Q 1 – State the effects of heat.
Ans – Heat can bring many changes to an object. An object might expand on heating, as it becomes hotter. Heat can also cause a change in the state of a body. For example, on heating, ice(solid), eventually changes into water (liquid). Heat can burn an object or even kill
harmful bacteria. It can also increase the speed of chemical reactions.
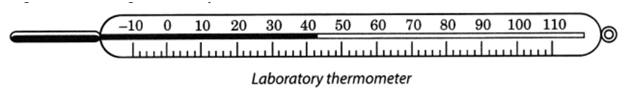
Q 2 – Write about the clinical thermometer.
Ans – A thermometer specifically designed for the measurement of the temperature of our body is called a clinical thermometer. It consists of a long, narrow glass tube. It has a bulb at one end, which contains mercury. It reads temperature from 35°C to 42°C.
Q 3 – Shopkeepers selling ice blocks usually cover them with jute sacks. Explain why.
Ans – As we know that jute sacks are thermal insulators, it helps ice not to be melt immediately. So, shopkeepers used to cover ice blocks with jute sacks.
Q 4 – What is a laboratory thermometer?
Ans – The thermometer which is used to measure the temperature of objects in the laboratory is called a laboratory thermometer. Its range is -10°C to 110°C.
Q 5 – To keep her soup warm, Paheli wrapped the container in which it was kept with woolen clothes. Can she apply the same method to keep a glass of cold drink cool? Give reason for your Answer
Ans – Yes, she can apply the same method to keep a glass of cold drink cool because wool is a thermal insulator, and it cannot allow to heat pass through it.
Q 6 – Write any three precautions to be taken while reading a clinical thermometer.
Ans –
- Do not hold the thermometer by the bulb.
- Read the thermometer keeping the level of mercury along the line of sight.
- Ensure that before use the mercury level is below 35°C.
Q 7 – A circular metal loop is heated at point O as shown in the figure.
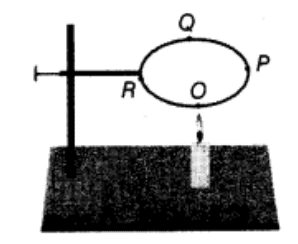
(a) In which direction, would heat flow in the loop?
(b) In which order, the pins at points P, Q and R fixed with the help of wax fall if points O, P, Q and R are equidistant from each other?
Ans – (a) Heat will flow in both directions from O to P and from O to R.
(b) First of all pin at P and R will fall simultaneously after that pin at Q will fall.
Q 8 – Can a clinical thermometer be used to measure the temperature of boiling water?
Ans – No, a clinical thermometer cannot be used to measure the temperature of boiling water because the temperature of boiling water is more than the fixed range of the clinical thermometer, i.e., 42°C. If we try to measure the temperature of boiling water, it will break down.
Q 9 – It is preferred to use two thin blankets rather than one thick blanket. Explain the reason.
Ans – In case of two thin blankets, there is an air gap which does not allow heat to pass out from the body and it is not as such as in case of one thick blanket.
Q 10 – Briefly mention one application of kink in the clinical thermometer.
Ans – The clinical thermometer consists of a kink which prevents the mercury level from falling on its own.
Q 11 – Explain how the temperature of the water can be measured by using a laboratory thermometer.
Answer:
To measure the temperature of water by using a laboratory thermometer, we follow the following steps:
1. Take water in a beaker.
2. Dip the laboratory thermometer in the water so that its bulb gets completely immersed in it, but make sure the bulb doesn’t touch the bottom of the beaker.
3. Hold the thermometer vertically.
4. Consider the movement of the thread of mercury.
5. After it becomes static, notice the reading.
Q 12 – Is the body temperature of every person 37°C?
Ans – No, the body temperature of every person is not 37°C. It is an average temperature. It could be slightly higher or slightly lower.
Q 13 – What is temperature? Describe two types of thermometers used to measure the temperature.
Ans – A reliable measure of the hotness of an object is called its temperature. It is measured by a device called a thermometer.
There are two types of thermometers:
(i) Clinical thermometer: The thermometer that measures the temperature of our body is called a clinical thermometer. It consists of a long, narrow, uniform glass tube. It has a bulb at one end which contains mercury. Outside the bulb, a small shining thread of mercury can be seen. There is also a scale on the thermometer. The scale used in it is the celsius scale, indicated by °C. A clinical thermometer reads temperature from 35°C to 42°C.
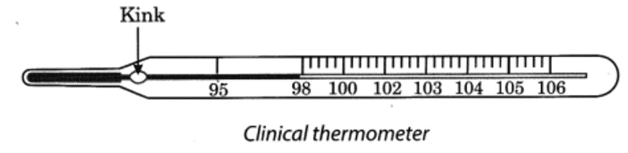
(ii) Laboratory thermometer: This type of thermometer is used to measure the temperature of different objects in laboratories. It is made of a thin glass tube sealed at one end and a bulb with mercury at the other end. The portion of the capillary tube above the bulb is graduated in degrees usually from -10°C to 110°C.
