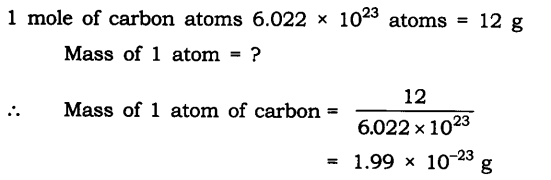Question 1. In a reaction, 5.3 g of sodium carbonate reacted with 6 g of ethanoic acid. The products were 2.2 g of carbon dioxide, 0.9 g water and 8.2 g of sodium ethanoate. Show that these observations are in agreement with the law of conservation of mass carbonate.
Question 2. In a reaction, 5.3 g of sodium carbonate reacted with 6 g of ethanoic acid. The products were 2.2 g of carbon dioxide, 0.9 g water and 8.2 g of sodium ethanoate. Show that these observations are in agreement with the law of conservation of mass carbonate.
Question 3. Hydrogen and oxygen combine in the ratio of 1: 8 by mass to form water. What mass of oxygen gas would be required to react completely with 3 g of hydrogen gas?
Ratio of H: O by mass in water is:
Hydrogen: Oxygen —> H2O
∴ 1 : 8 = 3 : x
x = 8 x 3
x = 24 g
∴ 24 g of oxygen gas would be required to react completely with 3 g of hydrogen gas.
Question 4 Which postulate of Dalton’s atomic theory is the result of the law of conservation of mass?
The postulate of Dalton’s atomic theory that is the result of the law of conservation of mass is—the relative number and kinds of atoms are constant in a given compound. Atoms cannot be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
Question 4. Which postulate of Dalton’s atomic theory can explain the law of definite proportions?
The relative number and kinds of atoms are constant in a given compound.
Question 5. Define the atomic mass unit.
One atomic mass unit is equal to exactly one-twelfth (1/12th) the mass of one atom of carbon-12. The relative atomic masses of all elements have been found with respect to an atom of carbon-12.
Question 6. Why is it not possible to see an atom with naked eyes?
Atom is too small to be seen with naked eyes. It is measured in nanometres.
1 m = 109 nm
Question 7. Write down the formulae of
(i) Sodium oxide
(ii) Aluminium chloride
(iii) Sodium sulphide
(iv) Magnesium hydroxide
The formulae are
Question 8. What is meant by the term chemical formula?
The chemical formula of the compound is a symbolic representation of its composition, e.g., the chemical formula of sodium chloride is NaCl.
Question 9. How many atoms are present in a
(i) H2S molecule and
(ii) P043- ion?
(i) H2S —> 3 atoms are present
(ii) P043- —> 5 atoms are present
Question 10. Calculate the molecular masses of H2, O2, Cl2, C02, CH4, C2H2, NH3, CH3OH.
The molecular masses are: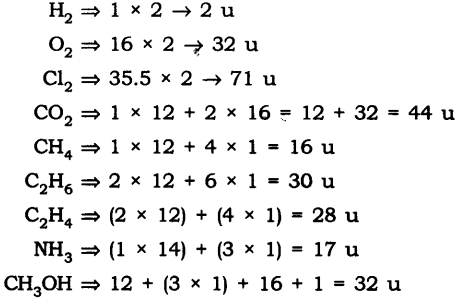
Question 11.Calculate the formula unit masses of ZnO, Na2O, K2C03, given atomic masses of Zn = 65 u, Na = 23 u, K = 39 u, C = 12 u, and O = 16 u.
