Q 1 – Which of the following can be made into crystals?
(a) A bacterium
(b) An amoeba
(c) A virus
(d) A sperm
Q 2 – Which tissue is present at the growing tips of stem and roots ?
(a) Permanent
(b) Meristematic
(c) Conductive
(d) Complex
Q 3 – Which plastids are colorless?
(a) Chromoplasts
(b) Chloroplast
(c)Leucoplasts
(d) All of the above
Q 4 – Who discovered the cell?
(a) Robert Hooke
(b) Leeuwenhoek
(c) Robert Brown
(d) T. Schwann
Q 5 – Engulfing of food materials or foreign bodies by cells like Amoeba is called
(a) diffusion
(b) endocytosis
(c) osmosis
(d) plasmolysis
Q 6 – Blood is a type of:
(a) connective tissue
(b) muscular tissue
(c) nervous tissue
(d) epithelial tissue
Q 7 – Girth of stem increases due to
(a) apical meristem
(b) lateral meristem
(c) intercalary meristem
(d) vertical meristem
Q 8 – The cell wall of a plant cell is made up of:
(a) glucose
(b) fructose
(c) protein
(d) cellulose
Q 9 – Which of these is not related to the endoplasmic reticulum?
(a) It behaves as a transport channel for proteins between the nucleus and cytoplasm.
(b) It transports materials between various regions in the cytoplasm.
(c) It can be the site of energy generation.
(d) It can be the site for some biochemical activities of the cell.
Q 10 – Mammary glands are modified
(a) Sebaceous gland
(b) Sweat gland
(c) Oil gland
(d) Lymph gland
Q 11 – Brain is composed of:
(a) muscular tissue
(b) connective tissue
(c) nervous tissue
(d) epithelial tissue
Q 12 – Which of the following controls all biological activities of a cell?
(a) Protoplasm
(b) Cell wall
(c) Nucleus
(d) All of these
Q 13 – Cartilage matrix is digested during its osteogenesis through:
(a) Intracellular autophagic activity
(b) Extracellular lysosomal activity
(c) Intracellular heterophonic activity
(d) Both B and C
Q 14 – Which of the following is known as the ‘Power House’ of a cell?
(a) Nucleus
(b) Golgi Bodies
(c) Ribosome
(d) Mitochondria
Q 15 – The heart of organisms is made up of:
(a) muscular tissue
(b) connective tissue
(c) nervous tissue
(d) epithelial tissue
Q 16 – Organelle other than nucleus, containing DNA is
(a) endoplasmic reticulum
(b) Golgi apparatus
(c) mitochondria
(d) lysosomes
Q 17 – Which of the following helps in the repair of tissue and fills up the space inside the organ?
(a) Tendon
(b) Adipose tissue
(c) Areolar
(d) Cartilage
Q 18 – Digestive Enzymes are found in:
(a) Protoplasm
(b) Cell wall
(c) Lysosomes
(d) Mitochondria
Q 19 – Skin of hand is composed of:
(a) muscular tissue
(b) connective tissue
(c) nervous tissue
(d) epithelial tissue
Q 20 – Flexibility in plants is due to
(a) collenchyma
(b) sclerenchyma
(c) parenchyma
(d) chlorenchyma
Q 21 – Which out of the following is not a function of vacuole?
(a) Storage
(b) Providing turgidity and rigidity to the cell
(c) Waste excretion
(d) Locomotion
Q 22 – The only cell organelle seen in prokaryotic cells is
(a) mitochondria
(b) ribosomes
(c) plastids
(d) lysosomes
Q 23 – Cells of squamous epithelium are
(a) Columnar
(b) Tall with elongated nuclei
(c) Flat plate-like
(d) Cube like
Q 24 – Which is the longest cell of the human body?
(a) Nerve cell
(b) Liver cell
(c) Kidney cell
(d) Cardiac cell
Q 25 – Which of the following cell organelles functions both as an intracellular transport system and as a manufacturing surface?
