Q 1 – What is the colour of the flame when magnesium is burnt?
Ans – White
Q 2 – What kind of change is shown by tearing of paper?
Ans – Tearing of paper is a physical change although, it cannot be reversed.
Q 3 – What kind of change is rusting?
Ans – Chemical
Q 4 – Name the gas which turns lime water milky
Ans – Carbon dioxide gas (CO2) turns lime water milky
Q 5 – Give an example of a physical change which occurs by the action of heat
Ans – Melting of ice to form water is a physical change which occurs by the action of heat.
Q 6 – Define galvanisation.
Ans – The process of depositing a layer of zinc over iron is called galvanisation.
Q 7 – Write the colour of copper sulphate solution obtained when iron nails are dipped in it?
Ans – When iron nails are dipped in copper sulphate solution, then the colour of the solution changes to green.
Q 8 – What colour of the flame is observed when magnesium ribbon is burnt in the air?
Ans – When magnesium is burnt in the air then a brilliant white flame is obtained.
Q 9 – What is the meaning of rusting?
Ans – The formation of rust over the surface of iron is known as rusting.
Q 10 – How can you say that the ripening of fruit is a chemical change?
Ans – Ripening of fruit is a chemical change because after ripening, a new product with different properties is formed.
Q 11 – The formation of rust over the surface of iron is known as rusting.
Ans – (i) Cutting a piece of paper
(ii) Melting of ice
Q 12 – Is the souring of milk a physical change or a chemical change? Why?
Ans – Souring of milk is a chemical change because original substances present in milk lose their nature and, identity and form new chemical substances
Q 13 –A piece of chalk becomes powdery on pressing. Which type of change is it?
Ans – Physical.
Q 14 – Name the two main kinds of changes.
Ans –
- Physical
- Chemical
Q 15 – Complete the following reaction
Ca (OH) 2 + CO2 →
Ans –

Q 16 – What is the nature of magnesium oxide solution?
Ans – Magnesium oxide is basic in nature because it turns red litmus solution to blue.
Q 17 – State the decomposition of calcium carbonate with the help of formulae and chemical reactions.
Ans –

Q 18 – What is a freezing mixture?
Ans – A mixture of ice and common salt.
Q 19 – Name the metal which is used for galvanising iron.
Ans – Zinc metal is used for galvanising iron.
Q 20 – Which gas is released when baking soda is mixed with vinegar?
Ans – Carbon dioxide (CO2)
Q 21 – Name the ultimate colour of the solution when iron nails are dipped in the solution of copper sulphate.
Ans – Green
Q 22 – Name the metals which are mixed (alloyed) with iron to make stainless steel. ?
Ans – Metals like chromium and nickel are mixed (alloyed) with iron to make stainless steel.
Q 23 – What is the nature of the aqueous solution of magnesium oxide?
Ans – The aqueous solution of magnesium oxide is basic in nature, as it turns red litmus blue
Q 24 – What happens when water is heated?
Ans – It gets converted into vapours.
Q 25 – Metals like chromium and nickel are mixed (alloyed) with iron to make stainless steel
Ans – The two methods to prevent rusting are:
- Painting the iron articles.
- Greasing or oiling the iron articles.
Q 26 – Define Rust?
Ans – Rust is a red or brown oxide coating on iron caused by the action of oxygen and moisture.
Q 27 – We should eat a freshly cut apples. Why?
Ans – We should eat freshly cut apple because if we leave the apple after cutting, it starts turn to brownish due to the oxidation of the essential nutrients present in it and its food value decreases.
Q 28 – What are physical properties?
Ans –Properties such as shape, size, colour and state of a substance are called its physical properties.
Q 29 – Is burning a physical change?
Ans – No
Q 30 – In which type of change, no new substance is formed?
Ans – Physical change
Q 31 –Write an equation for burning magnesium ribbon?
Ans – Magnesium (Mg) + Oxygen (O2) → Magnesium Oxide (MgO)
Q 32 – What type of change occurs when iron reacts with copper sulphate?
Ans – Chemical change
Q 33 – Which type of change is an explosion of a firework?
Ans – Chemical change.