The formula unit mass of
(i) ZnO = 65 u + 16 u = 81 u
(ii) Na2O = (23 u x 2) + 16 u = 46 u + 16 u = 62 u
(iii) K2C03 = (39 u x 2) + 12 u + 16 u x 3
= 78 u + 12 u + 48 u = 138 u
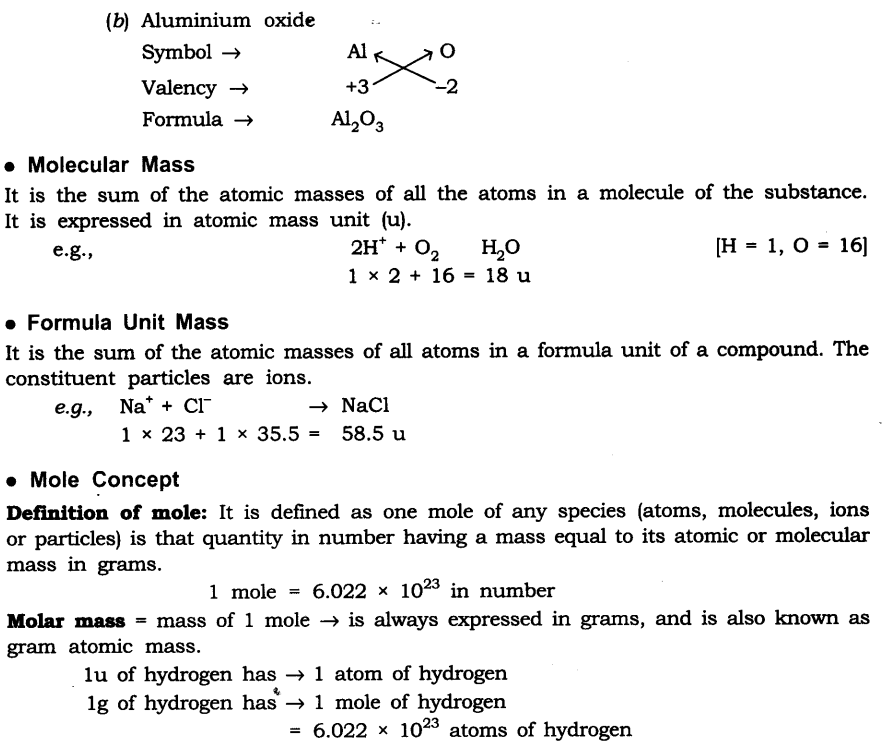
Question 12. If one mole of carbon atoms weighs 12 grams, what is the mass (in grams) of 1 atom of carbon?
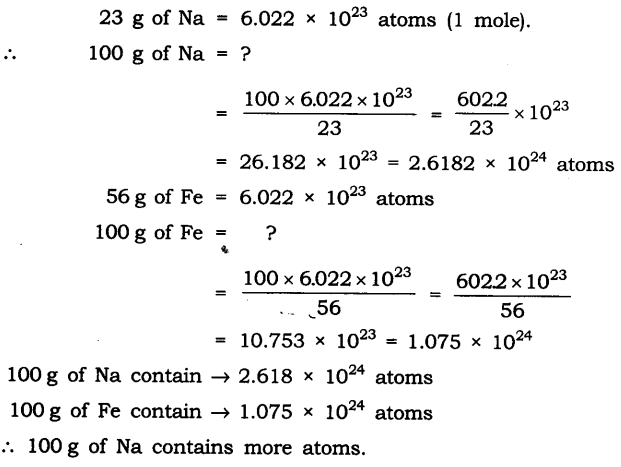
Question 13. Which has more atoms, 100 grams of sodium or 100 grams of iron (given atomic mass of Na = 23 u, Fe = 56 u)?
Question 14. A 0.24 g sample of a compound of oxygen and boron was found by analysis to contain 0.096 g of boron and 0.144 g of oxygen. Calculate the percentage composition of the compound by weight.
Boron and oxygen compound —> Boron + Oxygen
0.24 g —> 0.096 g + 0.144 g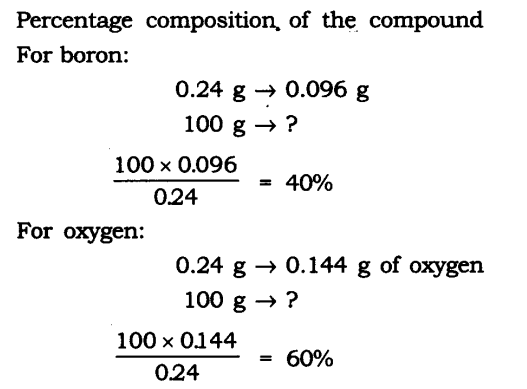
Question 15. When 3.0 g of carbon is burnt in 8.00 g oxygen, 11.00 g of carbon dioxide is produced. What mass of carbon dioxide will be formed when 3.00 g of carbon is burnt in 50.00 g of oxygen? Which law of chemical combination will govern your answer?