(a) Nucleus
(b) Mitochondria
(c) ER
(d) None of these
Q 26 – Water and minerals are transported by:
(a) phloem
(b) cavities
(c) xylem
(d) all of them
Q 27 – Which of the following cell organelles help in the storage, modification, and packaging of substances manufactured in the cell?
(a) Golgi apparatus
(b) Nucleus
(c) Mitochondria
(d) Chloroplasts
Q 28 – Who proposed the “Black Reaction”?
(a) Benda
(b) Camillo Golgi
(c) Schleiden
(d) None of them
Q 29 – Who discovered the nucleus in the cell?
(a) Leeuwenhoek
(b) Robert Brown
(c) Schleiden
(d) Robert Hooke
Q 30 – Stomata are found:
(a) in the epidermis of the leaf
(b) in xylem
(c) in phloem
(d) collenchymas
Q 31 – Lysosome arises from:
(a) endoplasmic reticulum
(b) Golgi apparatus
(c) nucleus
(d) mitochondria
Q 32 – Which muscles act involuntarily?
(i) Striated muscles
(ii) Smooth muscles
(iii) Cardiac muscles
(iv) Skeletal muscles
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Q 33 – Which is not a function of the epidermis?
(a) Protection from adverse condition
(b) Gaseous exchange
(c) Conduction of water
(d) Transpiration
Q 34 – Cartilage is not found in:
(a) nose
(b) ear
(c) kidney
(d) larynx
Q 35 – Which of the following are formed in bone marrow?
(a) RBC
(b) Cartilage cell
(c) Blood platelets
(d) Fibres
Q 36 – Chromosomes are made up of:
(a) DNA
(b) Protein
(c) DNA and protein
(d) RNA
Q 37 – Which of the following are covered by a single membrane?
(a) Mitochondria
(b) Vacuole
(c) Ribosome
(d) Plastid
Q 38 – The cell wall of which one of these is not made up of cellulose?
(a) Bacteria
(b) Hydrilla
(c) Mango tree
(d) Cactus
Q 39 – In a test of biology a figure of the smooth muscle is labeled as A, B, C, and D for different parts of the muscles. Four students P, Q, R, and S in a way to attempt the question named the four parts as given below. But only one student could name all the four parts correctly.
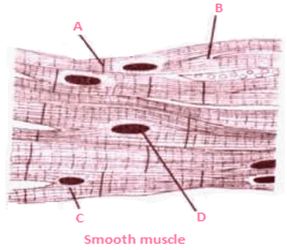
Which of the following options is the answer written by that student?
(a) A – Intercalated disc; B – Sarcoplasm; C – Branched fibres; D – Nucleus
(b) A – Intercalated disc; B – Branched fibres; C – Sarcoplasm; D – Nucleus
(c) A – Branched fibres; B – Intercalated disc; C – Sarcoplasm; D – Nucleus
(d) A – Branched fibres; B – Sarcoplasm; C – Intercalated disc; D – Nucleus
Q 40 – The kitchen of the cell is:
(a) mitochondria
(b) endoplasmic reticulum
(c) chloroplast
(d) Golgi apparatus
Q 41 – The nucleus controls all the activities of the cell and acts as a site of DNA material and protein synthesis. It is composed of some components which all together give the nucleus its functionality. Here is shown a figure of the nucleus with some of its components labeled as A, B, C, and D. can you name these components correctly?

(a) A – Nucleons; B – Chromatin; C – Nuclear membrane; D – Nucleoplasm
(b) A – Nucleus; B – Chromatin; C – Nuclear membrane; D – Nucleoplasm
(c) A – Nucleolus; B – Chromatin; C – Nuclear membrane; D – Nucleoplasm
(d) A – Nucleolus; B – Chromatin; C – Nuclear membrane; D – Nuclear wall
Q 42 – Given below is a diagram showing the structure of a neuron tissue.

Choose the correct labeling for parts A, B, C, D, and E.