Q 34 – What happens if a cut apple is kept open for a while?
Ans – The open surface acquires a brown colour.
Q 35 – Name two important factors responsible for rusting
Ans – Water (or moisture)
Oxygen
Q 36 – Write the necessary conditions for rusting.
Ans – Presence of water vapour and air
Q 37 – Is melting of ice a chemical change? Give reason.
Ans –No. When ice melts into water, no new substance is formed. Only the physical form of ice is changed. So, it is not a chemical change.
Q 38 – Define crystallization.
Ans – The process of obtaining pure crystals of substances from their solution is called crystallization.
Q 39 –What happens when a hack-saw blade is heated?
Ans – When a hack-saw blade is heated, it becomes red in colour. It starts emitting light.
Q 40 – What happens when magnesium oxide is dissolved in water? Write the chemical equation for the reaction.
Ans – On dissolving magnesium oxide in water, magnesium hydroxide is produced. This chemical change can be written in the form of the following equation:
Magnesium oxide (MgO) + Water (H2) → Magnesium hydroxide [Mg(OH)2]
Q 41 – What happens when carbon dioxide passes through lime water?
Ans – When carbon dioxide passes through lime water, calcium carbonate is formed and lime water turns milky.
Q 42 – Write two importances of chemical changes
Ans – 1. Extraction of all metals requires chemical changes.
2. Useful new materials, such as plastics and detergents, are produced by chemical reactions
Q 43 –Why is it advised not to play with fireworks?
Ans – The explosion of a firework is a chemical change. Such an explosion produces heat, light, sound and harmful gases that pollute the atmosphere. That is why it is advised not to play with fireworks.
Q 44 – Name some physical properties of a substance.
Ans – Shape, size, colour, state of a substance are some of its physical properties.
Q 45 – What is stainless steel?
Ans – Stainless steel is an alloy of iron which does not rust, hence the name stainless steel. It is made by mixing iron with carbon and metals like chromium, nickel and manganese
Q 46 – What happens when iron nail is dipped into copper sulphate solution?
Ans – The blue colour solution of copper sulphate changes into a green coloured solution.
The change of colour of the solution front blue to green is due to the formation of iron sulphate, a new substance. The brown substance deposit on the iron nail is copper, another new substance. We can write the reaction as:
Copper Sulphate solution (blue) + Iron → Iron Sulphate solution (green) + Copper (brown deposit).
Q 47 – Give some examples of physical changes
Ans – Following are some examples of physical changes:
- Melting of ice
- Glowing of electric bulb
- Change of water into steam
- Cutting of a block of wood
- Breaking of a glass tumbler
Q 48 – What happens when carbon dioxide is passed through lime water? Give chemical equation.
Ans – When carbon dioxide is passed through lime water, calcium carbonate is formed, which makes lime water milky. The turning of lime water milky is a standard test of presence of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (CO2) + Lime water [Ca(OH2) ] → Calcium Carbonate(CaCo3) + Water(H2O).
Q 49 – What does ozone do for us?
Ans – It protects us from the harmful ultraviolet radiation which come from the sun. Ozone absorbs this radiation and breaks down to oxygen.
If ultraviolet radiations were not absorbed by ozone, they would reach the earth’s surface and cause harm to us and other life forms. Ozone acts as a natural shield against these radiations
Q 50 – Give some examples of chemical changes
Ans – Following are some examples of chemical changes:
1. Curdling of milk
2. Burning of a piece of paper
3. Cooking of rice
4. Rusting of iron
5. Explosion of firecrackers
Q 51 –Why has a fraction of ships iron to be replaced every year?
Ans –Ships are made of iron and a part of them remains underwater. On the part above water also, water drops keep clinging to the ship’s outer surface. Moreover, the water of the sea contains many salts. The salt water makes the process of rust formation faster. Therefore, ships suffer a lot of damage from rusting in spite of being painted. So much so, that a fraction of the ship’s iron has to be replaced every year.
Q 52 –What happens when baking soda is added to vinegar and the resulting gas is passed through lime water?
Ans – On adding baking soda to vinegar, a hissing sound is heard and bubbles are seen coming out. When this gas is passed through lime water, it turns milky.