The reaction of the burning of carbon in oxygen may be written as:
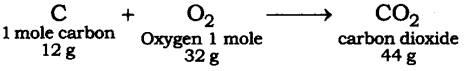
It shows that 12 g of carbon bums in 32 g oxygen form 44 g of carbon dioxide. Therefore 3 g of carbon reacts with 8 g of oxygen to form 11 g of carbon dioxide. It is given that 3.0 g of carbon is burnt with 8 g of oxygen to produce 11.0 g of CO2. Consequently, 11.0 g of carbon dioxide will be formed when 3.0 g of C is burnt in 50 g of oxygen-consuming 8 g of oxygen, leaving behind 50 – 8 = 42 g of O2. The answer governs the law of constant proportion.
Question 16. What are polyatomic ions? Give examples.
The ions which contain more than one atom (same kind or may be of a different kind) and behave as a single unit are called polyatomic ions e.g., OH–, SO42-, CO32-.
Question 17. Write the chemical formulae of the following:
(a) Magnesium chloride
(b) Calcium oxide
(c) Copper nitrate
(d) Aluminium chloride
(e) Calcium carbonate.
(a) Magnesium chloride
Symbol —> Mg Cl
Change —> +2 -1
Formula —> MgCl2
(b) Calcium oxide
Symbol —> Ca O
Charge —> +2 -2
Formula —> CaO
(c) Copper nitrate
Symbol —> Cu NO
Change +2 -1
Formula -4 CU(N03)2
(d) Aluminium chloride
Symbol —> Al Cl
Change —> +3 -1
Formula —> AlCl3
(d) Calcium carbonate
Symbol —> Ca CO3
Change —> +2 -2
Formula —> CaCO3
Question 18. Give the names of the elements present in the following compounds:
(a) Quick lime
(b) Hydrogen bromide
(c) Baking powder
(d) Potassium sulphate.
(a) Quick lime —> Calcium oxide
Elements —> Calcium and oxygen
(b) Hydrogen bromide
Elements —> Hydrogen and bromine
(c) Baking powder —> Sodium hydrogen carbonate
Elements —> Sodium, hydrogen, carbon and oxygen
(d) Potassium sulphate
Elements —> Potassium, sulphur and oxygen
Question 19. Calculate the molar mass of the following substances.
(a) Ethyne, C2H2
(b) Sulphur molecule, S8
(c) Phosphorus molecule, P4 (Atomic mass of phosphorus = 31)
(d) Hydrochloric acid, HCl
(e) Nitric acid, HNO3
The molar mass of the following: [Unit is ‘g’]
(a) Ethyne, C2H2 = 2 x 12 + 2 x 1 = 24 + 2 = 26 g
(b) Sulphur molecule, S8 = 8 x 32 = 256 g
(c) Phosphorus molecule, P4=4 x 31 = i24g
(d) Hydrochloric acid, HCl = 1 x 1 + 1 x 35.5 = 1 + 35.5 = 36.5 g
(e) Nitric acid, HN03 = 1 x 1 + 1 x 14 + 3 x 16 = 1 + 14 + 48 = 63 g
Question 20. What is the mass of
(a) 1 mole of nitrogen atoms?
(b) 4 moles of aluminum atoms (Atomic mass of aluminium = 27)?
(c) 10 moles of sodium sulphite (Na2S03)?
