Q 1 – △ABC ≅ △PQR, then which of the following is true?
(a) CB = QP
(b) CA = RP
(c) AC = RQ
(d) AB = RP
Q 2 – In a right-angled triangle where angle A = 90° and AB = AC. What are the values of angle B?
(a) 45°
(b) 35°
(c) 75°
(d) 65°
Q 3 – A diagonal of a Rectangle is inclined to one side of the rectangle at an angle of 25°. The Acute Angle between the diagonals is :
(a) 115°
(b) 50°
(c) 40°
(d) 25°
Q 4 – In △ABC and △DEF, AB = DE and ∠A = ∠D. Then two triangles will be congruent by SAS axiom if:
(a) BC = EF
(b) AC = EF
(c) AC = DE
(d) BC = DE
Q 5 – In a triangle ABC if ∠A = 53° and ∠C = 44° then the value of ∠B is:
(a) 46°
(b) 83°
(c) 93°
(d) 73°
Q 6 – In a right triangle, the longest side is:
(a) Perpendicular
(b) Hypotenuse
(c) Base
(d) None of the above
Q 7 – If the altitudes from vertices of a triangle to the opposite sides are equal, then the triangles is
(a) Scalene
(b) Isosceles
(c) Equilateral
(d) Right-angled
Q 8 – How many degrees are there in an angle which equals one-fifth of its supplement?
(a) 15°
(b) 30°
(c) 75°
(d) 150°
Q 9 – Sum of the measure of an angle and its vertically opposite angle is always.
(a) Zero
(b) Thrice the measure of the original angle
(c) Double the measure of the original angle
(d) Equal to the measure of the original angle
Q 10 – If ΔABC ≅ ΔPQR then which of the following is true:
(a) CA = RP
(b) AB = RP
(c) AC = RQ
(d) CB = QP
Q 11 – The diagonals of rhombus are 12 cm and 16 cm. The length of the side of rhombus is:
(a) 12 cm
(b) 16 cm
(c) 8 cm
(d) 10 cm
Q 12 – If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then the pairs of corresponding angles are congruent.
(a) Equal
(b) Complementary
(c) Supplementary
(d) corresponding
Q 13 – If two triangles ABC and PQR are congruent under the correspondence A ↔ P, B ↔ Q, and C ↔ R, then symbolically, it is expressed as
(a) ΔABC ≅ ΔPQR
(b) ΔABC = ΔPQR
(c) ΔABC and ΔPQR are scalene triangles
(d) ΔABC and ΔPQR are isosceles triangles
Q 14 – The bisectors of the base angles of an isosceles triangle ABC, with AB = AC, meet at O. If ∠B =∠C = 50°. What is the measure of angle O?
(a) 120°
(b) 130°
(c) 80°
(d) 150°
Q 15 – If the bisector of the angle A of an △ABC is perpendicular to the base BC of the triangle then the triangle ABC is :
(a) Obtuse Angled
(b) Isosceles
(c) Scalene
(d) Equilateral
Q 16 – In Fig., AB || CD and CD || EF. Also EA ⊥ AB. If ∠ BEF = 55°, find the values of x, y and z.
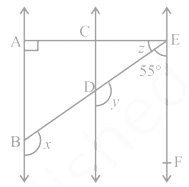
(a) x = 120º, y = 120º, z = 30°
(b) x = 115º, y = 105º, z = 25°
(c) x = 110º, y = 115º, z = 35°
(d) x = 125º, y = 125º, z = 35°
Q 17 – The angles of a triangle are in the ratio 2 : 3 : 4. The angles, in order, are :
(a) 80°, 40°, 60°
(b) 20°, 60°, 80°
(c) 40°, 60°, 80°
(d) 60°, 40°, 80°
Q 18 – If AB = QR, BC=RP and CA = QP, then which of the following holds?
(a) △BCA ≅ △PQR
(b) △ABC ≅ △PQR
(c) △CBA ≅ △PQR
(d) △CAB ≅ △PQR
Q 19 – An acute angle is:
(a) More than 90 degrees
(b) Less than 90 degrees
(c) Equal to 90 degrees
(d) Equal to 180 degrees
Q 20 – ABC is an isosceles triangle in which altitudes BE and CF are drawn to equal sides AC and AB respectively. Then:
(a) BE > CF
(b) BE < CF
(c) BE = CF
(d) None of the above
Q 21 – In Fig., if QT ⊥ PR, ∠ TQR = 40° and ∠ SPR = 30°, find x and y.
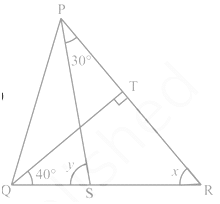
(a) x = 50°, y = 80°
(b) x = 60°, y = 50°
(c) x = 50°, y = 90°
(d) x = 40°, y = 80°
Q 22 – Two parallel lines intersect at:
(a) One point
(b) Two points
(c) Three points
(d) Null
Q 23 – Which of the following is not a criterion for congruence of triangles?