The change in the test tube is as follows:
Vinegar (Acetic acid) + Baking soda (Sodium hydrogen carbonate) → Carbon dioxide + other substances.
The reaction between carbon dioxide and lime water is as follows:
Carbon dioxide (CO2) + Lime water [Ca(OH)2] → Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3) + Water (H2O)
When carbon dioxide is passed through lime water, calcium carbonate is formed, which makes lime water milky. The turning of lime water milky is a standard test of carbon dioxide.
Q 53 – Explain the burning of magnesium ribbon.
Ans – Take a thin ribbon of magnesium. Gently clean the end of the ribbon with sandpaper and bring its tip near a candle flame. It is observed that the ribbon burns with a bright white light. After combustion, white powdery ash is left, which is called magnesium oxide.

Q 54 – Define chemical change. Give one example.
Ans – A change in which one or more new substance(s) is/are formed is called a chemical change; e.g., burning of a matchstick.
Q 55 – What do you mean by physical change?
Ans – A change in which a substance undergoes a change in its physical properties is called a physical change.
Q 56 – What are the characteristics of a chemical change?
Ans – The characteristics of a chemical change are:
1. They release or absorb energy.
2. Most of the changes are irreversible.
3. One or more new substances with new properties are formed.
4. The properties of products are entirely different from the reactants.
Q 57 – Write some points about the ozone layer.
Ans – It acts as a shield against the harmful radiation of the sun.
Its chemical formula is O3. Ozone is entirely different from oxygen.
Q 58 – Why is the burning of a candle considered a chemical change?
Ans – Candles are made of wax and a long thread of cotton (called wick of the candle). While the candle is burnt, the molten wax goes up through the thread and undergoes combustion to form carbon dioxide and water vapour. The ‘wick’ of the candle gets changed to a black mass. Over the process, heat and light energy is given out. It is not possible to recover the burnt wax again
(ii) recover the thread again.
Hence, the burning of a candle is a chemical change.
Q 59 – State the differences between chemical and physical changes
Ans –
| Chemical change | Physical change |
| (i) It is generally an irreversible process. | (i) It is generally a reversible process. |
| (ii) A new substance is formed. | (ii) No new substance is formed. |
| (iii) Properties of a substance change. | (iii) Properties of a substance does not changes. |
| (iv) Energy is given out or absorbed during the change. | (iv) No energy is given out or absorbed during the change. |
Q 60 – What happens when iron nails are dipped in copper sulphate solution?
Ans – When iron nails are dipped in copper sulphate solution, a brown layer of copper gets deposited on the surface of iron nails after some time. This happens due to the reaction between copper sulphate and iron. Also, the colour of copper sulphate changes from blue to green due to the formation of iron sulphate.
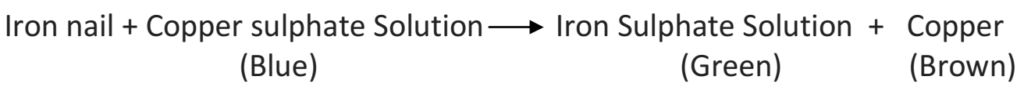
Q 61 – Most of the physical changes are reversible but some are irreversible. Explain the statement with examples
Ans – In a physical change, a substance undergoes a change in its physical properties only. A physical change occurs when there is a force applied, change in temperature, etc., on a substance. Most of the physical changes are reversible like rolling dough into a chapati and then again bringing it back into a dough.
Making a toy aeroplane by folding the paper and then again unfolding the toy aeroplane to recover the page. But when a physical change cannot be reversed or we cannot bring the substance back to its original shape, size, state, etc., is known as irreversible change. For example, baking chapati or making a toy aeroplane by cutting the paper instead of folding
Q 62 – Give an example of a chemical reaction for each of the following situations:
(a) A change in colour is observed.
(b) A gas is evolved.
(c) Sound is produced.
(d) Heat is produced.
(e) Change in taste is observed.
(f) Light is produced.
Ans – (a) Reaction between copper sulphate solution and iron metal. The blue colour of copper sulphate solution changes to green colour ferrous sulphate solution.