(a) Mass of 1 mole of nitrogen atoms = 14 g
(b) 4 moles of aluminium atoms
Mass of 1 mole of aluminium atoms = 27 g
∴ Mass of 4 moles of aluminium atoms = 27 x 4 = 108 g
(c) 10 moles of sodium sulphite (Na2SO3)
Mass of 1 mole of Na2SO3 = 2 x 23 + 32 + 3 x 16 = 46 + 32 + 48 = 126 g
∴ Mass of 10 moles of Na2SO3 = 126 x 10 = 1260 g
Question 21. Convert into mole.
(a) 12 g of oxygen gas
(b) 20 g of water
(c) 22 g of Carbon dioxide.
(a) Given mass of oxygen gas = 12 g
Molar mass of oxygen gas (O2) = 32 g
Mole of oxygen gas 12/32 = 0.375 mole
(b) Given mass of water = 20 g
Molar mass of water (H2O) = (2 x 1) + 16 = 18 g
Mole of water = 20/18 = 1.12 mole
(c) Given mass of Carbon dioxide = 22 g
Molar mass of carbon dioxide (CO2) = (1 x 12) + (2 x 16)
= 12 + 32 = 44 g
∴ Mole of carbon dioxide = 22/44 = 0.5 mole
Question 22. What is the mass of:
(a) 0.2 mole of oxygen atoms?
(b) 0.5 mole of water molecules?
(a) Mole of Oxygen atoms = 0.2 mole
Molar mass of oxygen atoms = 16 g
Mass of oxygen atoms = 16 x 0.2 = 3.2 g
(b) Mole of water molecule = 0.5 mole
Molar mass of water molecules = 2 x 1 + 16= 18 g .
Mass of H2O = 18 x 0.5 = 9 g
Question 23. Calculate the number of molecules of sulphur (S8) present in 16 g of solid sulphur.
Molar mass of S8 sulphur = 256 g = 6.022 x 1023 molecule
Given mass of sulphur = 16 g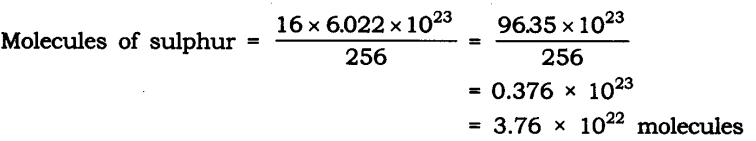
Question 24. Calculate the number of aluminium ions present in 0.051 g of aluminium oxide. (Hint: The mass of an ion is the same as that of an atom of the same element. The atomic mass of Al = 27 u)
Molar mass of aluminium oxide Al2O3
= (2 x 27) + (3 x 16)
= 54 + 48 = 102 g.
Question 25. Define the law of conservation of mass.
In a chemical reaction mass can neither be created nor destroyed.
E.g., 2Na + Cl2 ——–> 2NaCl
2 x 23 + 2 x 35.5 ——> 2(23 + 35.5)
Question 26. Explain law of constant proportion.
In a chemical substance the elements are always present in definite proportions by mass.
E.g., In water, the ratio of the mass of hydrogen to the mass of oxygen H: O is always 1:8
Question 27. Who coined the term atom?
John Dalton coined the term atom.
Question 28. Define atom.
The smallest particle of matter, which can take part in a chemical reaction is called an atom.
Question 29. Define molecule.
The smallest particle of an element or compound which can exist independently is called a molecule.
Question 30. Define atomicity.
The number of atoms constituting a molecule is known as its atomicity.
Question 31. What is the atomic mass unit?
The sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule of the substance is expressed. in the atomic mass unit. E.g., H20 = 1 x 2 + 16 = 18 atoms.
Question 32. How do atoms exist?
Atoms exist in the form of atoms, molecules or ions.
Question.33. Give the atomicity of phosphorous and nitrogen.
The atomicity of phosphorus is P4 i.e., 4.
The atomicity of nitrogen is N2 i.e., 2.
Question 34. What is an ion?
Charged atom is called an ion. The ion can be positively charged called cation or negatively charged called anion.
Question 35. Give one example of cation and anion.