(a) SSS
(b) SSA
(c) ASA
(d) ASS
Q 24 – The angle between the bisectors of two adjacent supplementary angles is :
(a) Acute angle
(b) Right angle
(c) Obtuse angle
(d) None of these
Q 25 – In △ABC, if ∠B = 30° and ∠C = 70°, then which of the following is the longest side?
(a) AB
(b) BC
(c) AC
(d) AB or AC
Q 26 – If an angle of a parallelogram is two-third of its adjacent angle, the smallest angle of the parallelogram is:
(a) 81°
(b) 54°
(c) 108°
(d) 72°
Q 27 – Which of the following statements is false?
(a) A line can be produced to any desired length.
(b) Through a given point, only one straight line can be drawn.
(c) Through two given points, it is possible to draw one and only one straight line
(d) Two straight lines can intersect in only one point
Q 28 – The angles opposite to equal sides of a triangle are:
(a) Equal
(b) Unequal
(c) supplementary angles
(d) Complementary angles
Q 29 – If ABC is an equilateral triangle, then each angle equals to:
(a) 90°
(b) 180°
(c) 120°
(d) 60°
Q 30 – If a side of a triangle is produced, then the exterior angle so formed is equal to the sum of the ____ interior opposite angles.
(a) Two
(b) Four
(c) One
(d) Three
Q 31 – △ ABC ≅ △PQR. If AB=5 cm, and then which of the following is true?
(a) QR = 5 CM, ∠R= 60°
(b) QP = 5 cm, ∠P= 60°
(c) QP = 5cm, ∠R = 60°
(d) QR = 5 CM, ∠Q = 60°
Q 32 – If two straight lines are perpendicular to a line l, then they are.
(a) The lines intersect each other when extended
(b) Parallel to each other
(c) The angle between the two lines is 180°
(d) Perpendicular to each other
Q 33 – Two angles whose measures are a & b are such that 2a – 3b = 60° then 5b = ?, if they form a linear pair:
(a) 120°
(b) 300°
(c) 60°
(d) None of these
Q 34 – It is not possible to construct a triangle when its sides are:
(a) 6 cm, 7 cm, 7 cm
(b) 5.4 cm, 2.3 cm, 3 cm
(c) 8.3 cm, 3.4 cm, 6.1 cm
(d) 3 cm, 5 cm, 5 cm
Q 35 – In a parallelogram the sum of two consecutive angles is
(a) 360°
(b) 100°
(c) 180°
(d) 90°
Q 36 – An angle is 14° more than its complementary angle, then angle is:
(a) 38°
(b) 52°
(c) 50°
(d) None of these
Q 37 – Two equilateral triangles are congruent when:
(a) Their areas are proportional
(b) Their sides are equal
(c) Their sides are proportional
(d) Their angles are equal
Q 38 – Two angles of a quadrilateral are 50° and 80° and other two angles are in the ratio 8 : 15. Find the measure of the remaining two angles.
(a) 100°, 130°
(b) 140°, 90°
(c) 80°, 150°
(d) 70°, 160°
Q 39 – Find the measure of the angle which is complement of itself.
(a) 30°
(b) 90°
(c) 45°
(d) 180°
Q 40 – It is not possible to construct a triangle when the lengths of its sides are
(a) 4 cm, 6 cm, 6 cm
(b) 9.3 cm, 5.2 cm, 7.4 cm
(c) 6 cm, 7 cm, 8 cm
(d) 5.3 cm, 2.2 cm, 3.1 cm
Q 41 – The opposite angles of a parallelogram are (3x – 2)° and (50 – x)° the measure of these angles is ______.
(a) 140°, 140°
(b) 20°, 160°
(c) 37°, 143°
(d) 37°, 37°
Q 42 – X lies in the interior of ∠BAC. If ∠BAC = 70° and ∠BAX = 42° then ∠XAC = ?
(a) 28°
(b) 29°
(c) 27°
(d) 30°
Q 43 – Which of the following statements is incorrect?
(a) Two squares having the same side length are congruent
(b) Two rectangles having the same area are congruent
(c) Two circles having the same radius are congruent
(d) Two lines having same length are congruent
Q 44 – The diagonals AC and BD of a parallelogram ABCD intersect each other at the point O. If ∠DAC = 32°, ∠AOB = 70°, then ∠DBC is equal to:
(a) 32°
(b) 88°
(c) 24°
(d) 38°
Q 45 – ABCD is a parallelogram, if the two diagonals are equal, then by what criterion are the triangles ABD and ABC congruent

(a) AAS
(b) SSS
(c) SAS
(d) RHS
Q 46 – If two lines intersect each other, then the vertically opposite angles are:
(a) Equal
(b) Unequal
(c) Cannot be determined
(d) None of the above
Download Answers PDF For Class 9 Maths Triangles, Line and Angles Combined MCQ Test Paper