(b) Reaction between baking soda and vinegar evolves carbon dioxide gas.
(c) Burning of crackers produces sound.
(d) Reaction between hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide produces heat.
(e) Setting of curd from milk. Taste of milk changes to sour in curd.
(f) Burning of fuel produces light
Q 63 – When we keep a piece of iron in the open area for few days, a brownish, flaky substance, called rust, is deposited on it
(a) Is rust different from iron?
(b) Is the formation of rust from iron a chemical change?
(c) Can you change rust back into iron by some simple method?
(c) Give some other examples of a similar types of changes
Ans – (a) Yes. Rust is an oxide of iron.
(b) Yes, it is a chemical change as the properties of iron has changed.
(c) No.
(d) 1.Setting of curd into milk.
2. Burning of magnesium ribbon in the air.
3. Cooking of food.
Q 64 – Why lime water turns milky on passing carbon dioxide gas into it?
Ans – Chemical formula of lime water is calcium hydroxide which is a colourless solution. When we pass carbon dioxide gas into lime water, it forms white coloured insoluble calcium carbonate.
Lime water + Carbon dioxide ➝ Calcium carbonate + Water
Q 65 – Why iron pillar in Qutub Minar in Delhi famous?
Ans –It is famous because it has not rusted though was built more than 1600 years ago.
Q 66 – Classify the following processes into physical or chemical changes.
(a) Beating of aluminium metal to make aluminium foil
(b) Digestion of food
(c) Cutting of a log of wood into pieces
(d) Burning of crackers
Ans – Physical changes are beating of aluminium metal to make aluminium foil and cutting of a log of wood into pieces.
Chemical changes are digestion of food and burning of crackers.
Q 67 – Explain the following
(a) Lime water turns milky on passing carbon dioxide gas through it.
(b) Bubbles are produced when acetic acid is added to a solution of sodium hydrogen carbonate
Ans – (a) Carbon dioxide gas produced in the reaction passing through freshly prepared lime water as shown in figure.

Lime water is a calcium hydroxide solution. When carbon dioxide gas is passed through lime water, then calcium hydroxide combines with carbon dioxide to form a white solid substance, calcium carbonate which makes lime water milky. This chemical change can be written in the form of a word equation as follows:

(a) The reaction between lime water and carbon dioxide gas is a chemical change because a new substance calcium carbonate is formed during this change. The turning of lime water into milky is a standard test of carbon dioxide.
(b) When baking soda (sodium hydrogen carbonate) and vinegar (acetic acid) are mixed together, then an enchemical change place between sodium hydrogen carbonate and acetic acid to form three new substances. The change in the test tube is as follows:

Q 68 – Is cloud formation a physical change or chemical change? Explain.
Ans –Formation of clouds is a physical change. Clouds are formed by the condensation of water vapours present in the atmosphere. When rainwater goes back on the earth, no new product is formed. Therefore, it is a physical change.
Q 69 – Write the differences between physical and chemical changes
Ans – Differences between physical and chemical changes are
| Physical change | Chemical change |
| No new substance is formed. | A new substance is formed. |
| It is a temporary change. | It is a permanent change. |
| Physical change is easily reversible. | A chemical change is irreversible. |
| Very little energy (heat, etc) is absorbed or given out in a physical change. | A lot of energy (in the form of heat, light, sound etc) is absorbed or given out in a chemical change |
Q 70 – In addition to the formation of new products, what changes do the chemical changes accompany?
Ans – In addition to new products, the following may accompany a chemical change:
- Heat, light or any other radiation (e.g. ultraviolet) may be given off or absorbed.
- The sound may be produced.
- A change in smell may take place or a new smell may be given off.
- A colour change may take place
- A gas may be formed.
Q 71 – Magnesium ribbon bums in air and changes to white substance, i.e. magnesium oxide. When magnesium oxide dissolves in water, what type of change take place? Give a reason in support of your answer. Express the change in the form of the equation.
Ans – Mixing of ash obtained by the burning of magnesium with water is a chemical change. When magnesium is burnt in air, it forms magnesium oxide in the form of white ash.
