron produced by local smelters.
All these reasons caused the decline of the Indian iron smelting industry.
Question 10.
What problems did the Indian textile industry face in the early years of its development?
During the early period of its development, the textile industry in India faced many problems.
- In most countries, governments supported local manufacturers by imposing heavy duties on imports. This finished the competition and protected their infant industries.
- English producers wanted a secure market within the country by preventing the entry of Indian textiles. British government enacted the Calico Act in 1720 which banned the use of printed cotton textiles – chintz – in England.
- The colonial government in India usually refused such protection to local industries.
Question 11.
What helped TISCO expand steel production during the First World War?
Before the First World War (1914 -1918) India imported British steel for rails. When in 1914 the war broke out, steel produced in Britain now had to meet the demands of the war in Europe. So, imports ‘of British steel into India declined and the Indian Railways turned to TISCO for the supply of rails.
As the war dragged on for several years, TISCO had to produce shells and carriage wheels for the war. By 1919 the colonial government was buying 90% of the steel manufactured by TISCO. Over time TISCO became the biggest steel industry within the British empire.
Question 12.
Find out about the history of any craft around the area you live in. You may wish to know about the community of craftsmen, the changes in the techniques they use, and the markets they supply. How have these changed in the past 50 years?
History of Handloom weaving:
- Spinning of thread
- Weaving by Julahas in village
- Sale of the fabric in the local market
- Looms were set up
- Fabric woven for local, national and international markets
- Powerlooms
- International markets.
Changes in the Past 50 years
- Constitution of All India Handloom board in 1952.
- Government support for the supply of yarn, dyes and chemicals, etc.
- Encouragement by giving awards.
- Insurance cover against natural calamities etc.
Question 13.
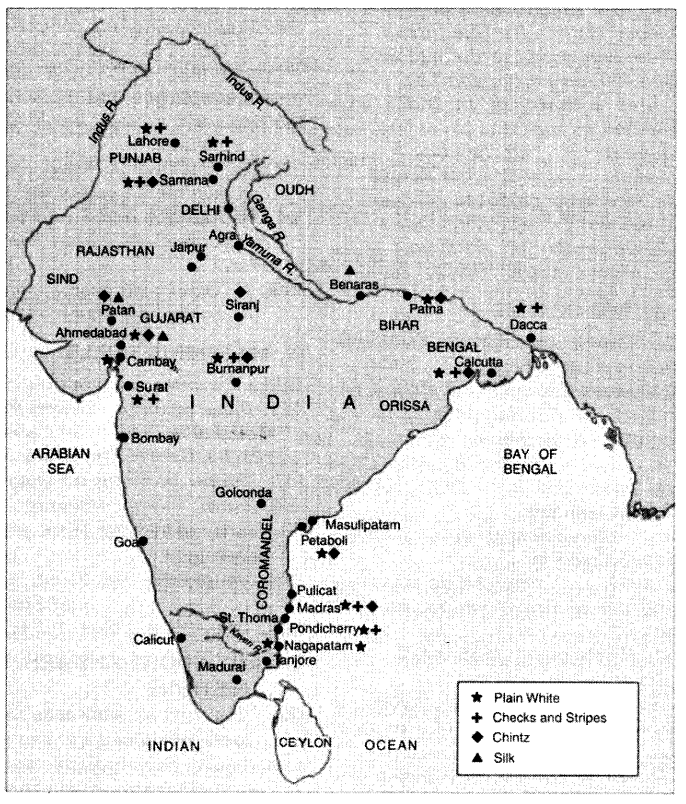
On a map of India, locate the centres of different crafts today. Find out when these centres came
Question 14.
Choose the correct option:
(i) One of the most important Indian ports of the 17th century.
(a) Bombay
(b) Madras
(c) Surat
(d) Vishakhapatnam
(ii) Bandana patterns were mostly produced in
(a) Rajasthan and Gujarat
(b) Rajasthan and Orissa
(c) Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh
(d) Chhattisgarh and West Bengal
(iii) The job of a rangrez was to
(a) Weave cloth
(b) Dye thread
(c) Transport goods to. the markets
(d) Spin thread on the charkha
(iv) The first cotton mill in India was established in
(a) Gujarat
(b) Bombay
(c) Madras
(d) West Bengal
(v) Wootz steel was produced all over
(a) South India
(b) North India
(c) Central India
(d) North-east India
(i)(c), (ii)(a), (iii)(b), (iv)(b), (v)(a)
Question 15.