Q 14 – No, the body temperature of every person is not 37°C. It is an average temperature. It could be slightly
higher or slightly lower.
Ans – Jerks are given to a clinical thermometer before using it to settle down the mercury level below normal temperature so that the measurement is taken of a body be accurate.
Q 15 – The handle of a pressure cooker is covered with thick plastic. Explain why.
Ans – As we know that plastic is a bad conductor of heat due to which the heat from the cooker does not flow to its handle and we can hold it easily.
So, this is a reason because of which the handle of a pressure cooker is covered with thick plastic.
Q 16 – Differentiate between two modes of transfer of heat, i.e. convection and conduction.
Ans – Difference between convection and conduction
| Conduction | Convection |
| The mode of transfer of heat from the hotter part material to its colder part or from a hot material to a cold material in contact with it without the movement of material as a whole. So, this the phenomenon is known as conduction | The mode of transfer of heat from the hotter part of a fluid to its colder parts by the movement of the liquid itself. So, this phenomenon is known as convection. |
| In all the solids, heat is transferred by the process of conduction | In all the liquids and gases, heat is transferred by the process of convection |
Q 17 – How is a thermometer read? What are the precautions to be observed while reading a clinical thermometer?
Ans – First, note the difference of temperature indicated between the two bigger marks. Also, note down the number of divisions (shown by smaller marks) between these marks. Suppose the bigger marks read one degree and there are five divisions between them. Then one
small division can read 1/5 = 0.2°C.
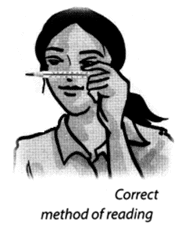
Now wash the thermometer, preferably with an antiseptic solution. Hold it firmly and give it a few jerks to bring the level of mercury down to below 35°C. Now place the bulb of the thermometer under your tongue or armpit and take it out after one minute and note the
reading. This is your body temperature. This should always be stated with its unit °C.
Some precautions one must observe while reading a clinical thermometer are:
1. It should be washed before and after use, preferably with an antiseptic solution.
2. It should be ensured that the mercury level is below 35°C before use.
3. It should be read keeping the level of mercury along the line of sight.
4. The thermometer must be handled with care.
5. It should not be held by the bulb while reading.
Q 18 – How does the heat travel in the air? Explain the sea breeze and land breeze in coastal areas in this reference.
Ans – Heat travels in air through the process of convection. The air near the heat source gets hot and rises up. The cool air from the sides comes in to take its place. In this way, the air gets heated up.

In the coastal areas, people experience an interesting phenomenon. The land gets heated faster than the water during the day. The air over the land becomes hotter and rises up. The cooler air from the sea rushes in towards the land to take its place. The warm air from the land moves towards the sea to complete the cycle.
The flow of cool air from the sea towards the land to replace the hot air on land is called sea breeze. At night it is just the reverse: The water cools down more slowly than land. So the cool air from land moves toward the sea. This is called land breeze.
Q 19 – While reading a clinical thermometer, what precautions should we take?
Ans – Reading a Clinical Thermometer
There are the following steps to read the temperature on a thermometer.
Step I
Firstly, wash the thermometer with an antiseptic solution and if in case, the antiseptic solution is not available, then wash it with clean water.
Step II
Gently, hold the thermometer tube in your hand and give it a jerk in such a way that the mercury thread in the thermometer tube falls below the reading of 35°C.
Step III
Now, put the bulb of the thermometer under the tongue of the patient for about one minute. Then take out the thermometer from patient’s mouth.
Step IV
In order to read the temperature, hold the thermometer horizontally in your hand and rotate it slowly. When we see a magnified image of the mercury thread in its tube, then a position will come. Now, read the temperature on the thermometer tube in level with the top of the mercury thread.
Precautions while Reading the Thermometer
A clinical thermometer should not be used for any object other than the human body. There are some
following precautions which are to be observed while reading a clinical thermometer.
1. Wash the clinical thermometer before and after using preferably with an antiseptic solution.
2. Be ensure that the mercury level before using the clinical thermometer should be below 35°C.
3. The clinical thermometer should be read by keeping the level of mercury along the line of sight.
4. While reading the clinical thermometer, it should never be held by the bulb.
5. The clinical thermometer should be carefully handled.
Q 20 – Explain the term radiation.
or
Explain how can heat travel in a vacuum or without a medium.