Magnesium (Mg)+ Oxygen (O2) → Magnesium oxide (MgO)
When magnesium oxide dissolves in water, it forms a new substance, magnesium hydroxide. Magnesium oxide (MgO) + Water (H2O) → Magnesium hydroxide Mg(OH)2 So, it is a chemical change.
Q 72 – What is stainless steel? How is stainless steel made? State an important property of stainless steel.
Ans – Stainless steel is an alloy of iron. When iron is mixed (or alloyed) with carbon, chromium and nickel, then stainless steel is obtained. Stainless steel does not rust at all.
Q 73 – Plants prepare their food by a process called photosynthesis. Can we call photosynthesis is a chemical change? Explain
Ans – During photosynthesis, the plants intake carbon dioxide and water in the presence of chlorophyll and sunlight to form two new substances, i.e. glucose (food) and oxygen gas. So, photosynthesis is a chemical change.
Q 74 – The process of digestion is a chemical change. Explain why.
Ans – In the process of digestion, the various food materials break down to form new substances which can be absorbed by the body. So, the process of digestion is a chemical change.
Q 75 – How ozone layer acts as a protective shield?
Ans – The ozone layer protects us from the harmful ultraviolet radiation which comes from the sun. Ozone absorbs ultraviolet radiations coming from the sun and breaks down to form oxygen.
In this way, the ozone layer absorbs harmful ultraviolet radiation.
Q 76 – Which type of change takes place in the following and state whether the energy is evolved or absorbed during the change?
Burning of a candle, lightning of a bulb, preparation of food by green plants, volcanic eruption, evaporation of petrol, burning of LPG.
Ans –
- Burning of a candle Chemical change as well as physical change and energy evolved.
- Lightning of a bulb Physical change, energy evolved Volcanic eruption Chemical change, energy evolved.
- Evaporation of petrol Physical change as no new chemical substance is formed, energy absorbed.
- Burning of LPG Chemical change because LPG on burning form CO2 and H2O, energy absorbed.
Q 77 – Sarita while helping her mother in kitchen work noticed that the slices of potato and brinjal have acquired a brown colour. She asked her mother the reason behind this change. Her mother said whenever we keep cut pieces of these vegetables open for a long time they acquire such colour.
(a) Are cutting vegetables and change in colour, physical or chemical changes?
(b) Why vegetables acquired brown colour?
(c) Do this brown colouration indicate that the vegetables are spoilt. Can we reverse this process? Why?
(d) Can you suggest ways to avoid this colouration of vegetables?
(e) What value of Sarita is shown here?
Ans – (a) Cutting vegetables is physical change and change in colour of vegetables is a chemical change
(b) Vegetables acquire brown colour due to chemical reaction and thus, formation of a new substance.
(c) No, vegetables are not spoilt and we cannot reverse this process because it is a chemical change.
(d) 1. By not keeping cut vegetables for a long time to exposed air.
2. By dipping cut vegetables in cold water.
(e) Sarita is helping in nature, thoughtful and inquisitive.
Q 78 – Ramesh and Shyam both bought a big iron table for their shop individually. Ramesh painted his table with paints whereas Shyam got it laminated.
(a) What conditions are necessary for the process of rusting?
(b) Whose method is effective in preventing rusting? How?
(c) How does rusting cause a great economic loss?
(d) What values of Ramesh and Shyam are shown here?
Ans – (a) For rusting, moisture and oxygen is necessary.
(b) Both, Ramesh’s and Shyam’s methods are effective in preventing rust. Painting and lamination, both, will prevent air and moisture from coming in contact with the iron table.
(c) Rusting cause a great economic loss as replacement of corroded equipment, their maintenance,
A contamination of other substances, etc., requires a huge amount to be spent on them.
(d) Ramesh and Shyam are both intelligent and responsible.
Q 79 – Give two examples for each of the following cases:
(a) Physical changes which are reversible.
(b) Physical changes which are not reversible.
(c) Chemical changes
Ans – (a) Folding of paper
Melting of ice
(b) Tearing of paper
Breaking of glass
(c) Reaction between vinegar and baking soda.