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words to complete each sentence.
- The cotton textiles which the Portuguese took back to Europe, along with the spices came to be known as …………..
- The …………….. was invented by John Kaye which increased the of the traditional spindles.
- Weavers often belonged to communities that specialized in ……………..
- ………….. and ………………. emerged as important new centres of weaving in the late 19th century.
- Indian Wootz steel fascinated ………………. scientists.
- The Tata Iron and Steel factory is situated on the banks of the river …………..
- TISCO had to expand its capacity and extend the size of its factory to meet the demands of the …………..
- Calico
- Spinning Jenny
- weaving
- Sholapur; Madurai
- European
- Subamarekha
- war
Question 16.
State whether each of the following statements is True or False.
- From the 1850s, Britain came to be known as the ‘workshop of the world’.
- The invention of the spinning jenny and steam engine revolutionized cotton textile weaving in England.
- European trading companies such as the Dutch, the French, and the English purchased cotton and silk textiles in India by importing diamonds.
- Men were usually involved in the work of spinning.
- Iron smelting in India was extremely common until the end of the 19th century.
- The Tata Iron and Steel Company began to produce steel after the First World War.
- True
- True
- False
- False
- True
- False
- Question 16.
- Match the items given in Column A correctly with those given in Column B.

- (i) – (c)
- (ii) – (a)
- (iii) – (e)
- (iv) – (b)
- (v) – (d)
Question 17.
Give two reasons why Indian textiles were renowned all over the world.
Their fine quality and beautiful craftsmanship made them renowned all over the world.
Question 18.
Why were printed Indian cotton textiles popular in England?
Printed Indian cotton textiles were popular in England for their exquisite floral designs, fine texture and relative cheapness.
Question 19.
During which period patola weaving was famous?
It was famous during the mid-19th century.
Question 20.
Name the origin of the word calico.
Calicut..
Question 21.
Name the important centres of jamdani weaving.
Dacca in Bengal and Lucknow in the United Provinces (U.P.).
Question 22.
Name two places where chintz was produced during the mid-19th century.
Question 7.
How did European trading companies purchase cotton and silk textiles in India?
European trading companies purchased cotton and silk textiles in India by importing silver.
Question 23.
Name the household spinning instrument.
Charkha and Takli.
Question 24.
What did Mahatma Gandhi urge people during the national movement?
During the national movement, Mahatma Gandhi urged people to boycott imported textiles and use hand-spun and hand-woven cloth.
Question 25.
What became a symbol of nationalism?
Khadi became a symbol of nationalism.
Question 26.
How did the growth of cotton mills in the country prove to be a boon for the poor peasants, artisans and agricultural labourers?
They got work in the mills.
Question 27.
How did Indian cotton factories prove to be helpful during the First World War?
They began to produce cloth for military supplies.
Question 28.
Why was Tipu’s sword so special?
Tipu’s sword was made of Wootz steel. Wootz steel, when made into swords, produced a very sharp edge that could easily rip through the opponent’s armour.
Question 29.
Why was the Wootz steel making process completely lost by the mid 19th century?
There are two reasons for it:
- The sword and armour making industry died with the conquest of India by the British.
- Imports of iron and steel from England displaced the iron and steel produced by craftsmen in India.
Question 30.
What were the furnaces made of?
The furnaces were made of clay and sun-dried bricks.
Question 31.
Why were bellows used?
Bellows were used to keep the charcoal burning.
Question 32.
What were the piece goods?
Piece goods were usually woven cloth pieces that were 20 yards long and 1 yard wide.
Question 33.
How were Indian textiles viewed in the world market?
India was the largest producer of cotton textiles in the world before the British conquered Bengal around 1750. Indian textiles had long been renowned both for their fine quality and exquisite craftsmanship. They were extensively traded in Southeast Asia (Java, Sumatra, and Penang) and West and Central Asia. From the 16th-century European trading companies began buying Indian textiles for sale in Europe.
Question 34.
How did the inventions of the Spinning Jenny and Steam Engine revolutionise cotton textile weaving in England?
Textile industries had just emerged in England in the early 18th century.
So, it was difficult for the English producers to compete with Indian textiles. This competition with Indian textiles led to a search for technological innovation in England. In 1764, the Spinning Jenny was invented by John Kaye which increased the productivity of the traditional spindles.
Then came the steam engine. It was invented by Richard Arkwright in 1786. These two inventions revolutionised cotton textile weaving in England. Cloth could now be woven in immense quantities and cheaply too.