Cation => Na+
Anion => Cl–
Question 36. Give one difference between cation and anion.
Cations are positively charged ions.
Anions are negatively charged ions.
Question 37. Give the chemical formula for ammonium sulphate.
Ammonium sulphate
NH4+ SO42-
Chemical formula —-> (NH4)2S04.
Question 38. What is Avogadro’s constant
The Avogadro’s constant (6.022 x 1023) is defined as the number of atoms that are present in exactly 12 g of carbon-12.
Question 39. Find the molecular mass of H20.
Molecular mass of H20
= (2 x 1) + (16)
= 2 + 16 = 18 u
Question 40. Give the unit to measure the size of an atom and give the size of the hydrogen atom.
The unit to measure the size of an atom, is a nanometer, the size of a hydrogen atom is 10-10m.
Question 41. What is IUPAC, give its one function?
IUPAC is International Union for Pure and Applied Chemistry. It approves the names of elements.
Question 42. Give the Latin name for sodium, potassium, gold and mercury.
Sodium —> Natrium, Gold —> Aurum
Potassium —> Kalium, Mercury —> Hydrargyrum
Question 43. What is the ratio by mass of combining elements in H20, C02 and NH3?
H2O ratio by mass of combining elements 2: 16 —>1: 8 (H: O)
C02 ratio by mass of combining elements 12: 32—> 3: 08 (C: O)
NH3 ratio by mass of combining elements 14 : 3—>14 : 3 (N: H)
Question 44. Define valency and give the valency for the following elements:
Magnesium, Aluminium, Chlorine and Copper.
Valency: The combining capacity of an element is called its valency. Valency of the following elements:
Magnesium – 2
Aluminium – 3
Chlorine – 1
Copper – 2
Question 45. What is a polyatomic ton? Give one example.
A group of atoms carrying a charge is known as a polyatomic ion.
E.g., Ammonium – NH4+
Nitrate – N03–
Question 46. Write down the formula for:
Copper nitrate, calcium sulphate and aluminium hydroxide.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Question 47. What is formula unit mass? How is it different from molecular mass?
The formula unit mass of a substance is a sum of the atomic masses of all atoms in a formula unit of a compound. The constituent particles of formula unit mass are ions and the constituent particles of molecular mass are atoms.
Question 48. Find the number of moles in the following:
(i) 50 g of H2O
(ii) 7 g of Na
Number of moles in
(i) Molar mass of H2O = 18 g
Given the mass of H2O = 50 g
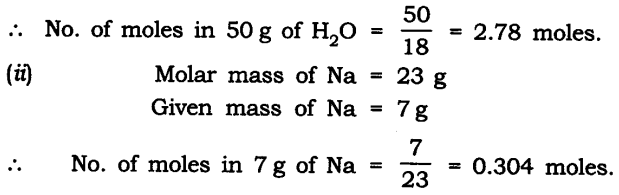
Question 49. Find the number of atoms in the following:
(i) 0.5 mole of C atom
(ii) 2 mole of N atom
(i) 0.5 mole of C atom:
Number of atoms in 1 mole of C atom = 6.022 x 1023 atoms
Number of atoms in 0.5 mole of C atom = 6.022 x 1023 x 0.5
= 3.011 x 1023 atoms
(ii) 2 mole of N atom:
Number of atoms in 1 mole of N atom = 6.022 x 1023 atoms
Number of atoms in 2 moles of N atom = 6.022 x 2 x 1023
= 1.2044 x 1024 atoms
Question 50. Find the mass of the following:
(i) 6.022 x 1023 number of O2 molecules
(ii) 1.5 mole of CO2 molecule
(i) 6.022 x 1023 number of 02 molecules:
Mass of 1 mole of O2 molecule = 6.022 x 1023 molecules = 32 g
(ii) 1.5 mole of CO2 molecule:
Mass of 1 mole of C02 molecule = 6.022 x 1023 molecules = 44 g
Mass of 1.5 mole C02 molecule = 44 x 1.5 = 66 g