Burning of a matchstick.
Q 80 – Explosion of a cracker is a chemical change Explain
Ans –When we burn a cracker, it explode Explosion produces heat, light, sound and unpleasant gases that pollute the atmosphere.
Many new products are formed. So, it is a chemical change
Q 81 – Why cannot a chemical change be normally reversed?
Ans –In a chemical change, the products are quite different from the reactants. Therefore, a chemical change cannot be normally reversed.
Q 82 – A student took a solution of copper sulphate in a beaker and put a clean iron nail into it and left it for about an hour
(a) What changes do you expect?
(b) Are these changes chemical in nature?
(c) Write a word equation for the chemical change, if any.
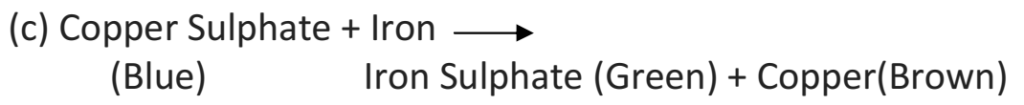
Ans – (a) Colour of the solution in the beaker changes from blue to green. A brown coloured deposit is found on the surface of the iron nail.
(b) The changes are chemical in nature as new substances, iron sulphate (green) and copper (brown) are formed
Q 83 – Describe two changes that are harmful. Explain why you consider them harmful? How can you prevent them?
Ans – Harmful changes are
- Rusting of iron.
- Decaying of fruits.
Rusting of iron is harmful because it slowly destroys iron articles and makes them useless. Since, iron is used in making a large number of objects or articles such as bridges, grills, railings, gates and bodies of cars, buses, trucks and ships, etc. Rusting of iron causes a great loss over a period of time. Prevention Rusting can be prevented by oiling, greasing or painting. It can also be prevented by galvanisation. Decaying fruits causes health hazards. Due to the decaying of fruits, there is a lot of monetary loss in the food industry. Prevention Fruits can be preserved by keeping them at low temperatures and by using some specific preservatives.
Q 84 – What happens when an iron blade of a knife is dipped in a copper sulphate solution? What kind of change takes place?
Ans – When an iron blade of a knife is dipped in a copper sulphate solution, then iron blade is coated with reddish-brown deposits of copper. And the blue colour of copper sulphate solution changes to light green due to the formation of iron sulphate. So, it is a chemical change.
Q 85 – Give an example of a chemical reaction for each of the following situations:
(a) A change in colour is observed.
(b) A gas is evolved.
(c) Sound is produced.
Ans – (a) Chemical reaction between copper sulphate solution and iron metal. In this reaction, blue colour of copper sulphate solution changes to light green colour due to the formation of iron sulphate.

(b) When baking soda and vinegar are mixed together then a chemical change takes place and bubbles of carbon dioxide gas are formed along with some other substances.
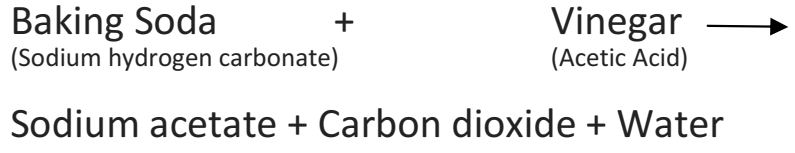
(c) Explosion of a firework produces heat, light, sound and unpleasant gases. The explosion of a firework is a chemical change
Q 86 – Rahul was a student of Class VII. His father purchased a new bicycle for him on his birthday. After few months, he found that the cycle chain and even the handle gets rusted. His father advised him to apply a coating of paint to the cycle and not to keep it in the open in future.
Now, answer the following questions:
(a) Why his cycle gets rusted?
(b) What do you mean by rusting of iron?
(c) What values are shown by Rahul’s father?
Ans –(a) Rahul’s cycle was kept in the open for a longer time. As air contains both oxygen and moisture. Thus, in the presence of oxygen and water, his cycle slowly gets rusted.
Iron(Fe) + Oxygen + Water →Rust (Iron oxide)
(b) If iron objects are left in humid conditions for a longer time, they get covered with reddish-brown ferric oxide (Fe2O3) layer. This is called rusting of iron.