(a) A – Nucleus; B – Cell body; C – Dendrite; D – Axon; E – Nerve ending.
(b) A – Nucleus; B – Dendrite; C – Cell body; D – Nerve ending; E – Axon.
(c) A – Nucleus; B – Axon; C – Cell body; D – Dendrite; E –Nerve ending.
(d) A – Nucleus; B – Dendrite; C – Cell body; D – Axon; E – Nerve ending
Q 43 – Given below is a diagram showing the Xylem and Phloem
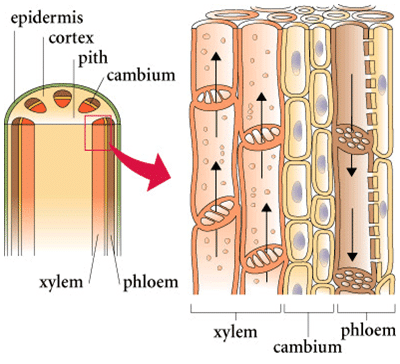
1. Which of the following tissues are involved in water conduction?
a) Xylem and Phloem
b) Tracheids and tracheae
c) Parenchyma and sclerenchyma
d) Xylem fibres and bast fibres
2. Vessels are present in all plants except
a) Pinus
b) Rose
c) Gnetum
d) mango tree
3. Xylem consists of
a) tracheids, vessels, fibres, and parenchyma
b) tracheids, vessels, and companion cells
c) tracheids, fibres, and parenchyma
d) tracheids, vessels, sieve cells, and companion cells
4. Which of the following water-conducting element is considered as most advanced
a) tracheids
b) multiple vessels
c) annular tracheids
d) simple vessels
5. Tracheids and vessels are present in all except
a) Marselia
b) Equisetum
c) Gnetum
d) Cycas
6. Wood parenchyma is formed from
a) fusiform initials
b) ray initials
c) collenchyma cells
d) all of these
7. Phloem consists of
a) vessels, sieve tube cells, phloem parenchyma, phloem fibres
b) sieve tube cells, companion cells, phloem parenchyma, phloem fibres
c) vessels, tracheids, phloem parenchyma, phloem fibres
d) vessels, tracheids, sieve tube cells, companion cells
8. Which of the following statement is true about sieve tube cells
a) Sieve tube cells are nucleated but devoid of mitochondria and ER
b) companion cells are non-nucleated and are regulated by nucleated sieve cell
c) Sieve tube cells are present in all plants
d) companion cells are nucleated and regulates activity of non-nucleated sieve tube cell
9. Which of the following are the examples of phloem fibres
a) jute
b) hemp
c) flax
d) all of the above
10. All the following plant groups possess phloem parenchyma except
a) Dicots
b) Monocots
c) Gymnosperm
d) Pteridophytes
Q 44 – Fill in the Blanks.
- The cells of permanent tissues do not ________
- When parenchyma contains chloroplast, then it is called _________
- ________ is the meristem at the base of the leaves or intemodes of stem
- When many tissues join together, they form an _________
- Phloem ________ food from leaves to other parts of the plant.
- _______ transports the water and minerals absorbed by roots to the other parts of the plant
- When many tissues join together, they form an _________
- _______ is made of neurons that receive and conduct impulses.
Q 45 – True/False
- Heart muscles are connected with skeleton.
- Liginified thickened walls provide mechanical strength to the plant
- Parenchyma with large air cavities are called aerenchyma
- Cork cambium is an example of lateral meristem
- Cartilage is present in the nose and larynx.
- Blood and lymph are vascular connective tissue.
- Heart muscles are voluntary muscles.
Q 46 – Match the following:
| A | B |
| 1. A method of plant breeding | (i) Protein factory |
| 2. Mitochondria | (ii) Cell wall |
| 3. Lysosome | (iii) Polyploidy |
| 4. Ribosome | (iv) Powerhouse of the cell |
| 5. Cellulose | (v) Suicidal bag |
Download PDF Link Tissue and The Fundamental Unit of Life Answer Sheet