Ans – The heat from the sun cannot reach us by conduction or convection as there is no medium such as air in most parts of the space between the earth and the sun. This is possible through the process of radiation. The mode of transfer of heat energy in which no medium is needed to transfer heat from a hotter body to a colder body is called radiation. It can take place whether a medium is present or not. For example, when we sit in front of a room heater we get heat by this process.

A hot utensil kept away from the flame cools down as it transfers heat to the surroundings by radiation. Our body too gives heat to the surroundings and receives heat from it by radiation. The figure below shows the radiation from the sun. It also shows that when radiation falls on an object a part of it is reflected, a part is absorbed and a part may be transmitted.
Q 21 – State the limitation of the clinical thermometer.
Ans – The clinical thermometer cannot be used for measuring the temperature of any object more than 42°C (i.e. more than the body temperature). If it is kept in the sun or near a flame, then this clinical thermometer can be a break.
Q 22 – List any four effects of heat. Explain them.
Ans – When heat energy is absorbed by a body various changes can happen. Some of them are:
1. Rise in temperature: When a body absorbs heat, it gains energy. As a result of this, the temperature of the body rises and the body becomes hot.
2. Change in state of matter: On heating, most of the substances change their state, like solid to liquid, liquid to gas, etc.
3. Expansion: All states of matter i.e., solid, liquid, or gas expand on heating and contract on cooling. Expansion is most in gases, less in liquids, and least in solids. Expansion due to heat is known as thermal expansion.
4. Combustion: On heating, some of the substance reach their ignition temperature and starts burning. So heat causes combustion.
Q 23 – Explain the reason for the shiny reflectors of room heaters.
Ans – Since the shiny surface absorbs very little heat due to which the reflectors reflect all the heat which makes the room heaters more effective. So, due to this reason, room heaters have shiny reflectors.
Q 24 – Describe the effects of heat.
Ans – The effects of heat are
(i) When an object is heated, then it becomes hotter and may get expand. So, this heat may change the
state of the body like ice can also get change into the water.
(ii) Heat sometimes acts as a catalyst to speed up the chemical reaction.
(iii) Heat can even kill the bacteria as well.
Q 25 – Instead of water explain the reason, why do mercury is used in the thermometer?
Ans – Due to the following reasons, mercury is used in the thermometers instead of water
1. When the thermometer breaks, the mercury can be easily collected.
2. Mercury can has more expansion than water.
3. Also, mercury does not stick on the walls of thermometer like water.
Q 26 – Explain the reason for the general fitting of the air conditioner at a higher level on the wall of the room.
Ans – As a fact that warm air is much lighter than cold air, so being heavier the cold air from the air conditioner moves downwards while the hot air moves upwards at the lower level and gets cooled and come downwards once again. So, due to this convection of heat is set in the air and the room gets warmer faster.
Q 27 – At a campsite, there are tents of two shades. One made with black fabric and the other with white fabric.
Which one will you prefer for resting on a hot summer afternoon? Give reason for your choice. Would you like to prefer the same tent during winter?
Ans – We will prefer a white fabric tent in case of summer because it reflects all the radiations from the sun and keeps us cool inside the tent. But in ease of winter, we should not use a white fabric tent, we should use a black fabric tent as it absorbs all colours of light from the sun and keeps us warm inside the tent.
Q 28 – The clinical thermometer is not used to measure high temperature. Why?
Ans – Clinical thermometer has the range 35°C to 42°C. If we use it to measure high temperature, it may break and mercury present in the clinical thermometer is harmful. So, we cannot use a clinical thermometer to measure high temperature.
Q 29 – Explain the differences between heat and temperature.
Ans – The differences between heat and temperature are given as below:
| Heat | Temperature |
| It is a form of energy that flows from one body to another when there is a difference in temperature between the objects. | It is the thermal condition of a body that indicates whether or not and in which direction, heat will flow from one body to the other. |
| It is equal to the sum of internal energies of the molecules of a body. | It is proportional to the average kinetic energy of the molecules of the body. |
| As a heat between two bodies, the total amount of heat of two bodies remains unchanged. | As a conclusion of exchange of heat between two bodies, the sum of their temperatures before and after exchange is not the same. |
| SI unit of heat is joule (J). | SI unit of temperature is kelvin (K). |
Q 30 – Explain the reason for the following statement, “When heat is applied at the bottom of the water vessel, then it gets heated more quickly than when it is heated at the top.”
Ans – The particles of water become lighter and rise up in the middle. Due to this, the cold particles of water that are heavier come down along the sides of the vessel. So, the convection currents of heat are setup and water becomes hot. The moment, when the heat is applied at the top, then the water present in the upper portion becomes hot and these hot water molecules get fixed over the surface. Since, water is a bad conductor of heat, due to which water present at the lower end (or bottom) of the vessel remains.