(c) Rahul’s father is caring, aware and intelligent.
Q 87 – In the summer holidays, Karan went to Rann of Kutch in Gujarat with his parents. Karan was aware that in the coastal regions of India especially in the Rann of Kutch common salt is obtained from sea water. Karan was very excited to see that place. He requested his father that he want to see the process of obtaining salt from sea. His father helped him and they went to see the place where common salt was collecting. And he also explained the whole process. Karan was very happy to see the process. Now, answer the following questions.
(a) How is common salt obtained from seawater?
(b) Name the process by which salt is collected from seawater.
(c) What values are shown by Karan?
Ans – (a) Seawater is collected in shallow pits. It is then allowed to evaporate in the sun. As, the water evaporates, the salt solution becomes supersaturated (concentrated). This supersaturated solution cannot hold the excess salt. Thus, it separates out in the form of salt crystals. These salt crystals are collected and are redissolved in water and filtered to remove insoluble impurities. The clear solution is again evaporated to obtain the crystals of pure salt.
(b) Salt is obtained from seawater by the process of evaporation.
(c) The values shown by Karan are curious, aware and intelligence.
Q 88 – When baking soda is mixed with vinegar, bubbles are formed with the evolution of a gas. Name the gas evolved. What happens when this gas is passed through lime water?
Ans – When baking soda (sodium hydrogen carbonate) and vinegar (acetic acid) are mixed together, then a chemical change takes place between sodium hydrogen carbonate and acetic acid to form three new substances.
The change in the test tube is as follows:


Carbon dioxide gas produced in the reaction passing through freshly prepared lime water as shown in figure

Lime water is calcium hydroxide solution. When carbon dioxide gas is passed through lime water, then calcium hydroxide combines with carbon dioxide to form a white solid substance, calcium carbonate which makes lime water milky. This chemical change can be written in the form of word equation as follows:
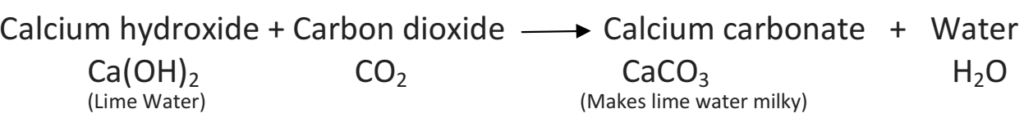
The reaction between lime water and carbon dioxide gas is a chemical change because a new substance calcium carbonate is formed during this change. The turning of lime water into milky is a standard test of carbon dioxide. When baking soda (NaHCO3) reacts with vinegar which contains acitic acid carbon dioxide comes out, which turns lime water milky, therefore it is a chemical change. In all these activities, we saw that in each change, one or more new substances are formed. When magnesium ribbon was burnt, the ash was the new substance formed
The reaction of copper sulphate with iron produced two new substances, i.e. iron sulphate and copper. Vinegar and baking soda together produced carbon dioxide which turned lime water milky. So, all those changes in which one or more new substances are formed, are called chemical changes. These are permanent changes which can usually not be reversed to form the original substance.
Q 89 – If you leave a piece of iron in the open for a few days, it acquires a film of brownish substance, called rust.
(a) Do you think rust is different from iron?
(b) Can you change rust back into iron by some simple method?
(c) Do you think formation of rust on iron is a chemical change?
(d) Give two other examples of a similar type of change.
Ans – (a) Yes, rust is iron oxide (Fe2O3). Thus, rust and iron are not the same substance.
(b) No, rusting of iron is a chemical change because in this reaction, a new substance, rust (iron oxide) is formed. It cannot be reversed by any method.
(c) Yes, rusting of iron is a chemical change. During the rusting of iron, it combines with the oxygen in the presence of water (moisture) to form a new compound ‘iron oxide’. This iron oxide is rust.

It is a permanent change which cannot be reversed back.
So, rusting of iron is a chemical change.
(d) Two other examples are:
- The setting of curd from milk.
- Burning of magnesium ribbon to form magnesium oxide.